-
The genus Flammulina belonging to the family Physalacriaceae (Agaricales) includes 35 species worldwide. Amongst them, F. velutipes (Curtis) Singer is a species that is known to be edible with both nutritional and medicinal properties. Earlier, this genus was known to be monotypic with the only type species F. velutipes, Arnolds[1] however in 1977 separated F. ononidis from F. velutipes which confirmed that Flammulina is not a monotypic genus. The genus Flammulina can be identified on the basis of characteristics such as having glabrous pileus that turns viscid when wet, yellowish lamellae usually with adnate to adnexed lamellae attachment, spores inamyloid; white spore print, and gelatinized pileipellis with pileocystidia. Species of the genus Flammulina are quite similar to each other so a detailed microscopic study is required for proper identification of different species. The type of suprapellis, spore characteristic, cheilocystidia shape, and size are important characteristics that have to be noted for the identification of this genus[2]. Species of Flammulina are said to be specially distributed in the Northern Hemisphere, however F. velutipes are also distributed in Australasia and South America[3,4]. Flammulina has not been studied critically in India, and only Flammulina velutipes have been reported[5].
-
Aligned sequences of the ITS (internal transcribed spacer region) dataset were 878 sites long. Among these, 623 were conserved sites, 207 variable sites, 95 informative sites, and 109 singletons. The phylogenetic tree obtained from ML (maximum likelihood) and MrBayes analyses almost showed the same topology. So, the Bayesian tree has been displayed (Fig. 1). The phylogenetic analysis of the nrITS (nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer region) sequences dataset placed the Indian collection (OM428205) together with the Chinese collection (DQ486704) with 100% bootstrap support value.
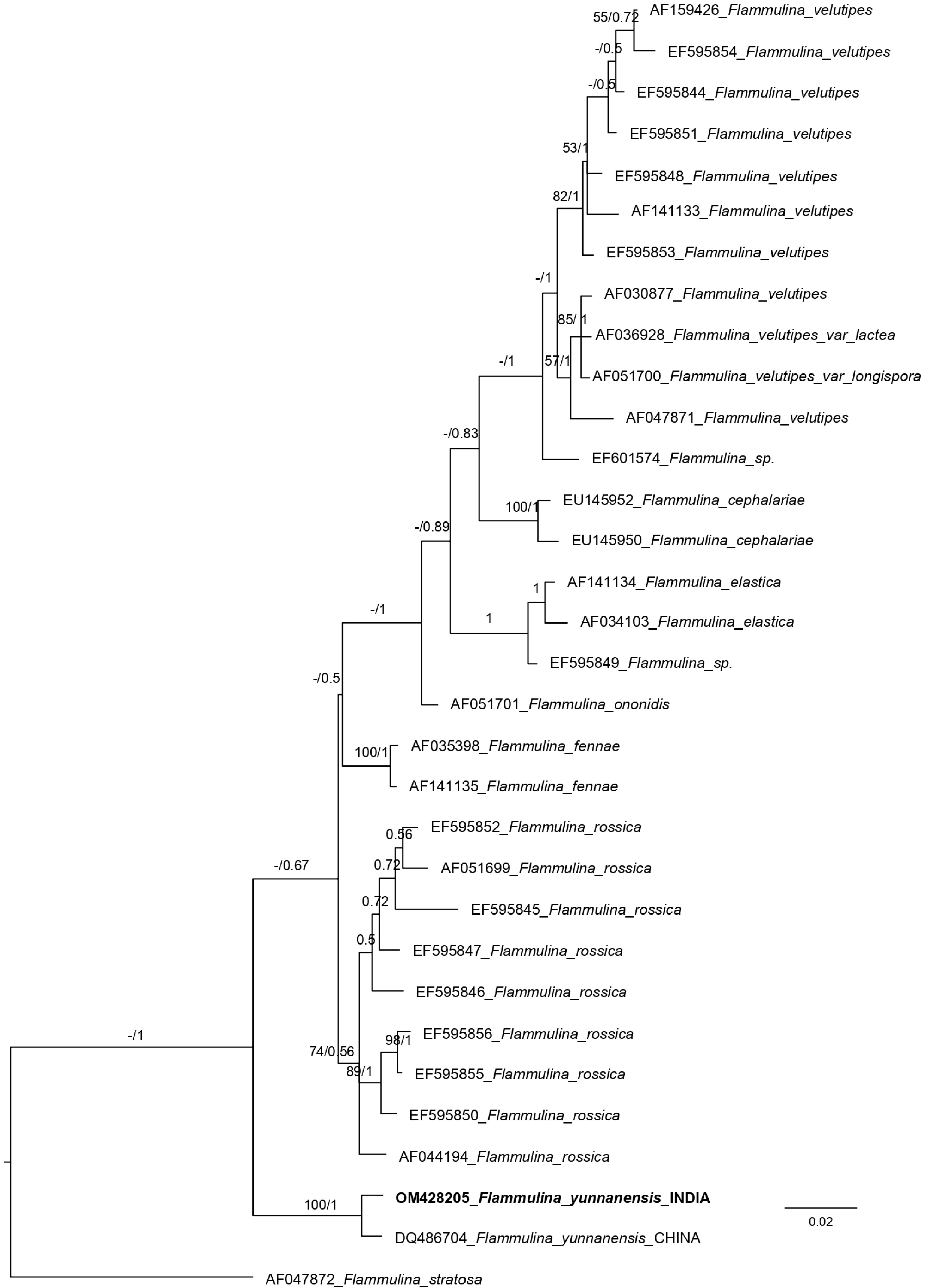
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree generated from Bayesian analyses (MrBayes) based on an ITS sequence dataset. Maximum likelihood bootstrap support values equal to or greater than 50% and Bayesian posterior probabilities equal to or greater than 0.50 are indicated on the nodes. The tree is rooted with Flammulina stratosa (AF047872).
Taxonomy
-
Flammulina yunnanensis Z.W. Ge & Zhu L. Yang, Fungal Diversity 32: 63 (2008) Fig. 2
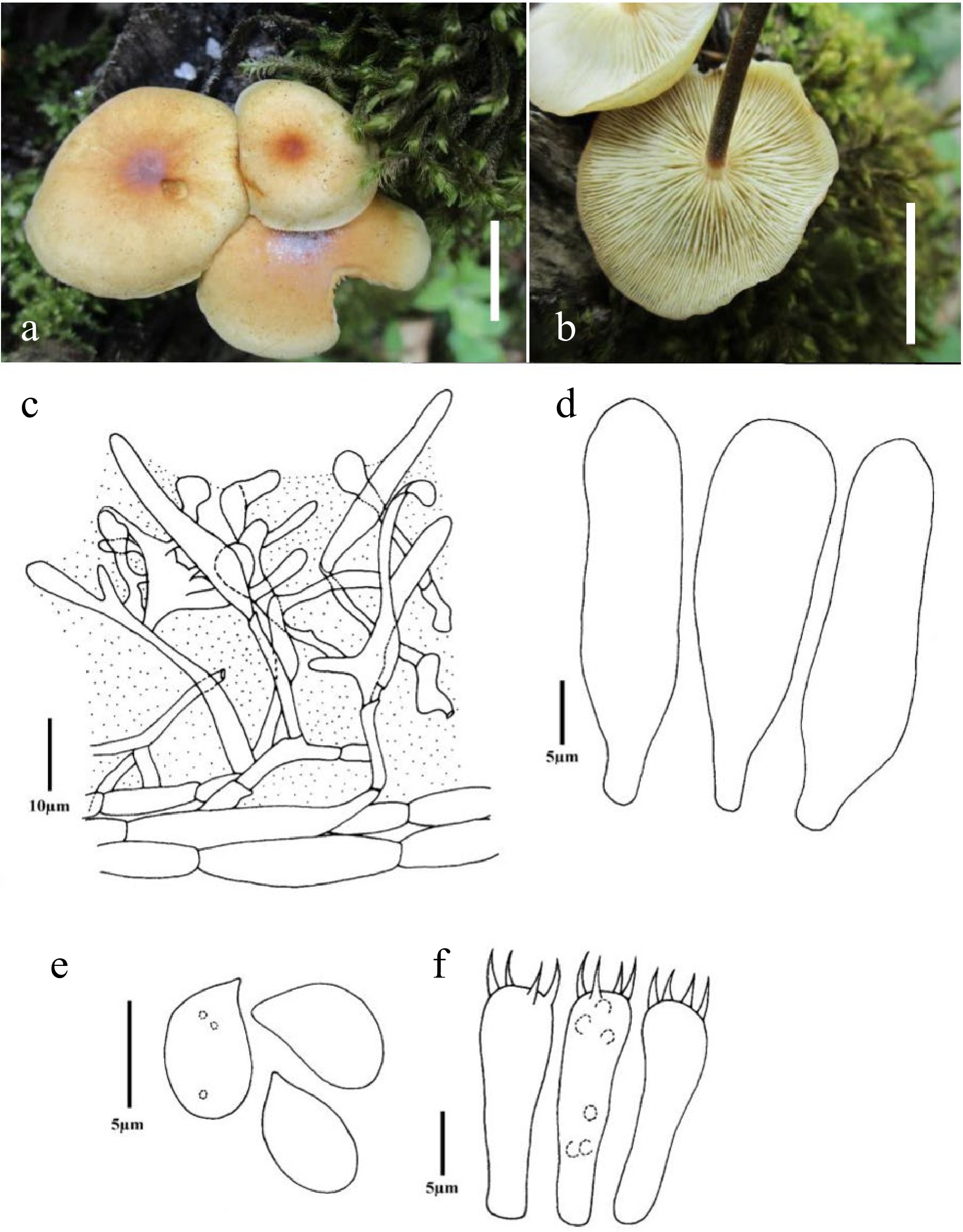

Figure 2.
Flammulina yunnanensis (CUH AM762). (a), (b) Habit in situ (Scale bars = 10 mm), (c) Pileipellis, (d) Cheilocystidia, (e) Basidiospores, (f) Basidia.
Index Fungorum number: IF 512371
