-
The genus Gnaphalium (family Asteraceae) contains ~200 species scattered throughout the world, including China, Mexico, Argentina, North Korea, Philippines, Indonesia, India, and Australia[1,2]. It is documented that several species have long been used for treating asthma, cough, phlegm, rheumatism, and other disorders. In addition, Gnaphalium affine and Gnaphalium hypoleucum are served as vegetables in southern China[3,4]. Although Zheng et al. reviewed several chemicals and pharmacological functions of Gnaphalium in 2013[5], many bioactive chemical compounds have been identified afterward in different Gnaphalium species to verify and validate their medicinal applications. Here, we summarize the recent achievements in investigation of the ethnopharmacological application, phytochemicals, pharmacological effect, and quality control study of genus Gnaphalium. Furthermore, the limitations of the existing studies and future directions of Gnaphalium research are discussed to provide ideas for future research and development.
-
Gnaphalium affine is an annual herb with a stem about 10−40 cm in length, covered with white thick cotton hairs. The leaf is oblanceolate or obovate, about 5−7 cm in length and 11−14 mm in width, usually with only one vein. The flower is capitulum that densely forms corymbs at the top of the branches, and is involucrally bell-shaped with 2−3 layers. The outer layer is obovate or spoon-shaped, the inner layer is long and spoon-shaped; the female flowers are very common, the corolla is tubular, the top of the corolla is enlarged with 3-tooth, and the lobes are glabrous.
Gnaphalium hypoleucum is an annual stout herb with an erect stem, about 10−40 cm in length. The leaf is linear, about 8 cm in length and 3 cm in width, usually with only one vein, which is obviously visible on the top but not on the bottom. The flower is capitulum that densely forms corymbs at the top of the branches, and is involucrally bell-shaped with four layers. The outer layer is obovate, the back surface is covered with white cotton wool, the inner layer is linear, the top is pointed or acute, and the back surface is usually glabrous. The male flowers are very common, the corolla is filiform.
Gnaphalium japonicum is an annual delicate herb with a slightly erect stem, about 8−27 cm in length. The leaf is sword-shaped linear, about 3−9 cm in length and 3−7 in width, covered with sparse hairs above and thick white cotton hairs on the bottom. The flower is compound capitulum, and forms radial or astral leaflets. The total bract is nearly bell shaped, the outer layer is broadly elliptic, membranous, reddish brown. The middle layer is obovate oblong, and the upper part is reddish brown. The inner layer is linear, and the top is blunt and reddish brown.
Gnaphalium liebmannii, known as 'gordolobo' in Mexico, is an annual herb, about 10−150 cm in length. The leaf is narrowly elliptic or oblanceolate, about 2−9 cm in length and 0.5−1.5 cm in width, corolla, tomentose, margin smooth, and sessile. The flower is corymb and bell-shaped, and 3−9 mm in length, 2.5−7 mm diameter.
Traditional applications
-
In China, the edible history of G. affine has been going on for thousands of years. As early as the Jin Dynasty, G. affine had been used together with glutinous rice to make cakes for human consumption (Fig. 1). Not only Chinese, the Japanese also used it for cooking porridge, and gradually people found that G. affine has certain pharmacological effects. To date, hundreds of species in Gnaphalium are found across the worlds, several of them have been recorded as traditional medicine in Asia, including China, Japan, and Korean, as well as countries in America (Mexico and Argentina). Most of these reports are related to the management of rheumatism, cough, and