-
Artemisia argyi Lévl. et Vant. is a perennial plant in the family Asteraceae. It has a long history of application as both a medicine and food and holds great cultural value. Moxa fumigation and moxibustion therapy, which are used to treat various ailments such as abdominal pain[1] and arthritis[2, 3], are included in Prescriptions of Fifty-two Diseases from the Western Han dynasty of China[4], representing the first record of A. argyi use for disease treatment. The plant is widely distributed across Asia, Europe, and the Americas, particularly in East Asian countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and Mongolia[5]. These regions contain abundant germplasm resources with extensive natural phenotypic variation.
Phytochemical research has revealed the presence of numerous classes of metabolites in A. argyi; flavonoids, phenolic acids, terpenoids, steroids, and fatty acids are the key active components conferring medicinal value. Pharmacological activities of A. argyi include anti-oxidation, anti-tumor, anti-inflammation, bacteriostatic, anti-hypertensive, anti-hyperglycemic, and anti-asthmatic effects[6]. Aside from medicinal applications, the young stems and leaves of A. argyi have been consumed as food since ancient times. The leaves are used to make sweet green rice balls for the Qingming Festival[7], and by-products are used as a feed additive in animal husbandry and aquaculture to promote animal growth and improve the quality of livestock products[8]. Furthermore, A. argyi is widely used in personal care products such as cosmetics, body washes, foot baths, toothpastes, mosquito-repellent incenses, and toilet waters[9]. Known as 'diamond in the grass' in China and 'fairy grass' in Japan and South Korea, A. argyi has additional value due to its rich cultural background, including widespread use in folk customs such as sacrifices, exorcisms, and blessings[10].
With the rapid development of the healthcare industry in recent years, the market demand for A. argyi has continually risen, requiring annual increases in the A. argyi cultivation area. China had a total A. argyi cultivation area exceeding 40,000 hectares in 2021, the largest A. argyi production area in the world. At present, annual yield in China is ~86,000 tons, representing a value of ~39.5 billion yuan. In recent years, efforts have been made to enhance scientific understanding of A. argyi. In this review, we summarize the current state of A. argyi research with respect to biological characteristics, geographic distribution, germplasm resources, evaluation methods, molecular biology, cultivation and planting techniques, pharmacological activities, and utilization development. This review provides a clear, comprehensive reference for future cultivation, identification, and utilization of A. argyi, adding further value to this already economically and culturally important plant.
-
A. argyi is widely distributed across the roadside wilderness and grasslands in middle- and low-altitude regions. It grows well from 0–1,200 m above sea level. A. argyi has strong adaptability to varying climate and soil types due to its thermophilic, photophilous, cold- and drought-tolerant nature. It is suitable for growth in deep-layer, fertile sandy, neutral, and slightly alkaline loamy soils. Wild A. argyi resources in China are primarily found in the areas surrounding the Yangtze River, Qichun County in Hubei Province, Nanyang City in Henan Province, Ningbo City in Zhejiang Province, Tangyin County in Henan Province, and Anguo City in Hebei Province[11]. In Japan, A. argyi is mainly distributed in regions such as Honshu, Kyushu, and Hokkaido. In South Korea, A. argyi is distributed in South Jeolla, North Chungcheong, Gyeonggi, and South Gyeongsang provinces[12]. All of these famous A. argyi habitats are located from 28–38 °N in latitude and the primary production areas are between 0–500 m in altitude, suggesting that these conditions are most suitable for A. argyi growth and reproduction.
A. argyi is a half-shrubby perennial herb, in the wild, it grows to a height of 80–150 cm and has a strong aroma. The main root of A. argyi is yellowish-brown, slightly thick, and long; the lateral roots are numerous and slender, with fibrous roots. In addition, it often contains horizontal underground rhizomes, which can be used in asexual reproduction[13]. The stems are longitudinally grooved and covered in gray and silky hairs. The leaves are flexible and thick, both the obverse and reverse side of the A. argyi leaves have glandular trichomes and non-gland trichomes. The mature glandular trichomes appear shoe-shaped and exist in 10-cell and 5-cell types[14].The glandular trichomes usually store some volatile substances, which contribute to the aromatic odors of A. argyi leaves. There are numerous non-glandular trichomes, all of which are T-shaped and composed of four to six cells[15]. Each side of the leaf has two to three lobes that are elliptical or inversely ovate-elliptical in shape. The fruit is an achene with a long oval or oblong shape. The blooming–fruiting stage lasts from July to October[16]. The morphological characteristics of A. argyi were shown in Fig. 1.
