Background: The optimal method of biliary drainage for biliary obstruction caused by hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is controversial, and the possible endoscopic application of plastic and metal stents is the least invasive procedure to improve patients' quality of life.
Aim: Our objective was to study cost evaluation based on a clinical efficacy of both procedures in a randomized trial comparing both approaches in patients with biliary obstruction caused by HCC.
Methods: The strategy of management was based on clinical effectiveness of biliary drainage with either metal or plastic stents in 90 patients over a 1-year follow-up period. Total (direct and indirect) costs were evaluated.
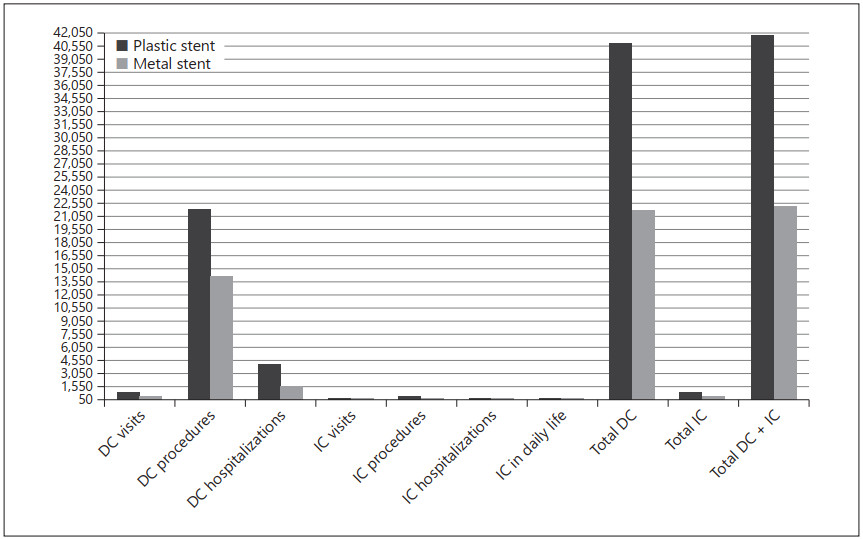
Results: The direct costs were EGP 40,857.84 and 21,802.62 per patient with plastic and metal stents, respectively. Concerning the indirect costs, EGP 888 and 454 were spent for each patient with plastic and metal stents, respectively. The differences in the costs resulted from patients with plastic stent insertion requiring more second endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography procedures and more medication, medical consultation, and hospitalization during the year of follow-up.
Conclusions: Based on this analysis, the use of metal stents rather than plastic stents in biliary drainage is more cost effective for this group of patients.