asthma. Additionally, some species are also used to treat bacterial and fungal infections, diarrhea, cancer, respiratory infections, and several other conditions (Table 1). In China, several registered drugs have been developed from Gnaphalium species, such as 'Fufang Fuercao Heji (复方佛耳草合剂)', containing G. affine as the main component, and used for the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPDs)[6]. Recently, G. affine can also be used as a vegetable for making spices and functional yogurts[7]. Apart from the medical and edible values, G. affine is also used as natural dye for silk coloring in Yunnan, China.
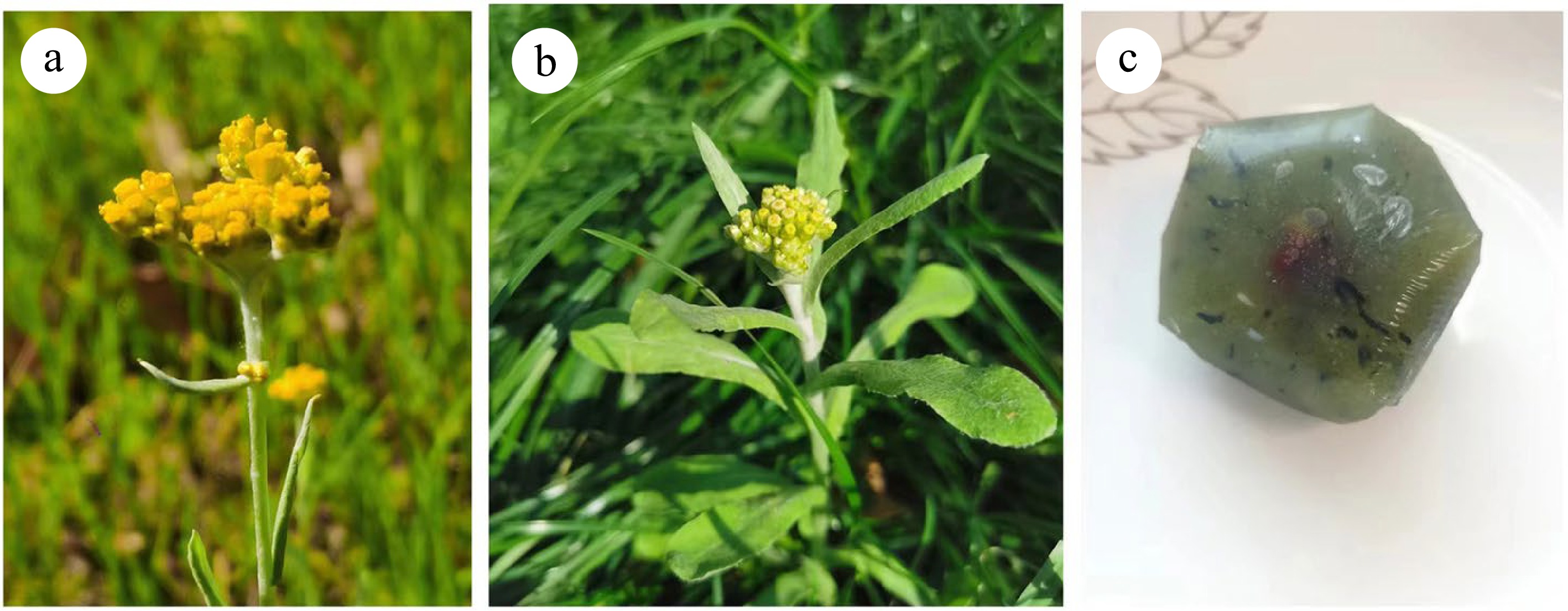

Figure 1.
The morphology of the Gnaphalium affine and its processed products. (a), (b) The overground part of G. affine. (c) The pastry of G. affine, called qingtuan, also known as Qingming food.
Table 1. Ethnopharmacological uses of reported Gnaphalium species.
Gnaphalium species Country Ethnopharmalogical uses Reference G. affine China, Mexico,
Latin AmericaPhlegm-removing, anemopyretic cold, antibacterial, bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, antihypertensive, ulcer, antitussive, expectorant, antiasthmatic, bronchial asthma, respiratory disease, diuretics, antipyretics and antimalarials, wound, backache, coronarism. [8−24] G. hypoleucum China Inflammation, cough, gout, expectorant. [25] G. polycaulon China Clear heat and dampness. [26] G. japonicum China Promoting blood circulation to relieve pain, promoting dampness, treating acne, irregular menstruation, abdominal pain and dysentery during menstruation, clearing away heat and toxins. [27,28] G. adnatum China Treat Helicobacter pylori. [29] G. uliginoshisum Russia, Bulgaria Hypertension, thrombophlebitis, venous thrombosis, ulcer. [30,31] G. stramineum Guatemala Gastrointestinal diseases. [32] G. gaudichaudianum Latin America, Argentina Subcutaneous mycoses, expectorant, hemostasis. [33,34] G. liebmannii Mexico Asthma, cough, bronchitis. [35] -
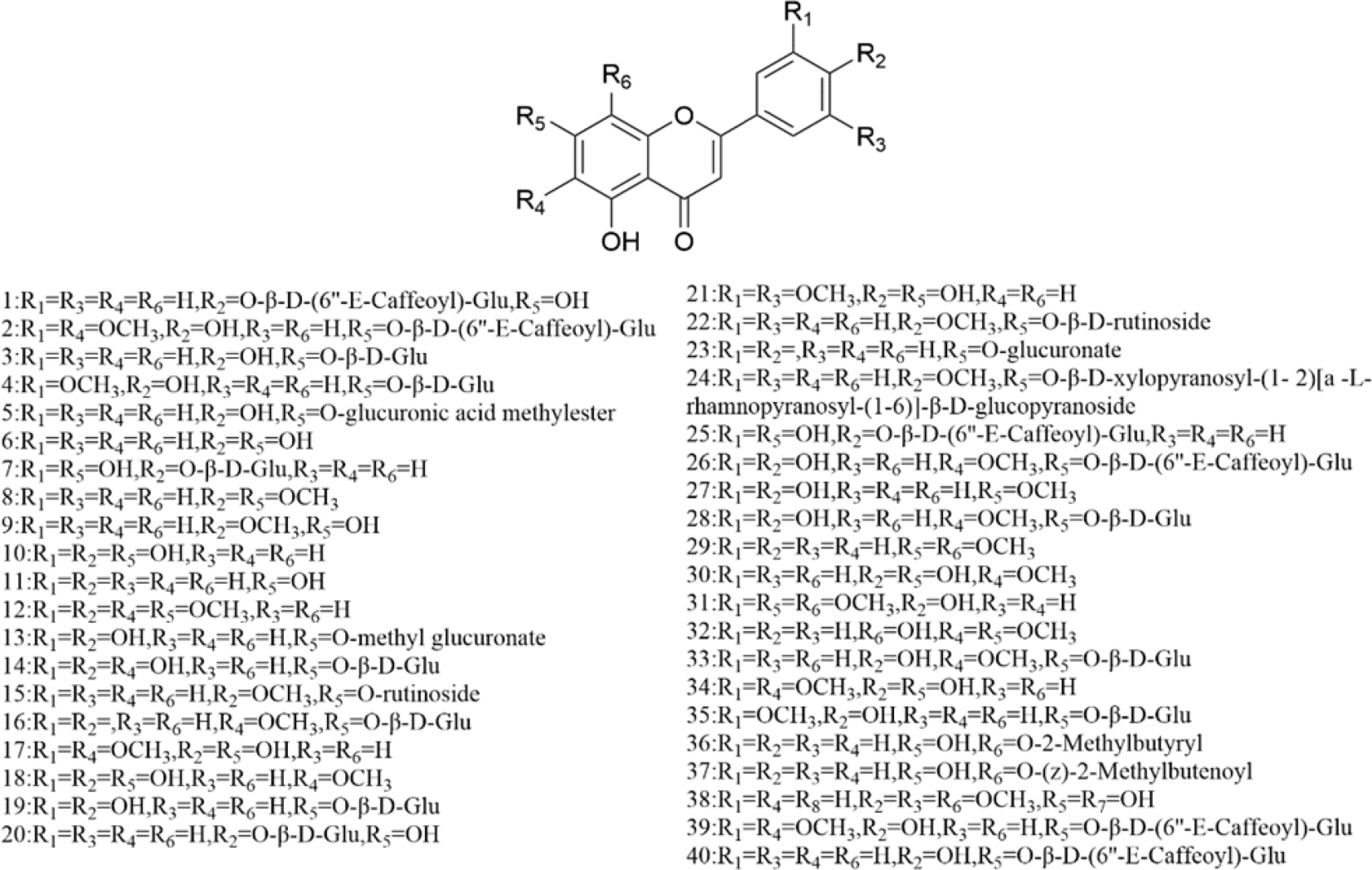
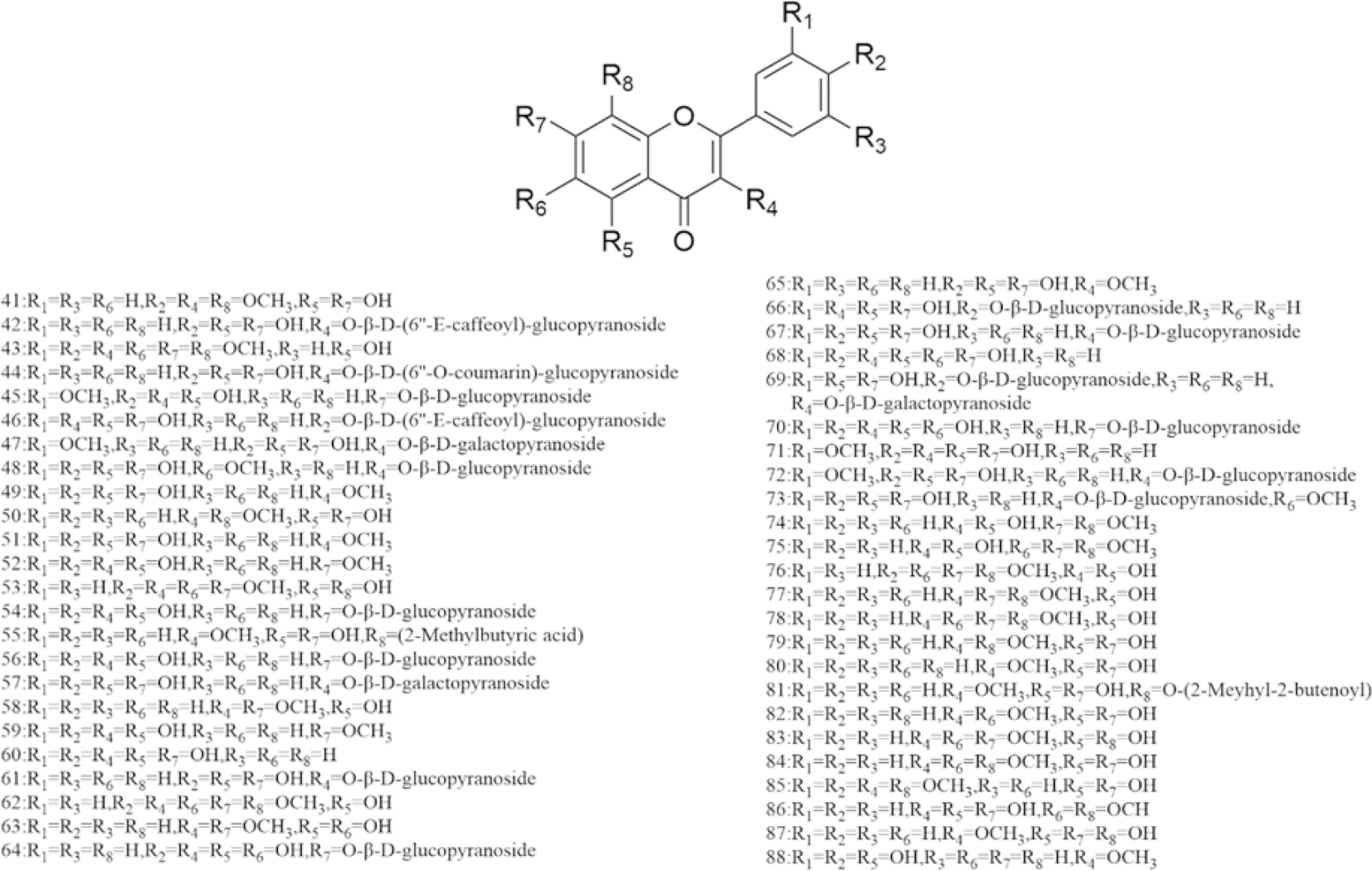
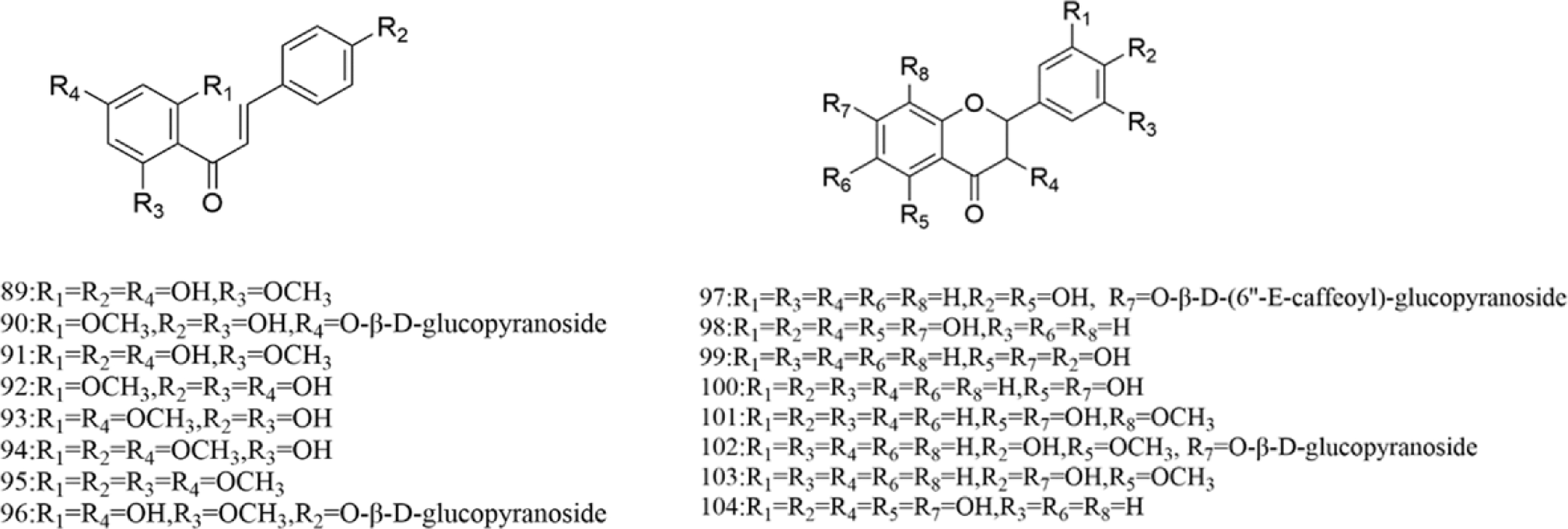
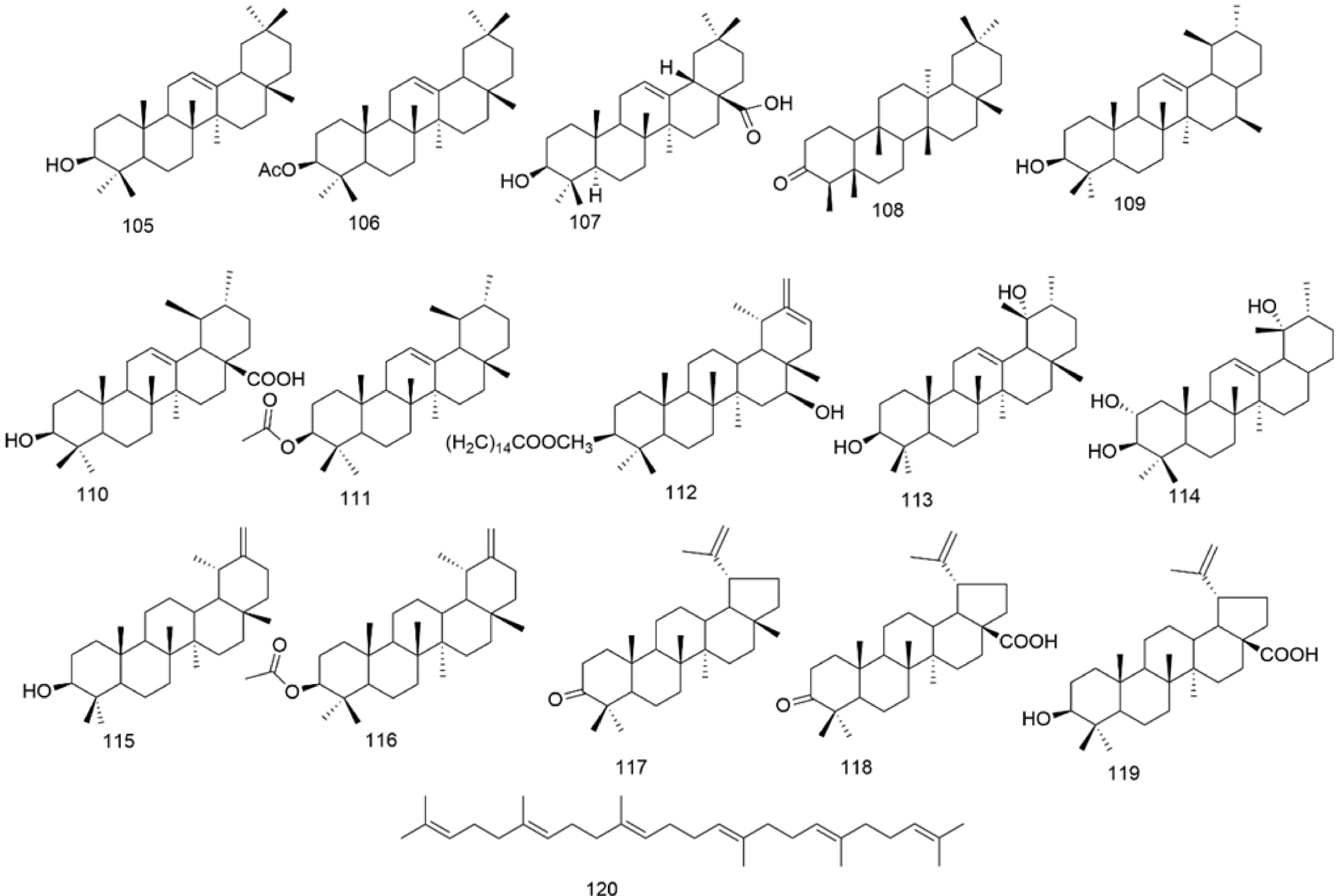
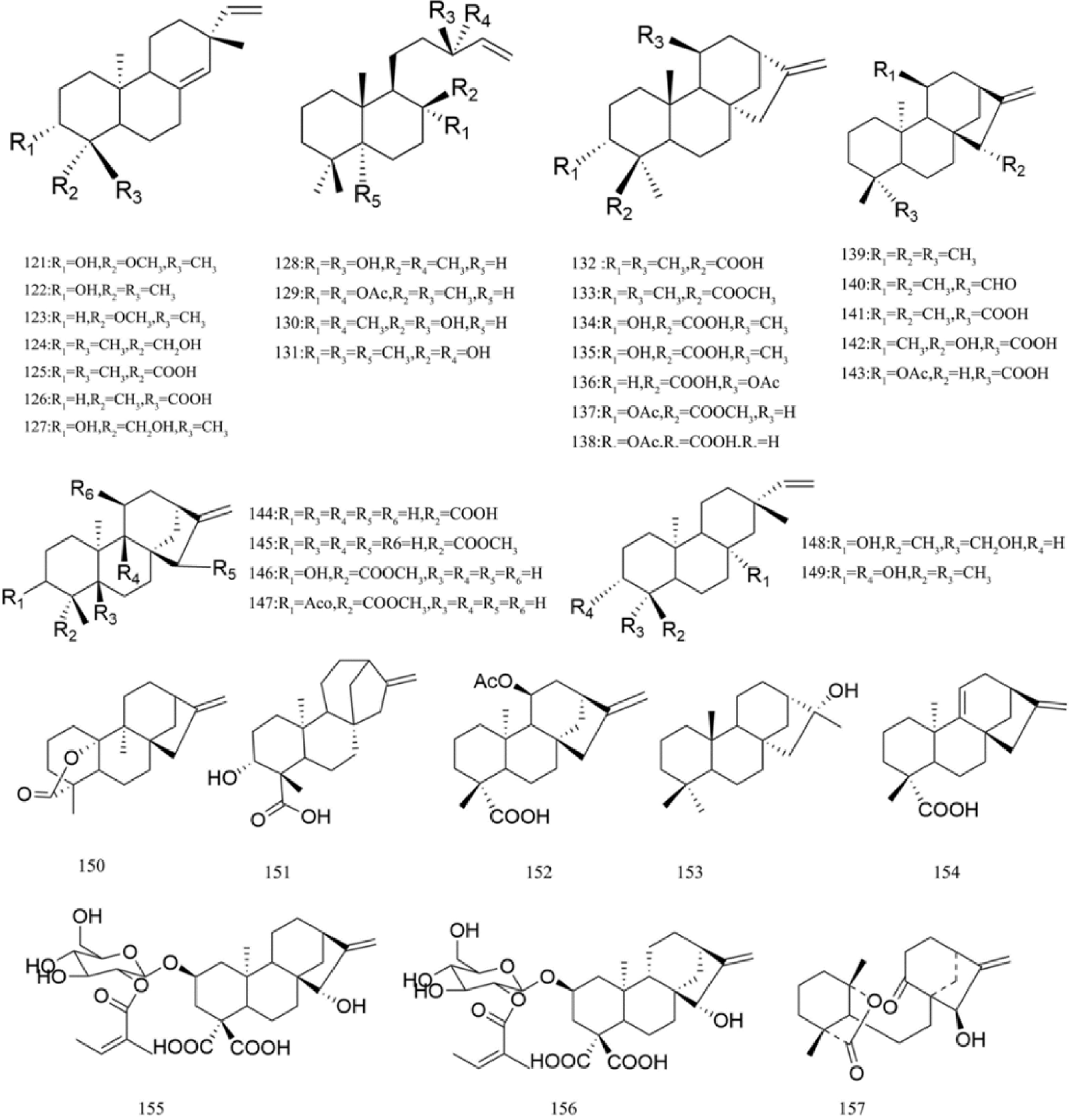
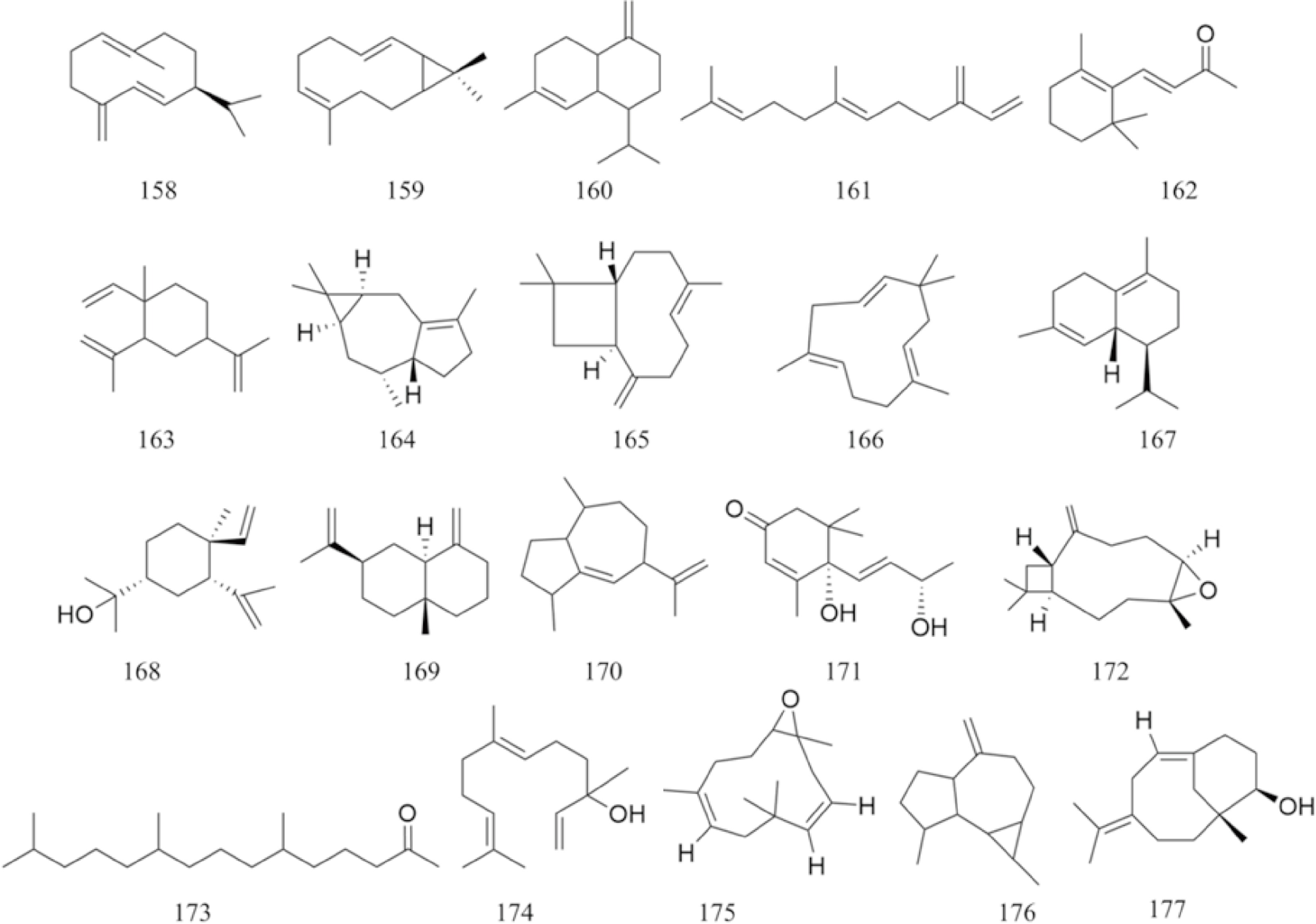
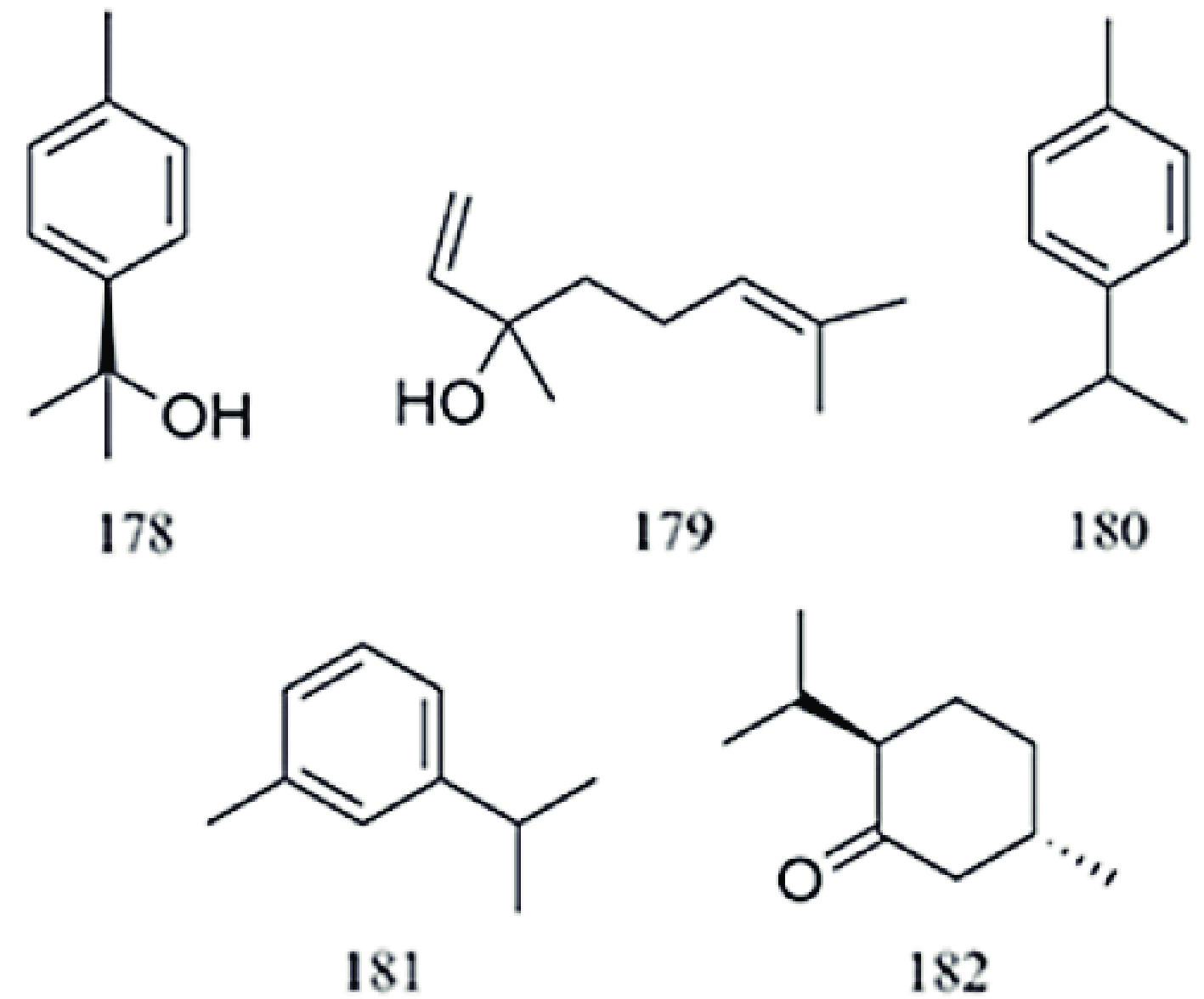
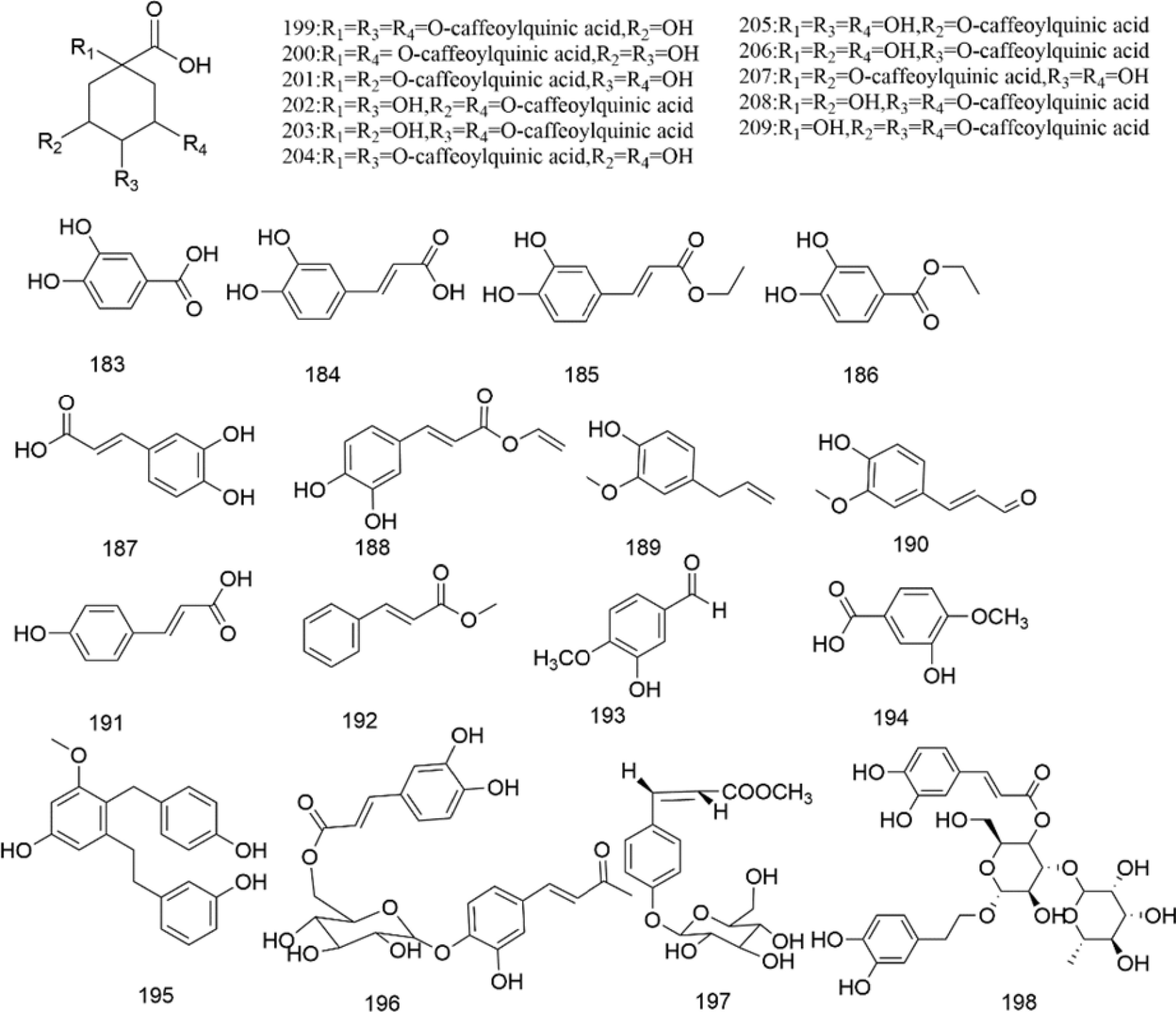
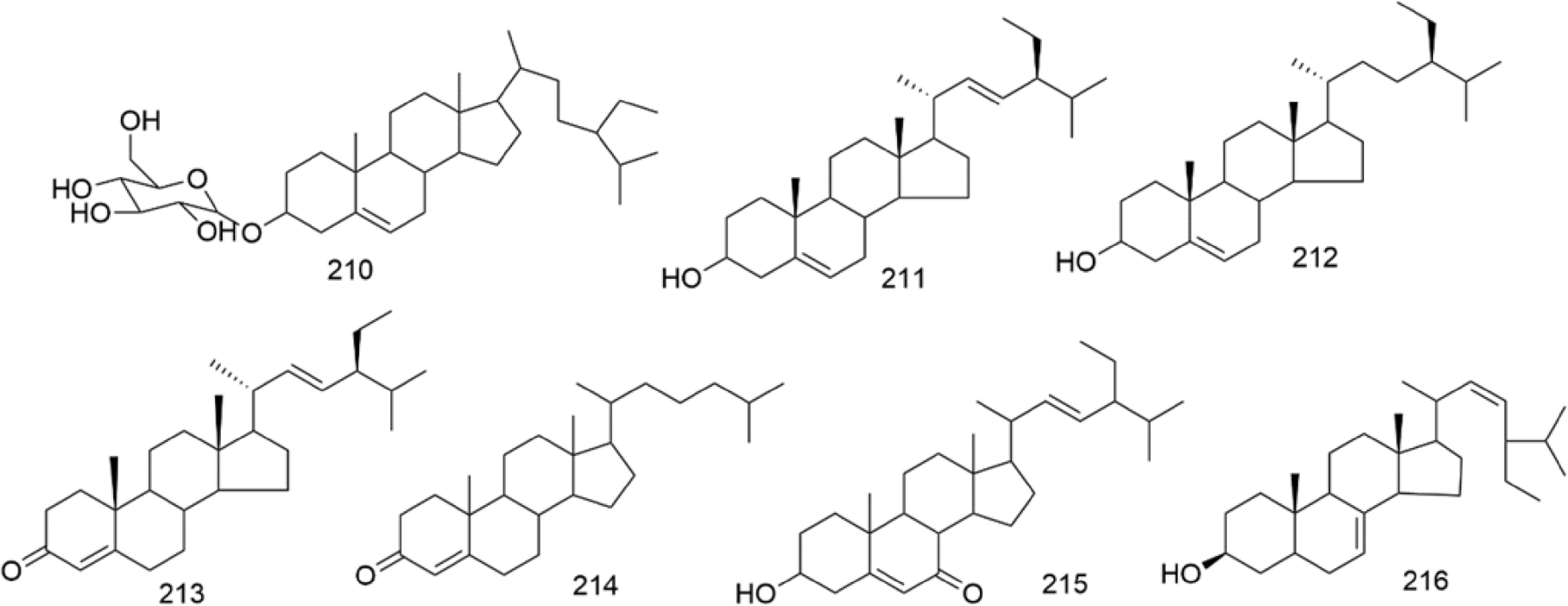
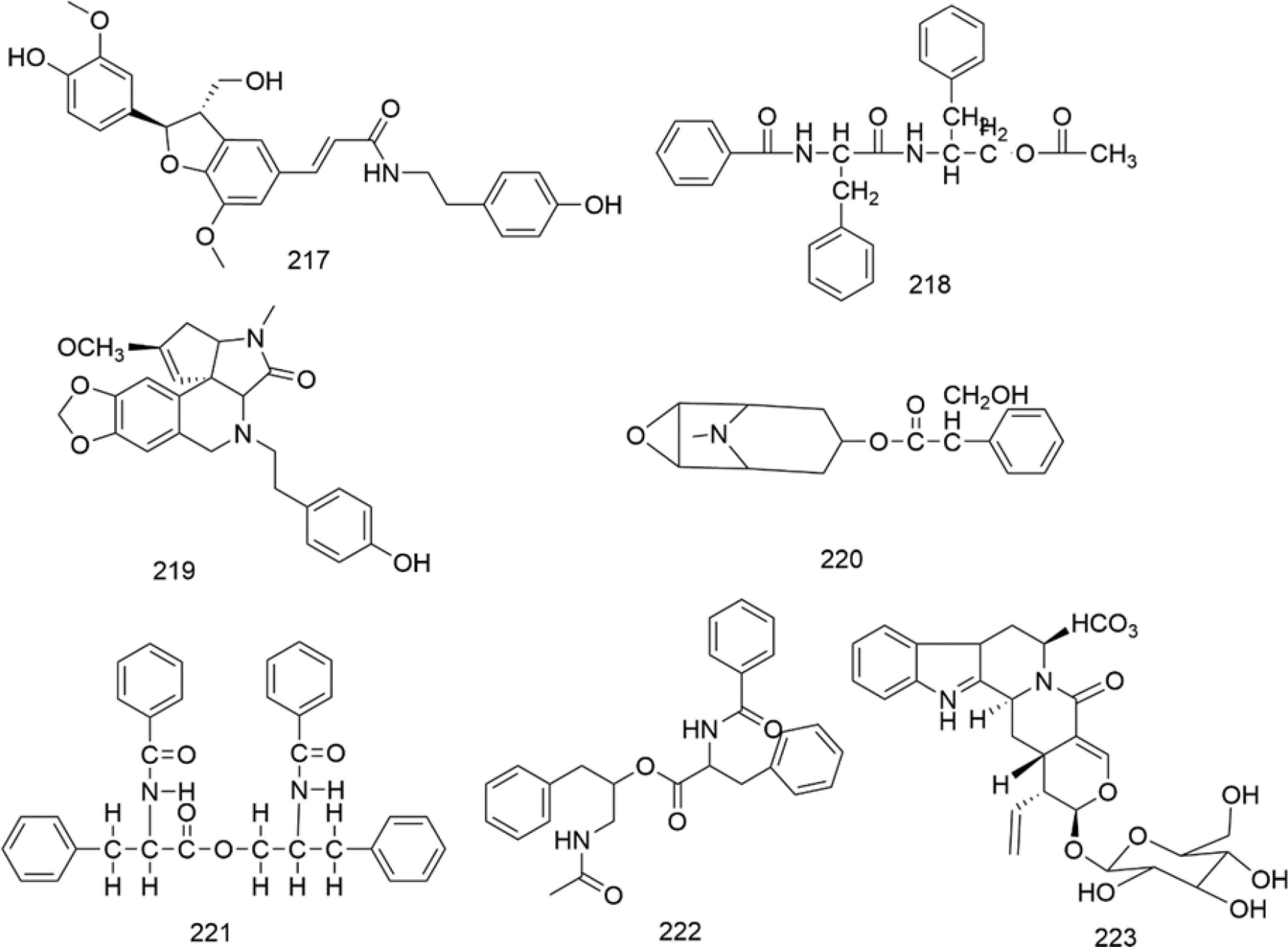
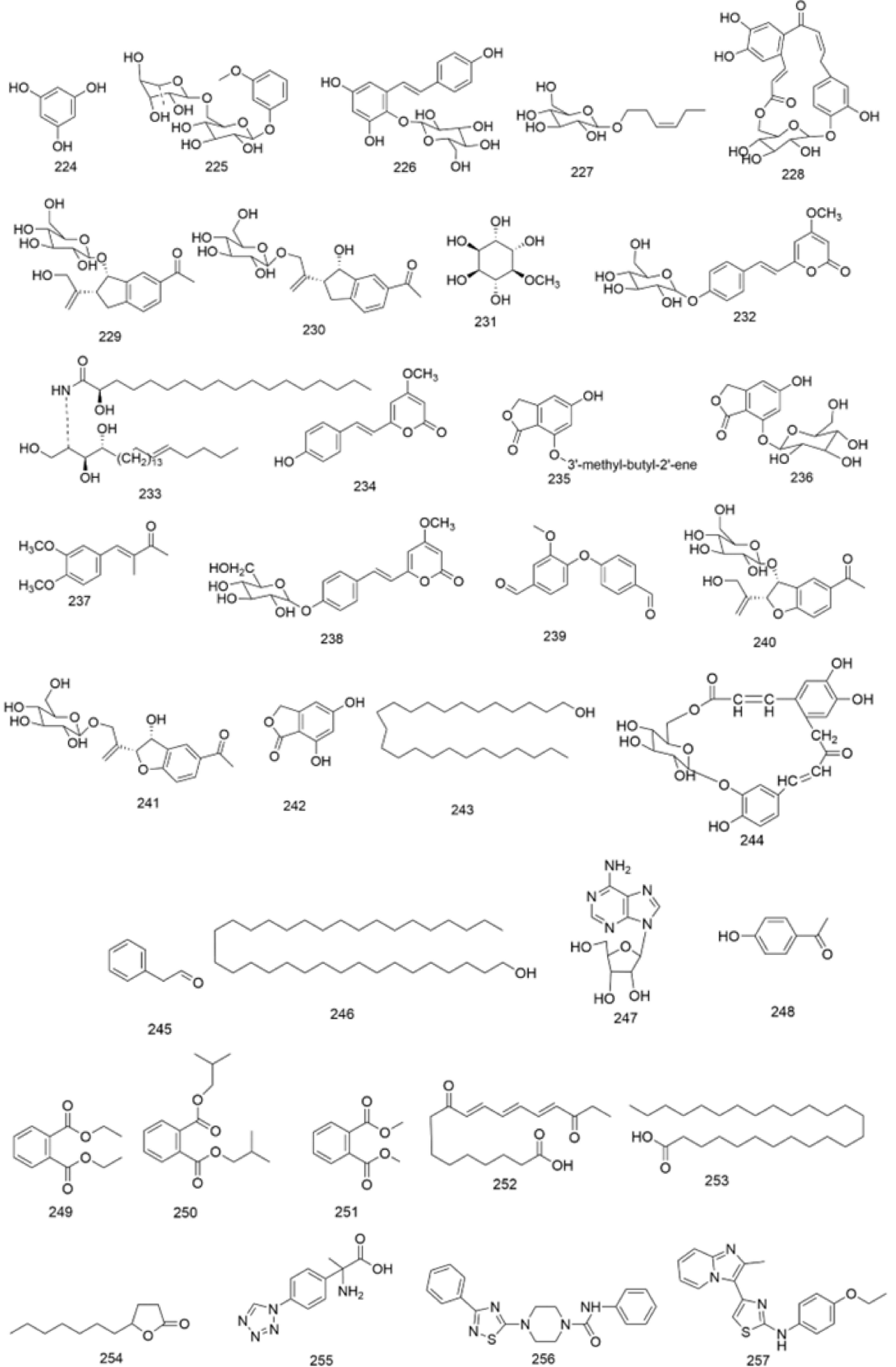
There are multiple previous studies focusing on the chemicals in Gnaphalium species. To date, 257 compounds have been identified and characterized. The existing literature indicates the existence of multiple components, predominantly in flavonoids, phenolic acids, alkaloids, and terpenoids. Some of these components are directly or indirectly attributed to the pharmacological activities of plants in the genus Gnaphalium. According to previous research, the chemical studies of the genus Gnaphalium have mainly focused on G. affine, G. hypoleucum, G. sylvaticum, G. undulatum, G. oligandrum, G. pellitum, G. oxyphyllum, and G. adnatum. Here, the structures and other information of these identified compounds are summarized in Figs 2−12 and Table 2, respectively.
Table 2. Compounds isolated and identified from the Gnaphalium L.
No. Compound Source Reference Flavones 1 Apigenin 4'-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside G. affine [3,5] 2 Gnaphaloside A G. tranzschelii [5] 3 Apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. tranzschelii, G. luteoalbum [3,5] 4 Chrysoeriol-7-O-β-D -glucopyranoside G. uliginosum [3] 5 Apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucuronic acid methylester G. affine, G. hypoleucum [5,38] 6 Apigenin G. affine, G. hypoleucum [36−38] 7 Luteolin-4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. affine, G. cheiranthifolium, G. hypoleucum,