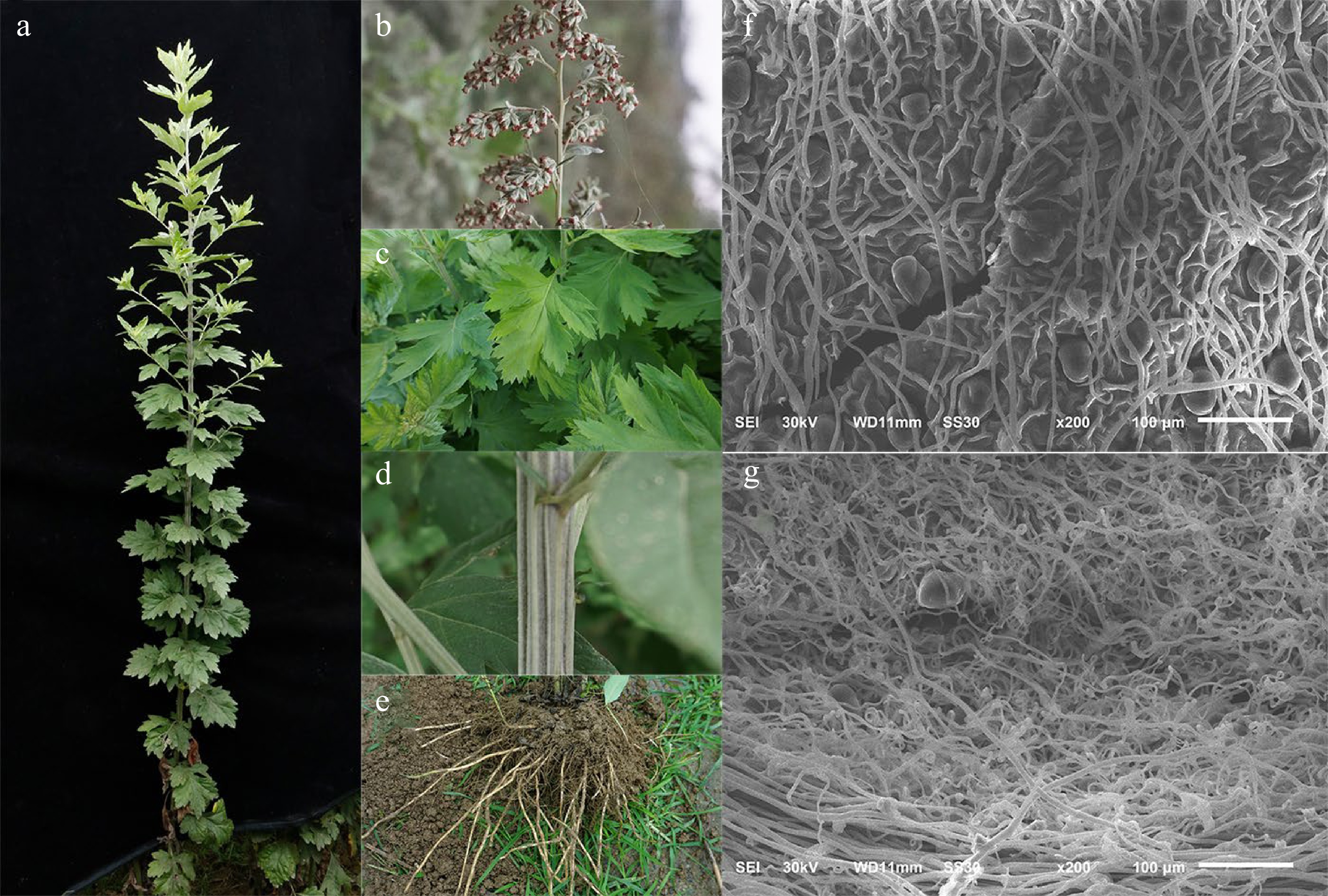

Figure 1.
Morphological characteristics of Artemisia argyi. (a) Aboveground parts of the A. argyi plant. (b) The inflorescence of A. argyi during its peak flowering period. (c) Morphology of the adaxial surface of leaves from A. argyi. (d) Morphology of the stem from A. argyi. (e) Underground parts of the A. argyi plant. (f), (g) Microscopic images of the abaxial surface of the leaves.
-
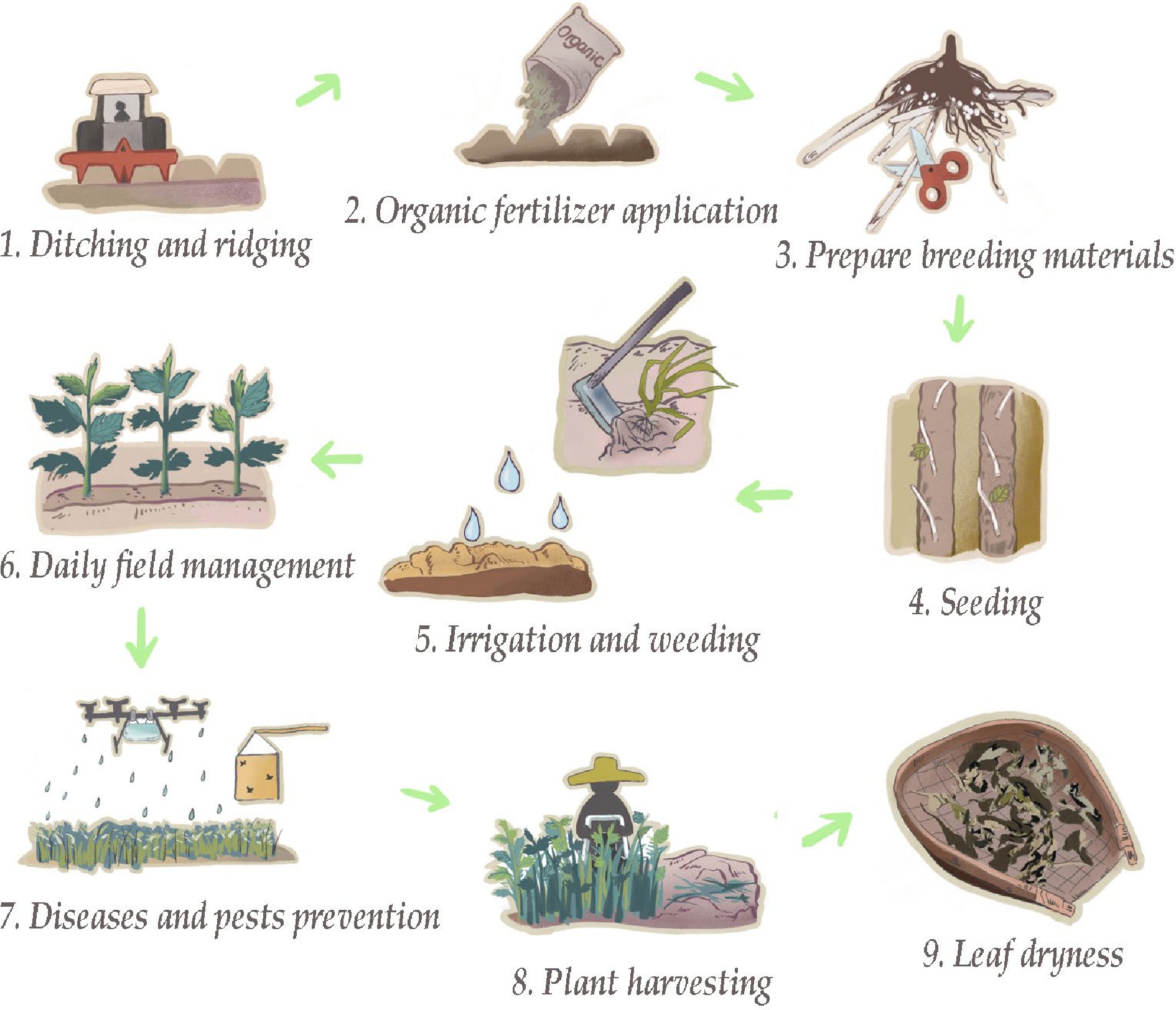
The primary A. argyi cultivation areas in China are located in Henan, Hubei, Sichuan, Anhui, and Hunan provinces. Regions with abundant sunshine, a mild climate, four distinct seasons, and ample rainfall are recommended for A. argyi cultivation. A. argyi also shows a preference for loose yellow-brown soil, red soil, and paddy soil. It is suitable for cultivation in hilly areas and regions with low to medium mountains and flat or gentle slopes, all with good drainage and sun exposure. The planting period runs from November to December[17]. Before sowing, a selected site should be prepared and basal fertilizer should be applied (Fig. 2). A. argyi is planted with rhizomes; two to three planting ditches should be dug along the ridge direction with a depth of 8–10 cm and a width of 10–15 cm. The rhizomes should be cut into small segments of 10–15 cm and planted horizontally in trenches 5–10 cm apart[18, 19]. Artificial watering is required during the dry season that is typical after planting. At three to five days after planting, the whole field should be sprayed with an herbicide such as glyphosate for weed control.
Field management
-
Tilling and weeding operations should be conducted in early March. Because A. argyi is intolerant of waterlogging, timely ditch cleaning is necessary in March and April to ensure adequate drainage, promote soil ventilation, and allow temperature increases. These measures reduce the risk of seedling death and stunting. Tilling and weeding should be conducted in early May (after the first harvest) and early July (after the second harvest). From June to September (during the dry season), shallow irrigation can be used to promote plant growth. After harvesting, the field should be turned over and sun-dried, and residual branches and leaves should be removed[20].
Comprehensive disease and pest prevention
-
A. argyi is susceptible to powdery mildew, leaf spot, and viral disease, aphids, Corythucha marmorata, and scale insects. Combinations of agricultural, physical, and biological methods are used for pest and disease prevention and control. High, narrow planting ridges and wide ditches promote field drainage and ventilation, control plant density, increase light access, and reduce the spread of diseases and pests. Organic and phosphorus-potassium fertilizer application promotes plant vigor and enhances stress resistance. Removal of residual plant materials from the field and intertillage weeding reduces overwintering pests. Harvesting is carried out around May 1st to avoid the critical aphid outbreak period and leaf spot disease during the rainy season. The use of insect-proof boards, botanical and biological pesticides, and natural insect enemies can effectively prevent and control pests and diseases[ 21].
Harvesting period
-
