-
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshinori Fujiwara, Masaharu Higashida, Hisako Kubota, Yuko Okamoto, Shumei Mineta, Shunji Endo, Tomio Ueno. 2021. Perioperative Predictive Markers for Recurrence of Esophageal Cancer after Esophagectomy. Gastrointestinal Tumors. 8:61 doi: 10.1159/000513961
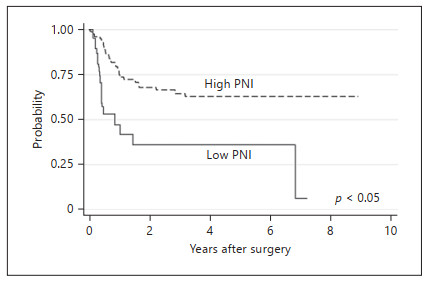
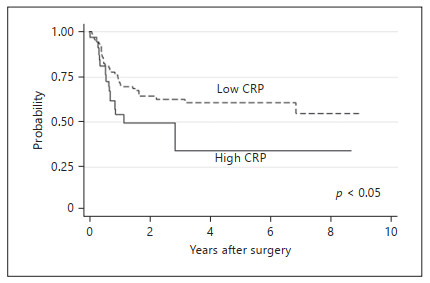
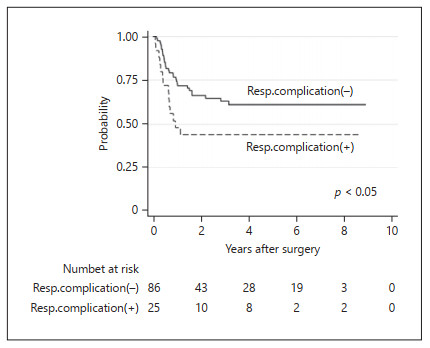
Perioperative Predictive Markers for Recurrence of Esophageal Cancer after Esophagectomy
- Received: 28 August 2020
- Accepted: 21 December 2020
- Published online: 17 March 2021
Abstract:
-
Key words:
- Esophageal cancer /
- Prognostic nutritional index /
- C-reactive protein /
- Cancer progression /
- Prognosis