G. luteoalbum[37,38] 8 5-hydroxy-4',7-dimethoxyflavonoid G. affine [38] 9 Acacetin G. affine [38] 10 Luteolin G. affine, G. hypoleucum, H. polycaulon,
G. luteoalbum, G. rufescens, G. sylvaticum,
G. oxyphyllum[36−38] 11 Chrysin G. affine [38] 12 5-hydroxy-6,7,3',4'-tetramethoxyflavone G. affine [39] 13 Luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucuronide methyl ester G. hypoleucum [3] 14 6-Hydroxyluteolin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. hypoleucum, G. affine, G. tranzschelii [5,40] 15 Acacetin-7-O-rutinoside G. affine [3] 16 Eupafolin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. affine [3] 17 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-6,3'-dimethoxyflavone G. luteoalbum [3] 18 6-MethoxyLuteolin G. uliginosum, G. tranzschelii [3,5] 19 Luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. luteoalbum, G. hypoleucum [3,5] 20 Apigenin-4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. affine [3] 21 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-3',5'-dimethoxyflavone G. sylvaticum [3] 22 Linarin G. hypoleucum [3] 23 Luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucuronide G. hypoleucum [3] 24 Acacetin-7-O-β-D-xylopyranosyl-[α-L- rhamnopyranosyl]-β-D-glucopyranoside G. hypoleucum [3] 25 Luteolin 4'-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside G. hypoleucum, G. affine [3,5] 26 5,7,3',4'-Tetrahydroxy-6-methoxyflavonoid-7-O-
β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranosideG. tranzschelii [5] 27 Luteolin 7-O-methyl ether G. rufescens [5] 28 5,7,3',4'-tetrahydroxy-6-methoxyflavonoid-7-O-β-
D-glucopyranosideG. tranzschelii [5] 29 5-hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavone G. pellitum [5] 30 Hispidulin G. antennarioides [5] 31 Velutin G. gaudichaudianum [5] 32 5,8-dihydroxy-6,7-dimethoxyflavone G. gaudichaudianum [5] 33 Hispidulin 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. antennarioides [5] 34 Jaceosidin G.luteoalbum, G.tranzschelii [5] 35 3,5,7,4'-tetrahydroxy-3'-methoxyflavonoid-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. tranzschelii [5] 36 8-O-(2-methylbutyryl)-5,7,8-trihydroxyflavone G. robuscum [5] 37 8-O-[(Z)-2-methyl-2-butenyl]-5,7,8-trihydroxyflavone G. robuscum [5] 38 Eupatilin G. affine [39] 39 5,7,4'-Trihydroxy-3'-methoxyflavonoid-
7-O-β-D-(6''-O-caffeoyloxy)-glucopyranosideG. affine, G. uliginosum [38] 40 Apigenin 7-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside G. affine [3,5] Flavonols 41 5,7-dihydroxy-3,8,4'-trimethoxyflavonoid G. hypoleucum, G. affine [38,40] 42 Tiliroside G. adnatum [41] 43 5-hydroxy-3,6,7,8,3',4'-hexamethoxyflavone G. affine, G. hypoleucum [2] 44 Kaempferol 3-O-β-D-(6''-O-coumarin)-glucopyranoside G. affine [42] 45 Isorhamnetin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. affine [38] 46 Quercetin 4'-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside G. hypoleucum, G. affine [3,5] 47 Isorhamnetin-3-O-β-D-galactopyranoside G. uliginosum [3] 48 Patuletin-3-O-β-D -glucopyranoside G. uliginosum [3] 49 5,7,3',4'-Tetrahydroxy-3-methoxyflavonoid G. indicum [3] 50 5,7-dihydrox-3,8-dimethoxyflavone G. gracile [3] 51 3-Methoxyquercetin G. gracile [3] 52 7-Methoxyquercetin G. pellitum [3] 53 5,8-Dihydroxy-3,6,7,4'-tetramethoxyflavonoid G. affine [42] 54 Quercitrin G. affine, G. sylvaticum [5] 55 8-O-(2-methylbutyrate)-5,7-dihydroxy 3-methoxyflavonoid G. robustum [3] 56 Quercimeritrin G. hypoleucum [43] 57 Quercetin-3-O-β-D-galactopyranoside G. hypoleucum [43] 58 5-hydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone G. uiscosum [42] 59 Rhamnetin G. pellitum, G. affine [5,38] 60 Quercetin G. affine, G. gracile, G. hypoleucum, G. polycaulon,