In China, the harvesting time for A. argyi in most regions is around May 1st, some regions can even harvest three crops, the second crop in early July, and the third crop in early October[22, 23]. Harvesting should be conducted on sunny days after field dew has dried. Farm tools or harvesting machinery can be used for on-site cutting. The entire plant should be cut and briefly air-dried in the field. After transportation to a shaded area, the leaves can be separated from the stems and spread out to sun-dry on a clean surface[24].
-
Artemisia species exhibit great heterogeneity in quality[25−28]. The 2020 Chinese Pharmacopoeia stipulates that eucalyptol and borneol contents in A. argyi should not be < 0.05% and < 0.02%, respectively. However, this standard is broad and has proven insufficient in effectively controlling A. argyi quality. This is because A. argyi contains numerous pharmacologically active substances that can impact its quality and medicinal efficacy. Distinct evaluation indicators are also required for A. argyi materials that are used in different applications. For example, evaluations of A. argyi for use in moxibustion should focus on the moxa output rate, whereas flavonoid and phenolic acid levels are more relevant for plants used in traditional Chinese medicine decoctions; volatile compound abundance should be regulated in A. argyi used to produce essential oils (Fig. 3). These applications of A. argyi are discussed in more detail below.
Moxa output rate
-
A. argyi leaves can be ground to created moxa for moxibustion, the primary component of moxa is non-glandular trichomes. Different types of A. argyi leaves thus vary in the moxa output rate. A. argyi leaves can be pulverized with an oscillating high-speed universal pulverizer, and the power residue can then be removed with a 10–20 mesh sieve to produce moxa[29]. Regional comparisons of A. argyi moxa output have shown that plants grown in China have higher moxa output rates than plants grown in South Korea, with the highest levels found among plants grown in the south-central and southeast regions and Nanyang[25,30].
Flavonoid and phenolic acid contents
-
A. argyi contains over 50 types of flavonoid compounds, the most abundant of which are flavones, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, and chalcones. Most of these exist in the form of glycosides, with the primary components including isorhamnetin, luteolin, apigenin, tamarixetin, quercetin, kaempferol, and myricetin[31]. The most abundant phenolic acid components in A. argyi include chlorogenic acid, neochlorogenic acid, cryptochlorogenic acid, isochlorogenic acid A, isochlorogenic acid B, and isochlorogenic acid C[28]. Although the types of flavonoid and phenolic acid components are similar between A. argyi varieties, the abundances of specific molecules vary significantly[26, 30, 32]. Chen et al. used ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) to analyze the contents of 12 flavonoids and phenolic acid components in 100 Chinese A. argyi germplasm resources, establishing a UPLC-based fingerprinting method to assess the metabolic composition of each accession[25]. Luteolin and isorhamnetin in particular are important indicator components. For example, A. argyi grown in Qichun County, Hubei Province have higher levels of these two metabolites than plants grown in other production areas, validating the excellent quality of A. argyi var. argyi cv. 'Qiai'[28].