Basidiocarp convex to broadly convex in shape, 1.1–2.1 cm in diameter, surface smooth, yellowish grey (4B2), to greyish orange (5B5), centre greyish orange (5B5), to dark orange (5A8), to greyish red (7B6) to reddish orange (7B7), shiny, viscid to subviscid when moist, glabrous, slightly depressed at the disc, pileus margin striate, incurved, crenate. Lamellae sinuate to adnexed, yellowish, up to 3 mm wide, regular, crowded to sub distant, cream to yellowish white (2A2) with lamellulae of four lengths. Stipe 3.5 cm × 0.3 cm, central, yellowish white at apex, brownish at lower parts, equal, hollow, surface smooth. Context white and unchanging. Spore print pure white (1A1).
Basidiospores 5.68–7.58 × 3.79–4.55 µm; Q = 1.4–1.8, Qm = 1.57, ellipsoid, sometimes oblong, inamyloid, smooth, thin walled, hyaline, with an apicule, germ pore absent. Basidia 21.98–25.01 × 6.06–7.2 µm, clavate in shape, 4–spored, sterigmata 3.03–4.2 µm long. Pleurocystidia ventricose to lageniform, scattered, 31.08–41.70 × 10.61–15.16 µm, hyaline, slightly thick walled. Cheilocystidia similar to pleurocystidia. Hymenophoral trama parallel to somewhat interwoven. Suprapellis 55–81 µm in thickness, somewhat gelatinized, with a hymeniform layer consisting of clavate shaped terminal elements 15.16–23.5 × 5.3–7.58 µm, ixohyphidia absent. Pileocystidia present, 41.69–90.96 × 6.8–10.99 µm, lageniform to ventricose. Clamp connections are present in all tissue.