H. pellitum, G. sylvaticum, I. G. uniflorum[36−38] 61 Kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. affine, G. uniflorum [5,38] 62 5-Hydroxy-3,6,7,8,4'-pentamethoxyflavone G. affine, G. hypoleucum [38] 63 5,6-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone G. affine [38] 64 Baicalein-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. tranzschelii [5] 65 Isokaempferol G. dioicum [5] 66 Quercetin 4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. affine, G. hypoleucum [5,40] 67 Isoquercitrin G. stramineu, G. sylvaticum, G. tranzschelii, G.uniflorum [5] 68 Quercetagetin G. affine [5] 69 Quercetin 3-O-β-D-galactopyranoside-4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. uniflorum, G. affine [5] 70 Quercetagetin 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. affine [5] 71 Isorhamnetin G. affine, G. hypoleucum [5] 72 3,5,7,4'-tetrahydroxy-3'-methoxyflavone-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. tranzschelii [5] 73 3,5,7,3',4'-Pentahydroxy-6-methoxyflavone-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. tranzschelii [5] 74 Gnaphaliin B G. affine, G. liebmannii [5] 75 3,5-dihydroxy-6,7,8-trimethoxyflavone G. chilense, G. microecephalum, G. robustum [5] 76 3,5-Dihydroxy-6,7,8,4'-tetramethoxyflavone G. affine [5] 77 5-Hydroxy-3,7,8-trimethoxyflavone G. affine, G. robustum, G. obtusifolium [5] 78 5-hydroxy-3,6,7,8-tetramethoxyflavonoid G. affine, G. hypoleucum,G. undulatum [5] 79 Gnaphaliin A G. affine, G. gracile, G. lanuginosum,
G. liebmannii, G. obtusifolium, G. robustum[5] 80 5,7-Dihydroxy-3-methoxyflavonoid G. gracile, G. robustum [5] 81 8-O-(2-methyl-2-butenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-3-methoxyflavonoid G. robustum [5] 82 5,7-dihydroxy-3,6-dimethoxyflavone G. wrightii [5] 83 5,8-dihydroxy-3,6,7-trimethoxyflavone G. affine, G. gaudichaudianum [5] 84 5,7-Dihydroxy-3,6,8-trimethoxyflavone G. affine, G. elegans [5] 85 5,7-Dihydroxy-3,8,3',4'-tetramethoxyflavone G. affine [5] 86 3,5,7-trihydroxy-6,8-dimethoxyflavone G. obtusifolium [5] 87 5,7,8-Trihydroxy-3-methoxyflavonoid G. robuscum [5] 88 Quercetin 3-methyl ether G. gracile, G. indicum [5] Chalcones 89 2',4',4-Trimethoxy-6'-methoxychalcone G. affine [5] 90 Gnaphalin G. affine, G. cheiranthifolium, G. multiceps,
G. purpurascens, G. luteoalbum, G. hypoleucum[5] 91 2',4,4'-trihydroxy-6'-methoxychalcone G. affine [38] 92 4,4',6'-Trimethoxy-2'-methoxychalcone G. affine [38] 93 2',4'-dihydroxy-4,6'-dimethoxychalcone G. affine [38] 94 2'-hydroxy-4,4',6'-trimethoxychalcone G. affine [38] 95 4,2',4',6'-Tetramethoxychalcone G. affine [38] 96 2',4,4'-trihydroxy-6'-methoxychalcone-4-glucopyranoside G. affine [3] Flavanones 97 Naringenin-7-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside G. affine [42] 98 Taxifolin G. affine [42] 99 Dihydroapigenin G. affine [38] 100 Pinocembrin G. purpurascens [5] 101 Wogonin G. affine [38] 102 4'-Hydroxy-5-methoxy-7-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-dihydroflavanone G. hypoleucum [43] 103 7,4'-Dihydroxy-5-Methoxydihydroflavonoids G. hypoleucum [43] 104 5,7,3',4'-tetrahydroxyflavone G. affine [42] Triterpenoids 105 β-Amyrin G. affine [5,38] 106 β-amyrin acetate G. affine [38] 107 Oleanolic acid G. affine, G. hypoleucum [38] 108 Friedelin G. affine [38] 109 α-Amyrin G. affine [5,38] 110 Ursolic acid G. affine, G. hypoleucum [38] 111 α-amyrin acetate G. affine [38] 112 Faradiol 3-O-palmitate G. affine [44] 113 19α-hydroxy ursolic acid G. affine, G. hypoleucum [38] 114 2α,3α,19α-trihydroxy-28-norurs-12-ene G. affine [38] 115 Taraxasterol G. affine [38] 116 Taraxasterol acetate G. affine [5,38] 117 Lupeone G. affine [38] 118 Betulonic acid G. affine [44] 119 Betulinic acid G. affine [5] 120 Squalene G. gaudichaudianum [5] Diterpenoids 121 Ent-pimara-8(14),15-dien-3a,19-diol G. affine [45] 122 Ent-pimara-8(14),15-dien-3α-ol