Volatile compound contents
-
The volatile oil of Artemisia argyi is the main effective constituent of Artemisia argyi. Common A. argyi volatile oil extraction methods include steam distillation, solvent extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, ultrasonic-assisted extraction, and microwave-assisted extraction. Steam distillation is the most commonly used of these methods[13]. Hu et al. extracted volatile oils from 29 samples of A. argyi collected from China and South Korea; the samples with the three highest volatile oil contents were all grown in Qichun County, Hubei Province[30]. Chen et al. found that the total volatile oil contents of 100 samples ranged from 0.53%–2.55%, but that the average volatile oil contents of samples from Qichun County were 1.61%, a full 1.43% higher than the average[33]. Other studies have also confirmed that the total volatile oil contents of A. argyi grown in Qichun County are significantly higher compared to plants grown in other regions[13].The chemical constituents of A. argyi volatile oils can be detected and analyzed with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)[33]. More than 200 chemical components have been identified, including monoterpenes and derivatives, sesquiterpenes and derivatives, aldehydes, ketones, and phenolic compounds. The monoterpenes such as eucalyptol, β-pinene, thujones, (–)-camphor, terpinen-4-ol, α-terpineol, camphor, borneol, are abundant in quantity and content, which have rich pharmacological activity[27].
Combustion heat value
-
The therapeutic effects of moxibustion treatment are believed to be primarily due to the warming effect produced by the process of moxa combustion. Within a certain range, greater heat levels generated by moxa combustion strengthen the warming effect[34]. Several studies have established a method for the determination of the combustion heat values of moxa, these studies collected multiple number of A. argyi samples from China, including Hubei, Henan, Shandong, Jiangxi and Anhui province, the environments and climates of these areas were varied. Using an oxygen bomb calorimeter to compare combustion heat values of moxa derived from multiple regions showed that moxa from Qichun County have the highest combustion heat values, whereas moxa from Ziyang City, Sichuan Province have the lowest values (88.96% of the Qichu County samples). Moxa from Tangyin County, Henan Province and Anguo City, Hebei Province have combustion heat values that are 96.28% and 96.03% of the Qichun County moxa values, respectively[35]. Other studies have analyzed the combustion heat values of 69 batches of commercial moxa and 36 batches of laboratory-made moxa samples from China. The results showed that Qichun moxa have a higher combustion heat value (18,762.2 J/g) than the average values of moxa from other regions in China (18,409.4 J/g)[21, 36].
-
Evolutionary research has greatly benefitted from the availability of cp genomes due to their simple structure, small size, and pattern of maternal inheritance[37]. The A. argyi cp genome was first assembled in South Korea[38]. In 2022, a Chinese group sequenced the cp genomes of 72 Chinese A. argyi germplasm resources[39], the cp genome was found to be ~151 kb in size and to contain 114 genes, including 82 protein-coding, 28 transfer RNA (tRNA), and four ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes. There was strong homogeneity in the cp genomes of different varieties; a total of 196 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were detected in the 72 A. argyi cp genomes, 14 of which were validated for use in intra-species identification. Moreover, according to the phylogenetic tree of 67 Asteraceae species, A. argyi was shown to be closely related to Artemisia lactiflora and Artemisia montana.
Nuclear genome
-
The first high-quality, chromosome-level nuclear genome assembly of A. argyi was constructed from PacBio-Hifi and Hi-C sequencing technologies by a Chinese group. The genome assembly was 8.03 Gb in size, characterized by high heterozygosity (2.53%), high repetitive sequence content (73.59%), and 279,294 protein-coding genes[40]. In another study, flow cytometry was used to analyze the genome sizes of 42 A. argyi accessions; these results were consistent with the genome assembly at 8.428–11.717 Gb[41]. The A. argyi genome shows evidence of at least three rounds of whole-genome duplication (WGD) events, including a recent (~2.2 million years ago) species-specific WGD event[40, 42]. This suggests that the three rounds of WGD and recent proliferation of long terminal repeats may explain the large genome size and polyploid formation.
Cloning and analysis of genes in specialized metabolite pathways
-
The A. argyi genome assembly has provided information about specialized metabolite biosynthesis in this species, enabling researchers to unravel the pathways involved in flavonoid and terpenoid synthesis. The genes in these pathways have undergone extensive amplification and tandem duplication, explaining the high levels of flavonoids and volatile oils in the plants. Transcriptomic analysis indicates that expression patterns of the genes encoding hydroxy-cinnamoyl transferase (HCT) and chalcone synthase (CHS) play critical roles in regulating lignin and flavonoid synthesis[40]. Additionally, 32 candidate genes encoding key enzymes such as 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase and 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate were shown to participate in the methylerythritol pathway (MEP) and mevalonate pathway (MVA) pathways upstream of terpenoid biosynthesis[42]. The lack of artemisinin production in A. argyi compared to other Artemisia species may be due to the absence of the key enzyme morpha-4,11-diene synthase (ADS), which is necessary for artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua[43]. Using a full-length transcriptome, the first gene encoding borneol dehydrogenase (AArBDH1) in A. argyi was identified and cloned[44]. Furthermore, the flavonoid O-methyltransferase gene family was identified, members of which encode enzymes involved in A. argyi flavonoid methylation[45]. An additional 23 candidate functional genes involved in thujone synthesis and 66 candidate genes encoding transcription factors that regulate thujone content have also been identified[46].