Known distribution: Yunnan, southwestern China[6].
Material examined: INDIA, West Bengal, 6th mile Lava, Kalimpong, Caespitose, lignicolous on cultivated Cryptomeria tree in India, 14th June 2019, coll. Thapa A, Tamang J, CUH AM762.
-
Flammulina yunnanensis is distinguished from other species of the genus by its morphological characteristics of small ellipsoid basidiospores, hymeniform suprapellis with clavate shaped terminal elements without ixohyphidia. Considering morphological features, the description of our Indian collected specimen matches the holotype reported from Yunnan, southwestern China[6]. The Indian collection was found on the trunk of the living Cryptomeria tree but the Chinese collection is reported to be found on the dead trunk of fagaceous plants and other broadleaved trees.
The morphological identification of F. yunnanensis is well supported by the phylogenetic analyses. Flammulina yunnanensis has been originally described from Yunnan, China and there is no record of its occurrence in other parts of the world. Thus, F. yunnanensis is reported for the first time in this study in an alternative location.
-
The specimen was collected during a field visit in the month of June 2019 from Darjeeling Hills, India. The morphological description of the specimen is based on the field data sheet and color image of the basidiocarp. Basidiocarps were carefully dried using a drier and preserved using self–indicating silica gel for further studies at a laboratory. Colour codes were designated as per Kornerup & Wanscher[7].
Micro-morphological details were observed from the dried specimens by making free hand sections using 5% KOH and staining with Congo red. Melzer's reagent was used to stain basidiospores. For basidiospores, the abbreviation 'Qm' denotes the average Q of all spores. The specimen was preserved following Pradhan et al.[8] and deposited to the Calcutta University Herbarium (CUHAM762).
DNA extraction and PCR amplification
-
DNA was isolated using an XcelGen Fungal gDNA Mini Kit following the protocol of the manufacturer. ITS1 and ITS4 primer pair[9] were used for the rDNA amplification. PCR product purification was performed using QIAquick® Gel Extraction Kit (QIAGEN, Germany). Sequencing was done on ABI3730xl DNA Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, USA) using the same primer pairs used for the amplification of the rDNA ITS region. BioEdit v.7.0.5 software was used for editing the newly generated sequence of F. yunnanensis and given for BLAST search (NCBI). A new generated sequence of F. yunnanensis was deposited in Genbank with accession number OM428205.
Sequence alignment and phylogenetic analyses
-
The nrITS sequence of F. yunnanensis along with the dataset of Hughes et al.[10] and Ge et al.[6] downloaded from GenBank was aligned using Mega v.7.0. The final ITS dataset (Table 1) consisted of 32 samples of Flammulina, where Flammulina stratosa was designated as an outgroup referring to the previous studies[9,10].
Table 1. A list of Flammulina species used in the molecular phylogenetic analyses with GenBank accession numbers.