G.affine [38] 123 Ent-pimara-8(14),15-dien-19-ol G. affine [38] 124 Ent-Pimara-8(14),15-diene-19-ol G. gaudichaudianum [5] 125 Ent-pimara-8(14),15-dien-19-oic acid G. gaudichaudianum [5] 126 Ent-pimara-8(14),15-dien-18-oic acid G.gaudichaudianum [5] 127 Ent-Pimara-8(14),15-diene-3α,19-diol G. gaudichaudianum [5] 128 Sclareol G. gaudichaudianum [5] 129 8α,13α-Diacetoxycinnamyl alcohol G. gaudichaudianum [5] 130 8-epi-Sclareol G. undulatum [5] 131 8-epi-Eni-sclareol G. gaudichaudianum [3] 132 Kaur-16-en-19-oic acid G. gaudichaudianum, G. inornatum, G. rufescens [5] 133 Methyl kaur-16-en-19-oate G. gaudichaudianum [5] 134 3α-hydroxykaur-16-en-19-oic acid G. gaudichaudianum [3,5] 135 Methyl 3α-hydroxykaurl-16-en-19-oate G. gaudichaudianum [5] 136 11β-Acetoxycoel-16-ene-19-oleic acid G. rufescens [5] 137 Methyl 3α-acetoxycol-16-ene-19-oate G. gaudichaudianum [5] 138 3α-Acetoxycol-16-ene-19-oleic acid G. gaudichaudianum [5] 139 Ent-Kauran-16-ene G. undulatum [5] 140 Ent-Kaur-16-en-19-al G. undulatum [5] 141 Ent-Kaur-16-en-19-oic acid G. affine, G. graveolens, G. oligandrum, G. pellitum,
G. undulatum, G. oxyphyllum, G. liebmannii[5] 142 15α-hydroxy-ent-kaur-16-en-19-oleic acid G. undulatum, G. viscosum [5] 143 11β-acetoxy-ent-kaur-16-en-19-oleic acid G. pellitum [5] 144 (−)-16-Kaurene-19-oic acid G. affine [3] 145 (−)-Methyl kaur-16-en-19-oate G.gaudichaudianum [3] 146 (3α,4α)-Kaur-16-en-18-oic acid-3-hydroxy-methyl ester G. gaudichaudianum [3] 147 3α-acetoxykaur-16-en-19-oic acid Me ester G. gaudichaudianum [3] 148 Ent-pimar-15-ene-8α,19-diol G. gaudichaudianum [5] 140 Ent-pimar-15-ene-3α,8α-diol G. gaudichaudianum [5] 150 Zoapatlin G. hypoleucum, G. affine, G. oxyphyllum,
G. liebmannii, G. viscosum[40] 151 Ent-3β-hydroxykaur-16-en-19-oic acid G. affine, G. viscosum [38] 152 (−)-11β-Acetoxy-16-kaurene-19-oic acid G. affine [3] 153 Kauranol G. rufescens [5] 154 Ent-Kaur-9(11),16-en-19-oic acid G. oligandrum, G. undulatum [5] 155 Sylviside G. sylvaticum [5] 156 Carnoside G. sylvaticum [3] 157 15β-hydroxy-Wedeliaseccokaurenolide G. undulatum [5] Sesquiterpenoids 158 Gemamane D G. oligandrum [5] 159 (2E,6Z)-7,11,11-trimethylbicyclo[8,1,0]undec-2,6-diene diterpene G. oligandrum [5] 160 γ-Cadinene G. affine [46] 161 (E)-β-Farnesene G. pensylvanicum [36] 162 Irisone G. pensylvanicum [36] 163 (−)-β-Elemene G. affine [48] 164 α-Gurjunene G. affine [48] 165 Trans-Caryophyllene G. affine [21] 166 α-Humulene G. affine [48,49] 167 δ-Cadinene G. affine [48] 168 α-elemol G. affine [48] 169 β-selinene G. affine [8] 170 γ-Gurjunene G. japonicum, G. affine [49] 171 Corchoionol C G. affine [38, 50] 172 Caryophyllene oxide G. affine, G. japonicum [51] 173 6,10,14-trimethyl-2-Pentadecanone G. affine [52] 174 Nerolidol G. affine [51] 175 1,5,5,8-Tetramethyl-12-oxabicyclo[9.1.0]dodeca-3,7-diene G. affine [51] 176 Aromadendrene G. affine, G. japonicum, G. pensylvanicum [8] 177 7R,8R-8-hydroxy-4-isopropylidene-7-methylbicyclo[5,3,1] undec-1-ene G. japonicum [46] Monoterpenoids 178 α-Terpineol G. affine [21] 179 Linalool G. affine [21] 180 p-cymene G. affine [21] 181 m-cymene G. affine [48] 182 Pulegone G. affine [52] Phenolic acids 183 Protocatechuic acid G. affine [46] 184 Caffeic acid G. affine [46] 185 Ethyl Caffeate G.affine [38] 186 Ethyl protocate G.affine [38] 187 Trans caffeic acid G. tranzschelii [5] 188 Caffeic acid ethylene ester G. hypoleucum [40] 189 Eugenol G. affine [36, 21] 190 Coniferylaldehyde G. affine [38] 191 P-hydroxycinnamic acid G. affine [38] 192 Methyl cinnaminate G. hypoleucum [47] 193 Isovanillin G. affine [38] 194 Isovanillic acid G. affine [38] 195 3',5-dihydroxy-2- (4-hydroxybenzyl) -3-methoxybibenzyl G. affine [44] 196 Everlastoside L G. affine [38] 197 Methyl p-hydroxycinolinate glucoside G. affine [38] 198 Acteoside G. affine [44] 199 