-
The leaves of Artemisia argyi contains multiple secondary metabolites, which have been proven to have various pharmacological activities, the primary known pharmacological effects of Artemisia argyi was shown in Fig. 4. Many studies have indicated that various components of A. argyi extracts have anti-inflammatory effects. Extracts generated with water, n-butanol, ethyl acetate, and petroleum ether have therapeutic effects on ulcerative colitis in a range of degrees; ethyl acetate extract has the best anti-inflammatory activity in vitro, and eupatilin may be one of the key anti-inflammatory active substances in this extract[47]. A. argyi methanol extracts can alleviate the inflammation response by inactivating inflammatory bodies of Caspase-11 in macrophages[48]. A. argyi essential oils can also exert anti-inflammatory effects by influencing arachidonic acid levels. Specifically, they inhibit PLA2 expression; reduce free arachidonic acid production; and block arachidonic acid metabolism by inhibiting 5-LOX and COX-2 expression, reducing production of downstream inflammatory mediators[49]. Monoterpenes are identified as the main components of A. argyi detected by GC-MS, among which eucalyptol, camphor, and borneol are found to be the predominant anti-inflammatory components, exhibiting superior bioavailability when administered through the skin compared to gavage[50]. Moxibustion can also exert therapeutic effects on rheumatoid arthritis by decreasing levels of interleukin (Il)-23 and Il-17, reducing the activity of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways, and regulating inflammatory reactions and autophagic activity[51].
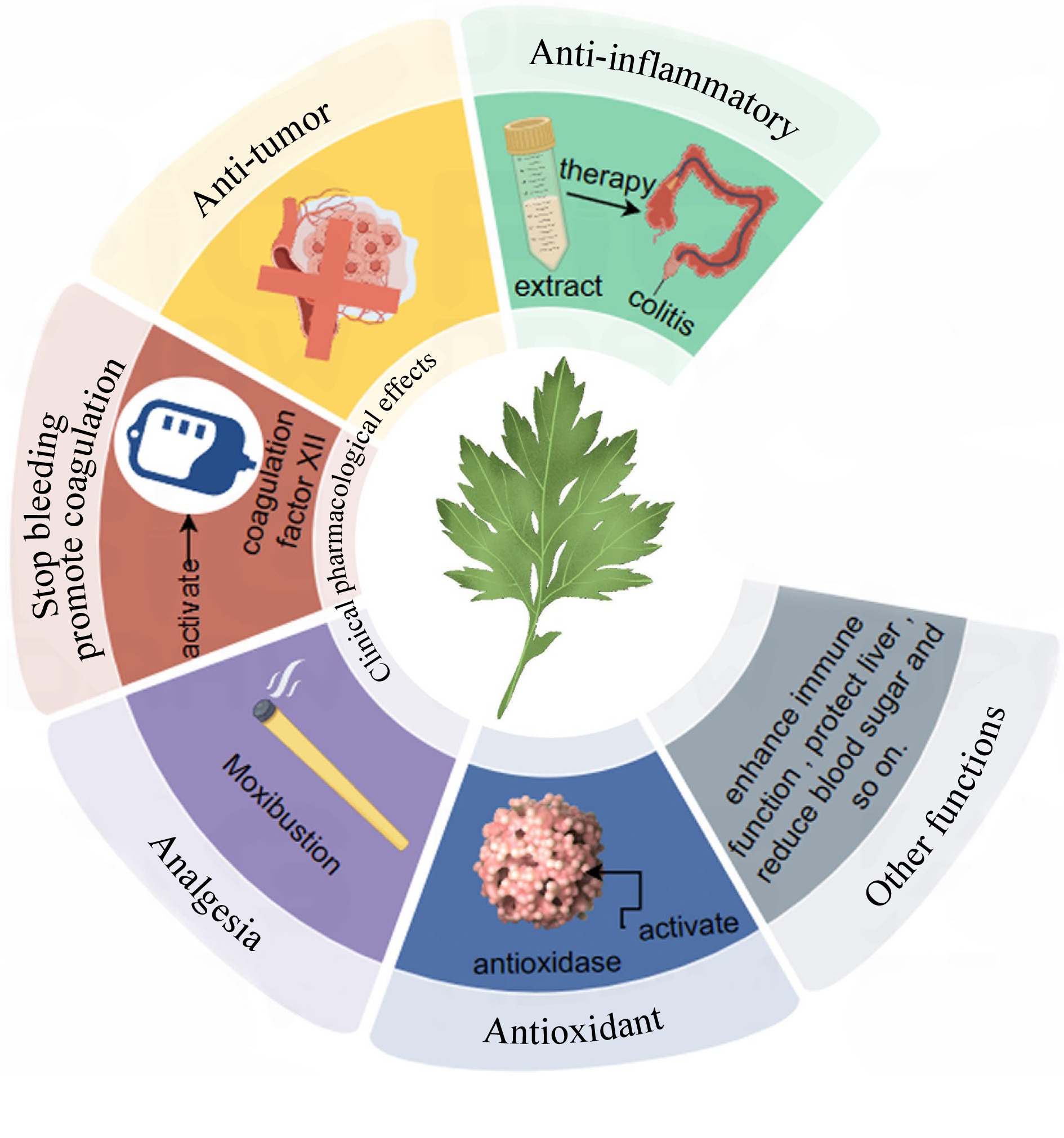
Figure 4.
Primary known pharmacological effects of Artemisia argyi. Note: This figure was drawn by Figraw.
Anti-tumor effects
-
A. argyi water extract can significantly reduce cell viability and induce apoptosis by regulating the PI3K/AKT and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways. A. argyi extract (AAE) promotes tumor globule reduction when combined with commercial chemotherapy drugs[52]. Water-soluble A. argyi-derived polysaccharides inhibit the growth of S180 transplanted tumors and prolong the survival time of tumor-bearing mice[53]. Total flavonoids extracted from A. argyi can inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in liver cancer SMMC-7721 cells via Caspase-3, BCL-2, and P21; both the growth inhibition and apoptosis rates show some concentration dependence[54]. The monomer flavonoid eupatilin inhibits malignant behavior in pancreatic cancer SW-1990 cells by regulating the DCST1AS1/Mir-138-5p axis[55]. Eupatilin also inhibits miR-1885p expression, preventing retinoblastoma cell invasion[56]. In cervical cancer cells, the A. argyi metabolite jaceosidin exhibits potentially therapeutic effects, inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing G2/M phase arrest[57]. Another A. argyi metabolite, hispidulin, regulates PIM1 expression through the ROS/Jak2/STAT3 signaling pathway, exerting an anti-colorectal cancer effect[58]. Guaiane-type sesquiterpenes isolated from A. argyi exhibit significant cytotoxic activity in human gastric adenocarcinoma (AGS) cells and could therefore be used in the development of clinical anti-tumor drugs[59].