Species Collections Location Substrate GenBank accession # F. elastica TENN 56057 Austria: Vienna On Salix alba AF034103 F. elastica TENN 54689 Netherlands On Salix AF141134 F. elastica HKAS 52018 Germany: Marburg EF595849 F. fennae Th.Kuyper 2220 Netherlands: Utreght, Breukelen AF141135 F. fennae TENN 54172 Switzerland: Canton Graubunden On Alnus incana AF035398 F. ononidis TENN 54743 Germany – AF051701 F. rossica I. Bulakh Russia: Terr. Primorsk – AF051699 F. rossica TENN 54169 United States: Alaska On Salix AF044194 F. rossica HKAS 46076 China: Tibet, Changdu On Salix EF595845 F. rossica HMJAU 20588 China: Jilin, Zuojia – EF595847 F. rossica HKAS 43699 China: Tibet, Leiwuqi On Salix EF595846 F. rossica HKAS 45970 China: Tibet, Changdu On Salix EF595850 F. rossica HKAS 32154 China: Sichuan, Xiangcheng On Salix EF595856 F. rossica HKAS 32155 China: Sichuan, Daocheng On Picea EF595855 F. rossica HKAS 7930 China: Jilin, Baihe In Betula forest EF595852 F. sp. HKAS 51191 China: Tibet, Mozhugongka On the base of a dead trunk EF601574 F. stratosa TENN 56240 New Zealand: South Island – AF047872 F. yunnanensis HKAS 32774 China: Yunnan, Lushui In forest with Schima trees DQ486704 F. velutipes TENN 56008 Canada: British Columbia. – AF141133 F. velutipes TENN 54748 Netherlands: Prov. Zeeland – AF036928 F. velutipes K 28262 United Kingdom: Surrey, Ham – AF030877 F. velutipes TENN55402 United States: California On Lupinus arboreus AF047871 F. velutipes TENN 56028 United States: Michigan – AF051700 F. velutipes HKAS 49485 China: Yunnan, Kunming Cultivated EF595844 F. velutipes HKAS 51962 China: Hubei, Wuhan On Broussonetia papyrifera EF595848 F. velutipes HKAS 47767 China: Hunan, Changsha On Broussonetia papyrifera EF595853 F. velutipes HKAS 47768 China: Hunan, Changsha On Broussonetia papyrifera EF595854 F. velutipes HKAS 51988 China: Jilin, Changbai Mt. On Betula platyphylla EF595851 F. velutipes FH DH97 –080 China: Sichuan, Gongga On dead hard wood AF159426 F. cephalariae SEST05120701 Spain – EU145952 F. cephalariae SEST04111402 Spain – EU145950 F. yunnanensis CUH AM762 India: Darjeeling hills On Cryptomaria OM428205 Maximum likelihood (ML) analysis in RAxML HPC2 v. 8.2.12[11] used the best fit nucleotide substitution model by jModelTest2 on XSEDE using CIPRES web portal. Bayesian analyses of this dataset were also estimated in MrBayes v.3.2.7[12]. The initial run of 106 generations using Metropolis Coupled Monte Carlo Markov (MCMC) chains was carried out as described by Vishal et al.[13]. Among 10,001 samples, a total of 7,501 trees were used to calculate the Bayesian posterior probability. Maximum Likelihood bootstrap (MLBS) and Bayesian posterior probabilities (pp) values over 50% and 0.50 respectively are considered in the phylogenetic tree.
The authors are very grateful for the facilities provided by the Department of Botany, University of Calcutta. Thapa (UGCRef. No: 600/CSIR – UGC NET JUNE 2017) duly acknowledges University Grant Commission for providing fellowship during the tenure of the work.
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
- Copyright: © 2022 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press, Fayetteville, GA. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Thapa A, Tamang J, Acharya K. 2022. Flammulina yunnanensis (Agaricales), a new record from Darjeeling Hills, India. Studies in Fungi 7:11 doi: 10.48130/SIF-2022-0011
Flammulina yunnanensis (Agaricales), a new record from Darjeeling Hills, India
- Received: 13 September 2022
- Accepted: 10 November 2022
- Published online: 22 November 2022
Abstract: Morphological and phylogenetic studies were carried out on the collected specimen of Flammulina yunnanensis. A detailed morphological description along with field images and ITS (internal transcribed spacer region) sequence analyses suggested that the collected specimen is F. yunnanensis. It has a hymeniform suprapellis with clavate-shaped terminal elements without ixohyphidia which is a distinguishing feature amongst other species of the genus Flammulina. Flammulina yunnanensis is recorded for the first time in India.
-
Key words:
- ITS /
- Phylogeny /
- White spore /
- New record