1,4,5-tri-O-caffeoylquinic acid G. affine [38] 200 1,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid G. affine [38] 201 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid methyl ester G. affine [38] 202 1,3-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid G. affine [38] 203 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid G. affine [20] 204 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid G. affine [20] 205 1,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid G. affine [42] 206 Chlorogenic acid G. affine [46] 207 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid G. stramineum [5] 208 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid G. stramineum [5] 209 3,4,5-tri-O-caffeoylquinic acid G. stramineum [5] Steroids and sterols 210 Daucosterol G. affine, G. adnatum, G. hypoleucum [50] 211 Stigmasterol G. affine, G. adnatum, G. gaudichaudianum,
G. viscosum, G. oxyphyllum, G. liebmannii[38] 212 β-sitosterol G. affine, G. hypoleucum, G. inornatum, G. pellitum,
G. oxyphyllum, G. liebmannii, G. viscosum[38] 213 Stigmasta-4,22-dien-3-one G. affine, G. adnatum [38] 214 4-Cholesten-3-one G. affine [5] 215 3β-hydroxy-stigmasta-5,22-dien-7-one G. affine [5] 216 α-spinasterol G. affine [38] Alkaloids 217 Grossamiade K G. affine [44,38] 218 Aurantiamide acetate G. hypoleucum [3] 219 Matrine G. sphacelatum [5] 220 Scopolamine G. affine [5] 221 Anabellamide G. affine [38] 222 Patriscabratine G. affine [38] 223 Longumoside A G. affine [44] Others 224 Phloroglucinol G. affine [53] 225 3-methoxyphenol1-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-4-
(1→6)-O-β-D-glucopyranosideG. affine [38] 226 2,3,5,4'-tetrahydtoxysilbene-2-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. affine [50] 227 (Z)-3-hexenyl O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. polycaulon [5] 228 Gnaphalium A G. affine [54] 229 Gnaphaliol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. polycaulon [5] 230 Gnafaliol 9-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. polycaulon [5] 231 (+)-Pinenutol G. pellitum [5] 232 Panamin G. hypoleucum [40] 233 Tithoniamide B G. affine [50] 234 4'-Hydroxydehydrogenase G. hypoleucum [3] 235 Anaphatol G. affine, G. adnatum [38,41] 236 7-O-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)-5-hydroxyisobenzofuran-1(3H)-one G. affine, G. adnatum [38,41] 237 4-(3',4'-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-butyl-3-ene-2-one G. affine, G.adnatum [38] 238 Desmethylyangonine-4'-glucopyranoside G. affine [38] 239 3-(4'-formylphenoxy)-4-methoxybenzaldehyde G. affine [38] 240 3-Hydroxydihydrobenzofuranose G. polycaulon [55] 241 Gnaphaliol 9-O-β-D-glucopyranoside G. polycaulon [55] 242 5,7-dihydroxyl-isobenzofuran-1(3H)-one G. affine, G. adnatum [41] 243 1-Hexacosanol G. affine [38] 244 Gnaohaliin C G. hypoleucum [3] 245 Benzeneacetaldehyde G. affine [48] 246 1-Tetratriacontanol G. affine [50] 247 Adenosine G. polycaulon [5] 248 4-hydroxyacetophenone G. affine [56] 249 Diethyl phthalate G. affine [38] 250 Diisobutyl phthalate G. pensylvanicum [36] 251 Dimethyl phthalate G. japonicum [46] 252 9,16-dixo-10,12,14-octadeca-trienoic acid G. affine [56] 253 N-hexacosanic acid G. affine [5] 254 Myristicin aldehyde G. affine, G. japonicum [46] 255 N-butyl-isobutyl terephthalate G. adnatum, G. affine [41,48] 256 1-Palmitoyl-rac-glycerol G. affine [50] 257 4'-hydroxydehydrokawain G. affine [38] Flavonoids
-
Flavonoids are very common compounds in the genus Gnaphalium. Several studies have described flavonoids as a chemical index for the quality study of the herbs in Gnaphalium, even though they are not included in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Nevertheless, the flavonoid content in Gnaphalium is not high and varies significantly in different regions[36,37].