Hemostatic effects
-
Both ancient Chinese medical records and modern pharmacological studies have confirmed the hemostatic effects of A. argyi. In addition to being used for small trauma hemostasis in clinical practice, A. argyi is also widely used among patients with thrombotic disease sequelae and congestion pain to alleviate symptoms and restore function. Numerous studies in animals have shown that the hemostatic and anticoagulant effects of A. argyi may be dependent on processing methods. For example, in a study of shortened clotting time in mice, sand-scalded A. argyi charcoal showed the best effect, followed in descending order of efficacy by raw A. argyi, baked A. argyi, fried A. argyi charcoal, and vinegar A. argyi charcoal[60]. Tannin compounds are the most effective coagulation substances present in A. argyi; a similar study of the efficacy of multiple A. argyi components in promoting blood coagulation found that tannic acid is most effective, followed by A. argyi tar, A. argyi charcoal, and A. argyi ash; A. argyi essential oil is the least effective[61]. Tannic acid activates coagulation factor XII (f XII), producing procoagulant activity via the EGF-Like2 domain[62].
Analgesic effects
-
Moxibustion is often used in folk medicine to fumigate the navel for pain relief, with ginger slices used to increase the efficacy. Fumigation of joints with moxibustion can also play a role in dispelling dampness and cold. A study of raw and processed A. argyi products in mice showed that vinegar A. argyi charcoal has a significant pain-inhibitory effect in mice[63]. Its efficacy in warming the meridians to dissipate cold and relieve pain may be related to heat-sensitive channels[64]. For example, A. argyi alcohol extract can activate the heat-sensitive ion channel TRPV1, generating transmembrane currents and thus analgesic effects. A. argyi can also achieve analgesic effects by influencing levels of inflammatory factors such as PGE2 and NO. A. argyi has less potential for addiction than many pain-relieving compounds used in Western medicine and can exert good analgesic effects when used externally. It could therefore be used to reduce human dependence on painkillers.
Antioxidant effects
-
Accumulation of excessive free radicals in the body leads to oxidative organ aging. An over-oxidated state requires artificial hydrogen supplementation to trigger reduction reactions, thus eliminating free radicals. Free radical scavenging tests have revealed antioxidant effects of various A. argyi compounds. The antioxidant activities of nonvolatile extracts are present mainly in the aqueous and ethanol phases, with flavonoids responsible for the bulk of observed antioxidant activities[65]. Variations in extraction methods may therefore lead to differences in antioxidant effects. The best extraction methods for optimal free radical scavenging and inhibition of xanthine oxidase (XOD) are alcohol extract, traditional extract, and water extract. All three of these extract types irreversibly inhibit XOD. A. argyi alcohol extract also has a reducing effect on serum uric acid, creatinine, and urea nitrogen levels in hyperuricemic mice, suggesting a potential for development of drugs for the prevention and treatment of hyperuricemia[66]. A. argyi essential oils also have protective effects on mouse organs affected by oxidative aging, increasing levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH) and decreasing levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and protein carbonyl (PCO) in the heart, liver, and kidney[67].
Other functions
-
In addition to the pharmacological effects enumerated above, various components and extracts of A. argyi have immunomodulatory[68], hematoprotective[69], and anti-hyperglycemic effects[70]. In the trachea, A. argyi-derived terpenes can directly exert anti-asthmatic, anti-tussive, and expectorant effects[71].
-
Moxibustion therapy is the primary A. argyi consumption method. Commercial moxa purity is typically expressed as the leaf:moxa ratio (i.e., the weight of leaves required to make 1 kg of moxa). The ratios of commercially available moxa vary from 2.5:1 to 45:1, and it is generally believed that a higher purity produces better-quality moxibustion products within a specific range. The process of moxa production leads to formation of high-volume by-products such as A. argyi powder. The low density and large volume of A. argyi powder hinder its development for industrial utilization. However, the large amount of space required for storage of A. argyi powder and other by-products (such as stems) necessitates identification of appropriate methods of utilization. The lack of available methods for appropriate use of A. argyi by-products is currently a bottleneck in sustainable development of this industry. Promisingly, studies conducted in recent years have shown that A. argyi by-products have a variety of significant biological activities. Some active components have been isolated and identified, and various non-medicinal applications have been developed, as discussed below (Fig. 5).

Figure 5.
The production process of Artemisia argyi powder and the development of its non-medicinal value.
Herbicide development
-
Allelopathy is very common in phytochemical interactions in nature. This phenomenon has great potential for application as an effective, environmentally sustainable method of weed management. At present, the primary technical measures for weed control in field crops that employ allelopathy are intercropping, crop rotation, cover crop use, and mulching[72]. Some plants contain powerful allelochemicals that can inhibit plant germination and growth and increase crop plant stress resistance without residual or toxic effects. These are considered suitable substitutes for chemical herbicides[73]. A. argyi has strong allelopathy, conferring extreme environmental adaptability and niche competitiveness in this species. Several studies have examined the effects of A. argyi allelochemicals that show herbicidal activity. Li et al. found that adding A. argyi powder to the soil strongly inhibits germination and growth of Portulaca oleracea, Oxalis corniculata, and Setaria viridis[74]. Furthermore, application of A. argyi powder to the field can also significantly reduce weeds and promote active compound accumulation in Chrysanthemum morifolium cultivation without negatively impacting yield[75]. The results of herbicidal activity tests with various polar components of A. argyi extracts show that water-soluble extracts are most effective in weed suppression, followed by a 50% ethanol extract and a pure ethanol extract[74]. This is consistent with other reports that plant water extracts rich in phenolic acids have stronger allelopathic activity than those with lower levels of phenolic acids[76]. A study using UPLC–quadrupole time-of-flight (QTOF)–MS was used to analyze the pharmacodynamic substances present in A. argyi water extracts, finding that phenolic acid compounds such as caffeic acid, cryptochlorogenic acid, neochlorogenic acid, and chlorogenic acid are the primary weed-suppressing active ingredients[77]. Further bioactivity-directed separation confirmed that isochlorogenic acid A is another key active substance in A. argyi. This compound has broad-spectrum herbicidal activity and could be used as a lead compound for botanical herbicide development[78]. Mechanistic studies have found that A. argyi water extract can inhibit plant growth by interfering with multiple targets and pathways, including hormone pathways, mineral element absorption mechanisms, and photosynthesis[79].
The monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes that are abundant in aromatic plant essential oils have significant phytotoxicity[80]. However, essential oils have little to no toxicity to mammals and do not pollute the soil or surrounding environment[81]. Such mixtures are thus valuable resources for the development of safe, efficient botanical herbicides. Essential oils of Artemisia fragrans[82] and Artemisia herba-alba[83] are known to have herbicidal activity, and a recent study confirmed the phytotoxicity and herbicidal potential of A. argyi essential oil. In vitro, miniscule amounts of A. argyi essential oil can significantly inhibit germination of Setaria viridis, Echinochloa crus-galli, Portulaca oleracea, and Amaranthus retroflexus. Furthermore, the short-contact killing effects of A. argyi essential oil aqueous emulsions on weeds have been proven in situ in pots and fields[84]. A. argyi essential oil has many negative impacts on weeds: decreasing the photosynthetic pigment content; increasing MDA contents, membrane leakage, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) abundance; and disrupting the antioxidant system. Together, these effects ultimately induce severe photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative damage, causing death. 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) may be a target of A. argyi essential oil, leading to herbicidal effects[84].
Bacteriostatic agent development
-
A. argyi has a broad antibacterial spectrum, strong antibacterial abilities, high antibacterial efficiency, and low toxicity to humans. Bacteriostatic activity has been clearly observed in A. argyi essential oil. For example, in vitro antibacterial experiments show that A. argyi essential oil has good antibacterial effects on Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus albus, and Staphylococcus citreus[85]. Liu et al. screened quality markers of A. argyi essential oil antibacterial activity and found that potential quality markers for antibacterial activity were eucalyptol, camphor, and bornol[86]. A. argyi extract was tested for antibacterial activity against Pasteurella, which causes disease in poultry; the minimum inhibitory concentration was measured at 7.8 g/L, suggesting future applications of A. argyi extract as a veterinary antibacterial agent. In vitro, A. argyi shows additive and synergistic antibacterial effects with Coptis chinensis, Phellodendron amurense, and Sanguisorba officinalis[87]. Flavonoids extracted from A. argyi ash via ultrasound and total alkaloids extracted via ultrasound and enzymatic methods also have antibacterial activity against E. coli and S. aureus[88,89].
In addition to significant antibacterial activity, A. argyi has been tested against plant fungal pathogens to develop pesticide dosage forms suitable for agricultural production. A. argyi ethyl acetate extract (EAEA) has inhibitory effects on Sclerotium rolfsii, Magnaporth grisea, Gloeosporium theae-sinensis, Alternaria alternata, Cercospora nicotianae, Rhizoctonia solani, Fusarium proliferatum, Fusarium solani, and Fusarium graminearum. This demonstrates the value of EAEA as a natural fungicide for the prevention and control of southern blight, rice blast, camellia anthracnose, frogeye, sheath blight, and root rot[90]. The antifungal activity of A. argyi is mainly derived from the ester- and alcohol-soluble portions, which are rich in flavonoids[90]. Verticillium wilt is known as a 'cancer' of cotton, causing a sharp decline in yield and huge economic losses; EAEA significantly inhibits spore germination and mycelial growth of the causative agent, Verticillium dahliae, with an MIC of 1.0 mg/ml, a minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of 6.0 mg/ml, and a half-maximal dose (EC50 value) of 1.227 mg/ml. EAEA also exerts bacteriostatic activity by destroying the cell membrane structure; inducing ROS bursts; and reducing respiratory enzyme activity[91]. In summary, the antibacterial and antifungal effects of A. argyi components make them strong candidates for future development of plant-derived bacteriostatic agents. This could minimize the damage caused by chemical pesticides, such as enhanced drug resistance, toxicity, and environmental pollution.
Food preservative development
-
As a powerful antioxidant and bactericidal agent, A. argyi essential oil is considered a suitable alternative to chemical preservatives in some contexts. For example, applying 300 μL A. argyi essential oil to 1 kg of grapes can prolong the storage life by nine days[92]. An A. argyi essential oil microemulsion coating can reduce decay and effectively maintain color, soluble solid content, and water content in cherry fruits[93]. Combined with storage at low temperature, a composite coating of C. chinensis and A. argyi oils can effectively maintain hardness and reduce the post-harvest cracking rate, mold rate, and browning index in annua fruit[94]. Another preservative agent composed of A. argyi ethanol extract, Bletilla striata, and Pueraria montana can also significantly reduce the rate of grape rot and improve fruit hardness[95]. Furthermore, A. argyi can maintain the freshness of meat products, including chicken breast[96], pork[97], sausage[98], and chicken feet[99], during transportation and storage.