To date, over 100 flavonoids have been authenticated in genus Gnaphalium, which are mainly classified as flavonol, dihydroflavone, chalcone, and others. In flavonol, quercetin is the most significant aglycone, while luteolin and apigenin are the main skeletons in other flavonoids. Among the flavone glycosides in Gnaphalium, glucose is the main substituted group, which are mostly located in C-7 of flavonoids, except for C-3-substituted glucose in isorhamnetin-3-O-β-D-galactopyranoside (47), patuletin-3-O-β-D–glucopyranoside (48), quercetin-3-O-β-D-galactopyranoside (57), kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (61), 3,5,7,4'-tetrahydroxy-3'-methoxyflavonoid-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (72), and 3,5,7,3',4'-pentahydroxy-6-methoxyflavonoid-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (73). Interestingly, another type of flavone glycosides, including quercetin-4'-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside (46), apigenin-7-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside (40), apigenin-4'-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside (1), luteolin-4'-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside (25), 5,7,3',4'-Tetrahydroxy-6-methoxyflavonoid-7-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside (26), and naringenin-7-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside (97), were isolated from G. affine, which contain an E-caffeoyl group in the flavone glycosides[57]. The information of the aforementioned flavonoids are presented in Figs 2−4 and Table 2, respectively.
Terpenoids
-
Terpenes and terpenoids are very common natural products in the world, and over 22,000 chemicals have been identified from various plants[58]. Because of the basic five-carbon isoprene units in terpenes and terpenoids, they were divided into monoterpenoids, sesquiterpenes, diterpenoids, and triterpenoids with distinct functional groups[59,60]. Due to its diverse structures, several activities, such as anti-inflammatory, antiparasitic, antioxidant, anticancer, antiviral, and antimicrobial properties, have been reported[61]. In this review, 50 terpenes and terpenoids were identified in genus Gnaphalium (Figs 5−8, Table 2). Here, we will focus on these compounds and provide an overview of terpenes and terpenoids in genus Gnaphalium.
Triterpenoids
-
Triterpenoids usually contain six five-carbon isoprene units. Normally, these units can be connected into different carbon ring and formed different types of triterpenoids. The major triterpenoids (105–120) isolated from genus Gnaphalium mainly use amyrin and ursolic acid as structural skeletons, and most of them are distributed in G. affine, except for squalene in G. gaudichaudianum. Among them, eight ursane triterpenes (109–116) are the most abundant, followed by four oleanane triterpenes (105–108). Also, three lupane triterpenes (117–119) and one chain triterpene (120) identified in G. affine. All information, including names, structures and source plants of triterpenoids, are listed in Table 2 and Fig. 5.
Diterpenoids
-
Up to now, 37 diterpenoids are identified in genus Gnaphalium, and most of them possess (–)-pimara-8(14), 15-diene and (–) kaurene as chemical skeletons. In total, 22 kaurane diterpenes (132–147, 151–156), nine pimarane diterpenes (121–127, 148, 140), four labane diterpenes (128–131) were identified. In addition, there is one rare diterpene (157), which was a 15-hydroxy substituted wedeliaseccokaurenolide, from G. undulatum. The structures, names and source plants of diterpenes in genus Gnaphalium are presented in Fig. 6 and Table 2. By comparing the distribution of different compounds in genus Gnaphalium, it is found that diterpenes are the main component of G. gaudichaudianum, which can be regarded as a marker of G. gaudichaudianum to distinguish from other species.
Sesquiterpenoids
-
A total of 20 sesquiterpenoids were isolated from genus Gnaphalium. Among them, 185 and 186 are isolated from G. oligandrum, while 170, 172, 176, and 177 are from G. japonicum. The specific information, including names and source plants of these compounds, are listed in Table 2.
Monoterpenoids
-
Five monoterpenoids were identified from G. affine (178–182).
Phenolic acids
-
Phenolic acids are normally considered as antioxidants because of the presence of phenol moiety and the ability to induce endogenous protective enzymes[62]. Also, phenolic acids have demonstrated anti-diabetic potential by inhibiting alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase, converting carbohydrates into glucose[63]. Furthermore, compared to methyl ester and butyl ester, the inhibitory effect of phenolic acid on microbial growth has been extensively investigated[64]. In genus Gnaphalium, 27 phenolic acids are isolated and identified, most of them are from G. affine. Additionally, caffeoyl substituted quinic acid is a special type of phenolic acids, in which quinic acid and caffeioyl groups are connected via the ester bond (Fig. 9, Table 2).
Steroids and sterols
-
Sterol compounds are structurally composed of four-cyclic compounds with a cyclopentanoperophenanthrene nucleus[65]. However, only seven steroids have been authenticated in the genus Gnaphalium. Among them, β-sitosterol (212) was confirmed to exist in G. affine, G. hypoleucum, G. inornatum, G. pellitum, G. oxyphyllum, G. liebmannii, and G. viscosum. Among the species, all the steroids were identified from G. affine. One glycosides, β-daucosterin (210), was isolated from G.affine, G.adnatum, and G.hypoleucum[38].
Alkaloids
-
Alkaloid compounds typically contain nitrogen atoms in their structures[66]. Currently, seven alkaloid (217–223) compounds have been found in the genus Gnaphalium.
Others
-
In addition to the previously reported compounds, other types of compounds, including sterols, amino acids, tannins, polysaccharides, etc., have also been isolated from genus Gnaphalium[48] (Fig. 12, Table 2) .
-
Most varieties of Gnaphalium are traditionally used to treat several respiratory diseases, such as asthma, cough, bronchitis, and bronchial infections. In the guinea pig tracheal experiment, the effect of methanol extract of G. conoideum on contractile agonist response was studied, and it was found that G. conoideum significantly reduced the contractile response to histamine by partially blocking Ca2+ channels[67]. Likewise, the tension change experiment of guinea pig tracheal segments was used to evaluate the anti-asthmatic effect of G. liebmannii, showing that the hexane extract can cause the concentration response curve of aminophenol to shift parallel to the right in a competitive manner, rather than causing the concentration response curve of histamine to shift parallel to the right, indicating that G. liebmannii can act as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor for tracheal muscle relax[68]. Additionally, G. affine is used as traditional medicine to treat expectorant and cough in China. Ye et al. evaluated the antitussive and expectorant activities of total flavonoids from G. affine in vivo, showing that macroporous resin-purified total flavonoids (purity: 40.13%) significantly decreased the number of cough times during 5 min and alleviated sputum secretion[69,70]. Similarly, the pretreatment of G. affine significantly decreased the inflammatory cytokines in alveolar lavage fluid of COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) rats[70]. Moreover, eight bioactive compounds were identified from G. affine extract through activity-guided fractionation, in which luteolin-4'-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucoside (27) displayed remarkable noncompetitive inhibition kinetics against human neutrophil elastase (HNE)[71].
Antimicrobial activity
-
The crude extracts and isolated plant compounds extracted from different species in Gnaphalium have antibacterial properties. For example, Caceres et al. investigated the antibacterial activity of the ethanolic extract from G. stramineum and G.viscosum against eight strains of bacteria including Escherichia coli, Salmonella enteritidis, Salmonella typhi, Shigella dysenteriae, Shiegella flexneri, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus pneumonia, and Staphylococcus pyogenes. Interestingly, extract from G. stramineum showed promising inhibitory effect against S. typhi and S. dysenteriae (≥ 9 mm), which are involved in gastrointestinal disorders; while extract from G. viscosum had a strong inhibitory effect against S. pneumonias and S. pyogenes that are associated with respiratory disease[32,72]. Additionally, G. gaudichaudianum methanol extract suppressed the growth of Sporothrix schenckii and Fonsecaea pedrosoi with MIC values of 50 and 12.5 μg/mL, respectively; and methanol, hexanic, and chloroformic extracts of G. hirsutum inhibited the growth of Streptococcus pyogenes[73]. The antimicrobial activity of extracts from different parts of G. oxyphyllum var. oxyphyllum hexanic was also evaluated, and demonstrated that the flower extract showed more broad-spectrum antimicrobial effect compared with the leaves extract[74].
Currently, it is believed that the antibacterial effect of G. polycaulon is related to its secondary metabolites. Previous study used Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus pneumoniae strains to test the antibacterial activity of chemicals in G. polycaulon, showing that the antibacterial activity of 255–257 with MIC values of 0.0077–44.85 μM[75]. Moreover, eugenol and linalool, the main essential oil in G. affine showed remarkable antimicrobial effect in food-borne microorganisms test[7]. In addition, eugenol could significantly reduce biofilm formation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Ashrafudoulla et al.'s research[76].
Antioxidant activity
-
The ethanol extract of G. roseum, which mainly contained flavonoids and phenols, exerted an antioxidant effect by the free radical scavenging test of α, α-diphenyl-β-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of ~72.9 ± 3.2 μg/mL. The antioxidant capacity of G. affine ethanol extract was demonstrated with the H2O2-induced oxidative stress, in which G. affine extract ameliorated oxidative reaction via the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway in H9c2 cells, and 17 compounds including phenols and flavonoids, were identified in this extract by LC-MS analysis[77]. Moreover, 2,2'-Azinobis-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonate) (ABTS), superoxide, and hydroxyl radical scavenging assays were used to bio-guided isolate the antioxidant compounds in G. affine, revealing quercetin (60) as the main antioxidant component[78]. In addition, flavonoids including apigenin (6), chrysin (11), wogonin (101), and luteolin (10) were well-represented in the ethanol extract of G. affine, and showed remarkable free radical scavenging capacity[38].
Anti-inflammatory and anti-complementary activities
-
Carrageenan-induced paw edema and collagen-induced arthritis models were used test the anti-inflammatory activity of G. affine ethanol extract, showing that the swelling caused by carrageenan and the inflammation caused by collagen were inhibited or reduced by 600 and 300 mg/kg extracts, respectively[79]. Another study showed that the methanol extract of G. affine decreased the expressions of iNOS and COX-2 in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells by inhibiting the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathways[80]. Apart from G. affine, different polar solvent extracts of G. stramineum demonstrated that the methanol extract suppressed the carrageenan-induced edema in rats[81]. Bioassay-guided fractionation of the methanol extract of G. affine resulted in the isolation of four anti-inflammatory compounds, quercetin (60), luteolin (10), quercetin-4'-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucoside(46) and luteolin-4'-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucoside (25), according to NO expression in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Furthermore, luteolin-4'-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucoside (25) was confirmed to exert anti-inflammatory effect via suppressing the expression of COX-2[71].