Animal feed development
-
A. argyi leaves have a higher crude protein content than four popular energy feeds (corn, sorghum, wheat, and rice bran) and three roughage feeds (alfalfa, grass, and flour). Furthermore, they have a higher crude fiber content than the same four energy feeds and a higher crude ash content than four common protein feeds (soybean, rapeseed cake, rapeseed meal, and sesame cake). They have higher magnesium (Mg) and manganese (Mn) contents than all 11 of the common feeds listed above. Therefore, A. argyi leaves could function as a valuable substitute in animal feeds[100]. A. argyi is also rich in medicinal value for animals. Supplementation with A. argyi powder can regulate the intestinal immune function of rabbits, reducing the diarrhea rate and diarrhea index[101]. Adding 1.5% A. argyi powder to the diet significantly improves pig disease resistance, decreasing the incidence of respiratory diseases and diarrhea by 4% and 4.66%, respectively[102]. A. argyi also has fetal protective effects in cattle, reducing threatened miscarriage and slippery fetus[103]. In summary, there are many potential benefits to applying A. argyi as an animal feed, including reduced costs, improved productivity, reduced disease occurrence, and improved feed conversion rate. It also has great potential for development as a herbal additive to animal feeds.
-
A. argyi is a commonly used bulk medicinal herb and folk plant in China. Rapid development of the healthcare industry has led to constant increases in the demand for A. argyi over the past several years. This plant has long relied on private collection of wild seedlings and asexual reproduction without scientific domestication efforts. The increased demand has resulted in challenges with respect to A. argyi materials, including mixed germplasm resources, a shortage of excellent varieties, and a weak research foundation. Over the past 10 years, large-scale domestic cultivation of A. argyi has been prioritized in multiple Chinese provinces such as Hubei, Henan, and Hebei, resulting in a planting area of over 600,000 acres nationwide. However, due to the short history of domestication and cultivation, many issues such as those mentioned above have remained, forming bottlenecks that limit sustainable, healthy development of this industry.
Germplasm resources lay a rich foundation for studying the origin and evolution of crops and for cultivating new crop varieties. As a special agricultural germplasm resource, materials used in traditional Chinese medicine can improve A. argyi production quality and technologies. Strengthening the collection, preservation, and innovative utilization of A. argyi germplasm resources will enable future selection of new varieties, sustainable utilization of traditional Chinese medicine resources, and protection of biodiversity. In recent years, the release of a genome assembly has promoted genetic breeding and molecular research in A. argyi, but the research foundation has remained relatively weak. There is an urgent need to systematically evaluate A. argyi germplasm resources in multiple dimensions, including from genotypic, phenotypic, and biochemical perspectives. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and metabolome GWAS (mGWAS) of germplasm resources could be combined with genome sequencing to identify genes underlying important phenotypic traits and the functional genes producing key metabolites. Overall, researchers would be well served by establishing an A. argyi core germplasm resource bank, identifying molecular markers related to yield and quality, and conducting precise resource identification, evaluation, and germplasm innovation.
Moxibustion therapy is the most common method of A. argyi consumption, but this usage produces huge volumes of by-products. In recent years, many studies have found that the by-products have a variety of significant biological activities; active components have been isolated and identified, and various non-medicinal applications have been developed. Plant-derived pesticides (e.g., herbicides and antibacterial agents), plant-derived preservatives, and plant-derived veterinary drugs are all considered to have strong prospects for future application. However, current research in these areas remains theoretical, without mature dosage forms, preparation systems, or clear application targets. Further study in this area is expected to solve the problem of by-product utilization in the A. argyi industry, fully realizing the application value of this economically and culturally important species.
-
The authors confirm contributions to the paper as follows: study conception and design: Liu D, Miao Y; data collection and analysis: Chen C, Li J; draft manuscript preparation: Chen C, Li J, Chen H, Cai H, Zhang Y, Guo L, Miao Y, Liu D; funding acquisition: Liu D, Miao Y. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32270391), the Earmarked Fund for CARS (CARS-21), the Hubei Provincial Department of Education Excellent Young and Middle-aged Science and Technology Innovation Team Project (T2021008), and Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China (2023AFA032).
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Lanping Guo is the Editorial Board member of Medicinal Plant Biology who was blinded from reviewing or making decisions on the manuscript. The article was subject to the journal's standard procedures, with peer-review handled independently of this Editorial Board member and the research groups.
-
# Authors contributed equally: Changjie Chen, Jinxin Li
- Copyright: © 2024 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press, Fayetteville, GA. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Chen C, Li J, Chen H, Cai H, Zhang J, et al. 2024. Comprehensive review of botanical characteristics, artificial cultivation methods, quality evaluation, genome research, and potential applications of Artemisia argyi Lévl. et Van.. Medicinal Plant Biology 3: e002 doi: 10.48130/mpb-0024-0002
Comprehensive review of botanical characteristics, artificial cultivation methods, quality evaluation, genome research, and potential applications of Artemisia argyi Lévl. et Van.
- Received: 11 May 2023
- Revised: 26 December 2023
- Accepted: 08 January 2024
- Published online: 24 January 2024
Abstract: Artemisia argyi Lévl. et Vant. is a traditional Chinese medicinal plant that is widely distributed across Asia, Europe, and the Americas, especially in East Asian countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and Mongolia. The widespread application of A. argyi in medicine, foods, and folk customs gives it great economic value and strong cultural relevance in China. It has been used in treating diseases for over 2000 years, with modern pharmacological research validating diverse functions (including anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, antioxidant, and analgesic activities) of metabolites produced by A. argyi. Surges in clinical demand have led to the formation of a domesticated A. argyi industry, which has produced a relatively mature artificial planting technology system and comprehensive quality evaluation standards in China. In recent years, the assembly and release of A. argyi chloroplast and chromosome-scale nuclear genomes have enabled identification of key genes in the biosynthetic pathways of various important active compounds. In addition, non-medicinal applications of A. argyi have received widespread attention due to the plant's promising herbicidal, antibacterial, and preservative effects, which could allow its use in place of chemical products. We here review recent progress in A. argyi research with a focus on botanical characteristics, artificial cultivation methods, quality evaluation, genomic and molecular research, pharmacological effects, and non-medicinal value development. This review lays a strong foundation for future research to develop and increase the value of A. argyi and other traditionally medicinal plants.