The complement system is an essential part of the innate immunity and plays an important role in inflammatory reaction[82]. The anti-complementary activity of G. hypoleucum ethanol extract and its fractions were assayed based on the classical pathway of the complement system in vitro, revealing that the total ethanol extract possessed a more potent anti-complementary effect (CH50 = 0.165 ± 0.025)[83]. Through a systematic chemical study of G. hypoleucum, ursolic acid and luteolin-4'-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside (25) were showed to have a strong inhibitory effect on the complement activation, with CH50 values of 0.014 and 0.045 mg/mL, respectively. Additionally, 27 flavonoids were isolated from G. affine, providing a basis for exploring the structure-activity relationship of flavonoids in G. affine. By investigating the anti-complementary effect of each flavonoid, the flavonol–sugar–aromatic side chain and the hydroxy group in C-4' in flavonoids played an important role in anti-complementary activity[57].
Antidiabetic effect
-
Persistent hyperglycemia is generally considered to be related to insufficient insulin secretion and islet dysfunction or insulin resistance, which can cause a variety of complications, including diabetes nephropathy and diabetes eye disease. For now, treatment for hyperglycemia is mainly through the promoting glycolysis (dimethylbiguanide) and lowering postprandial blood sugar (acarbose). Several studies showed that various species in genus Gnaphalium can exert antidiabetic effect. Sun et al. evaluated the antidiabetic activity of total flavonoid extract of G. hypoleucum in both in vivo and in vitro models, and isolated the relevant compounds that may function in this process[84]. Total flavonoid extract of G. hypoleucum showed a significant α-glucosidase inhibitory activity (IC50 = 20.30 ± 3.45 μM) in vitro, and total flavonoids at 150 mg/kg significantly decreased the levels of fasting blood glucose (FBG) after 10 d (p < 0.05) in vivo in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice. Moreover, components including oleanolic acid (107), ursolic acid (110), 19α-hydroxyl ursolic acid (113), and luteolin-4'-O-β-D-(6''-E-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside (25) showed significant α-glucosidase inhibitory activities, more effective than acarbose. In another study, Lu et al. isolated three compounds, including 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (203), 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (204), and 2',4,4'-trihydroxy-6'-methoxychalcone-4'-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (96) from G. affine, which can inhibit α-amylase activity[85].
Anti-hyperuricemia and gouty effect
-
Hyperuricemia is often associated with excessive production or insufficient excretion of uric acid (UA) in the body. When the serum uric acid concentration exceeds the solubility of uric acid, uric acid crystals will form in tissues such as the kidneys and joints, leading to kidney disease and gout[86]. Previous literature has reported several renal organic anion transporters, such as glucose transporter 9 (GLUT9) and uric acid transporter 1 (URAT1), involved in mediating uric acid excretion. Moreover, xanthine oxidase (XO) is a key enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and further to uric acid. Thus, mediating uric acid excretion and xanthine oxidase activity is the most effective way to treat gout and hyperuricemia. Several species in Gnaphalium have been used as a folk medicine for the relief of anti-inflammatory, antitussive, gout and expectorant activities, etc. Therefore, the anti-hyperuricemia and acute gouty effects of G. affine and G. pensylvanicum were investigated by determining the uric acid content in potassium oxonate induced hyperuricemic mice, revealing the significant anti-hyperuricemia and acute gouty effects of G. affine and G. pensylvanicum ethanol extracts via inhibiting xanthine oxidase activity in a concentration dependent manner (100, 200, and 400 mg/kg)[87,88]. Notably, the expressions of GLUT9 and URAT1 were also increased in mice treated with G. affine and G. pensylvanicum extracts for seven days compared with that in the control group. These studies suggest that the mechanism of anti-hyperuricemia and acute gouty effects by G. affine and G. pensylvanicum might be involved in both xanthine oxidase inhibition and uric acid excretion.
In order to verify the functional chemicals produced by G. hypoleucum in this process, the anti-gouty chemicals were screened in G. hypoleucum via xanthine oxidase inhibition assay. Luteolin-4'-O-glucoside (7) and luteolin (10) were identified, showing strong xanthine oxidase inhibition activities with IC50 values of 0.26 and 0.43 μg/mL, respectively. Moreover, their significant anti-hyperuricemia and acute gouty effects were further confirmed in vivo via inhibiting the xanthine oxidase activity in a concentration dependent manner (20, 40, and 100 mg/kg). In addition, the expressions of GLUT9 and URAT1 were increased in mice treated with luteolin-4'-O-glucoside (7) and luteolin (10) for six days compared with that in the control group. The paw swelling was also decreased by luteolin (10) and luteolin-4'-O-glucoside (7) in a dose-dependent manner in monosodium urate (MSU) crystal-induced mice[89].
Other activities
-
Apart from the above pharmacological effects, other activities of Gnaphalium have been reported recently. The water extract of G. affine exhibited a protective effect for carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury[90]. A polysaccharide of G. affine could enhance the expression of ALPase expression synergistically with ascorbate from the early differentiation stage of MC3T3-E1 cells[91]. Two flavone isomers from G. elegans exibited remarkable anti-tumor effects, and four flavonoids 78, 62, 63, and 92 isolated from the root of G. affine have antifeedant activity, and studies have suggested that the introduction of a methyl ether on the B-ring of the flavonoid decreased antifeedant activity in insect[92,93].
-
At present, there is no national standard for Gnaphalium in China, and its quality control is mainly based on local standards. Therefore, it is necessary and urgent to strengthen research on the quality control of Gnaphalium. Regarding the quality standards of Gnaphalium, literature reports mostly focus on the qualitative and quantitative analysis of flavonoids and phenolic components. The content of quercetin (60) in G. affine, G. pensylvanicum, G. japonicum, and G. adnatum was basically determined by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometry (UV–vis)[94]. Additionally, Tian used high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to determine the contents of quercetin (60), luteolin (10), and luteolin-4'-O-β-D-glucose (7) in G. affine[37], as well as several phenols including protocatechuic acid (183), chlorogenic acid (206), caffeic acid (184), and 1,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid (200)[95]. HPLC-tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) were also used to determine and compare the contents of 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (203), chlorogenic acid (206), kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucoside (61), apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucoside (3), quercetin (60) and luteolin (10) in G. affine[96]. Quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker (QAMS) method was recently established to determine the contents of chlorogenic acid (206), caffeic acid (184) and eupatilin (38) in G. affine, using chlorogenic acid (206) as the reference substance[97,98]. In addition, pharmacokinetic studies have shown that caffeic acid and caffeioylquinic acids in G. affine have a significant accumulation effect in uric acid nephropathy (UAN) rats, suggesting caffeic acid and caffeioylquinic acids might be the active components to treat UAN[99]. The above detection methods provide a certain basis for the quality evaluation research of Gnaphalium, but more detection technologies are still needed, such as gene sequencing and fingerprint chromatography, to verify confused varieties and establish a scientific quality control system.
-
As a medical plant used worldwide, Gnaphalium plants are traditionally used to treat cough, phlegm, asthma, rheumatism, and other disorders. Flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenolic acids are the main chemical components and pharmacological ingredients in Gnaphalium. The pharmacological effects of Gnaphalium are mainly manifested in pulmonary protection, antimicrobial activity, anti-inflammatory and anti-complementary activities, antioxidant activity, antidiabetic effect, anti-hyperuricemia and gout effect, etc. There are also traditional Chinese medicine preparations with G. affine as tea on the market, which are mainly used for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. This review summarized previous research on genus Gnaphalium, including traditional uses, phytochemistry, bioactivities and quality control. However, there are several key issues worth pondering to further develop the medicinal potential of Gnaphalium.
First, more than 200 species in Gnaphalium have been found worldwide and over 200 compounds have been isolated and identified from Gnaphalium including flavonoids, terpenoids, phenolic acids, steroids, sterols, and other components. However, there are still disputes about the classification of Gnaphalium. Recently, Nie et al. divided Gnaphalium into two clades, Gnaphalium and Pseudognaphalium, using ITS and ETS sequencing[100]. Therefore, more comprehensive detection methods, including botanical phenotype, chemical interpretation and gene sequencing of each species, are still needed to describe the Gnaphalium taxonomy precisely.
Second, the present toxicological research of genus Gnaphalium needs to be further strengthened. As we know, some species in Gnaphalium are used as vegetable and food ingredients, with relatively low toxicity. However, further toxicological research is still required, especially for the long-term uses with large doses of poor extracts. The toxicity of each species of Gnaphalium should be comprehensively evaluated, including heavy metals and contaminations of pesticide residues, to provide a scientific basis for the safe use as both drug and food.
Third, at present, there is no unified national quality standard for genus Gnaphalium, and most of them are based on local standards. Moreover, only TLC or HPLC methods were used in some local standards, which might not reflect the comprehensive quality of Gnaphalium. Therefore, it is necessary to further strengthen the basic research on quality control, such as HPLC fingerprint, multiple component determination, and Q-marker establishment in Gnaphalium as soon as possible.
-
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: conceptualization and supervision: Xiao Y, Sun L; draft manuscript and figure preparation: Wang X, Yang Y; manuscript review and editing: Liu D, Xiong L, Dunzhu B, Zhang L, Chen W. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
Data sharing not applicable to this article.
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFC3504800, 2022YFC3501700), National Natural Science Foundation of China (32170402), and Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Committee of Shanghai outstanding academic leaders plan (23XD1423500).
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Wansheng Chen, Lianna Sun and Ying xiao are the Editorial Board members of Medicinal Plant Biology who were blinded from reviewing or making decisions on the manuscript. The article was subject to the journal's standard procedures, with peer-review handled independently of these Editorial Board members and their research groups.
-
# Authors contributed equally: Xiujuan Wang, Dongtian Liu
- Copyright: © 2024 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press, Fayetteville, GA. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Wang X, Liu D, Xiong L, Dunzhu B, Zhang L, et al. 2024. Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, bioactivities and quality control of the Gnaphalium genus: an updated review. Medicinal Plant Biology 3: e005 doi: 10.48130/mpb-0024-0003
Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, bioactivities and quality control of the Gnaphalium genus: an updated review
- Received: 17 October 2023
- Revised: 23 December 2023
- Accepted: 08 January 2024
- Published online: 19 March 2024
Abstract: The genus Gnaphalium (Asteraceae) is distributed across most regions of the world. Some of them are not only used as a food source, but has also been used for the treatment of various diseases including pain, rheumatism, chronic pharyngitis and arthritis in China since ancient times. In this review, we would like to summarize previous research on genus Gnaphalium, including traditional uses, phytochemistry, bioactivities and quality control. The data presented here on genus Gnaphalium was generated based on various scientific research databases, including SciFinder, PubMed, ScienceDirect, Wiley library, Web of Science, and CNKI. Analysis of these findings showed that plants in genus Gnaphalium have a capital power in various therapeutic uses, including pulmonary protection, antimicrobial activity, antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory and anti-complementary activities, and antidiabetic effect. Consistent with this, the chemicals from the plant extracts revealed its richness in various chemicals, including flavonoids, phenolic acids, terpenoids, sterols, and others. In spite of its wide applicable value worldwide, the quality control of genus Gnaphalium is still based on local standards. Thus, we argue that a national standard is required for genus Gnaphalium in China, to validate its bioactivity and future clinical trials rigorously.
-
Key words:
- Gnaphalium /
- Morphology /
- Phytochemistry /
- Ethnopharmacology /
- Pharmacological activities