-
The Trichoderma genus encompasses a wide-ranging collection of filamentous fungi, prevalent in various natural ecosystems[1]. Trichoderma species within this genus have earned acclaim for their exceptional capacity to inhabit plant roots, stimulate plant growth, and showcasing biocontrol attributes against a spectrum of fungal adversaries[2]. Employing tactics like mycoparasitism, antibiosis, competitive resource acquisition, and plant resistance induction, these species effectively manage fungal diseases[3]. Notably, they are increasingly utilized in agriculture as biofertilizers and biopesticides[1]. Trichoderma-based bio-fungicides, available in different formulations like wettable powders, granules, and flowable concentrates, offer a convenient application to seeds, seedlings, soil, and foliage[4,5]. Besides their disease-fighting properties, these bio-fungicides promote plant growth through various mechanisms such as phytohormone production, nutrient solubilization, and stress tolerance enhancement[3]. Recent progress in Trichoderma-based formulations has led to innovative materials, advanced nanotechnology strategies, and genetic engineering techniques aimed at boosting stability, shelf life, and efficacy[4]. Among these advancements, biochar has shown promise as an ideal carrier for Trichoderma formulations due to its high porosity, surface area, and soil stability maintenance abilities[6]. New research indicates that biochar can strengthen Trichoderma's biocontrol properties[7,8]. Experiments show that using Trichoderma bio-fungicides on soil blended with biochar is more effective in fungal disease control than on unamended earth[9]. Likewise, applying these bio-fungicides on biochar-coated seeds provides better resistance against fungal diseases in seedlings[7,10]. Such biotechnological advancements in Trichoderma-based formulations can promote sustainable agricultural practices by reducing reliance on chemical pesticides[11]. This, in turn, helps mitigate the ecological impact of agricultural activities and enhances food and feed safety[12]. By protecting plants from fungal diseases and improving soil fertility, Trichoderma-based bio-fungicides hold promise for enhancing crop yield[1]. Trichoderma formulations play a crucial role in minimizing harm to non-target organisms while maximizing the effectiveness of the active ingredient[13]. While Trichoderma is significant in ensuring agronomic safety, challenges in their formulation persist due to potential degradation of the biomass or bioactive metabolite caused by factors like exposure to air, light, and temperature[14]. Additionally, these products need to be easy to handle, apply, and produce[15,16]. To address this objective, the present study aims to offer a comprehensive examination of various technological advancements that enhance the efficiency of natural preparations. Distinguishing itself from typical literature reviews that predominantly delve into the biological attributes of metabolites, this review incorporates a bibliometric analysis of biopesticides and their formulations[17]. This analysis employs quantitative and statistical indicators to identify patterns related to the most critical pest issues, agriculture's susceptibility, sources of biological control, innovative methodologies, and the current status of Trichoderma formulations. The insights presented in this analysis significantly contribute to the bibliometric methodology, potentially promoting positive strides in the advancement of technology for Trichoderma formulation. Additionally, it offers valuable suggestions for researchers engaged in this field.
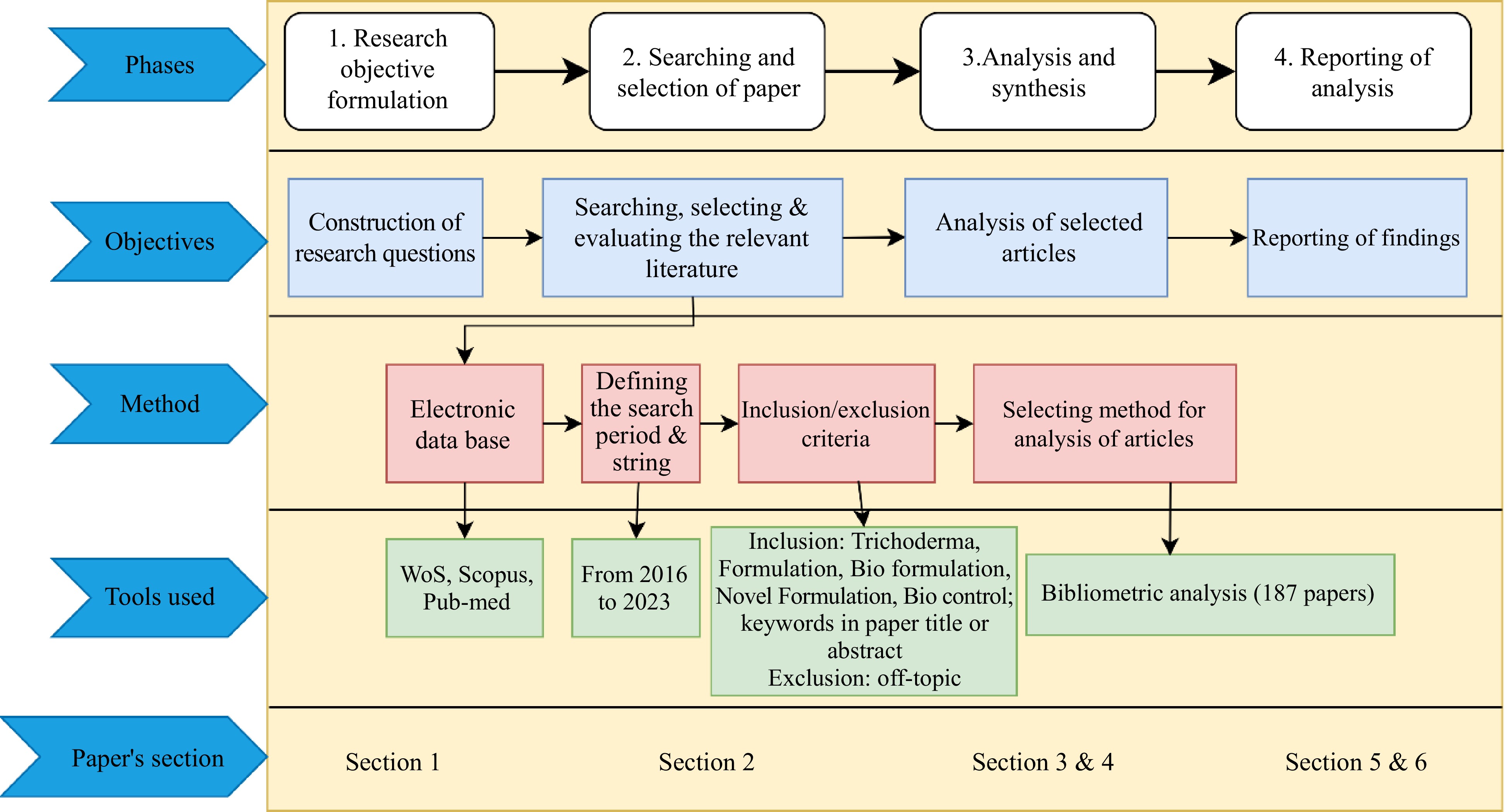
Bibliometric analysis is a technique employed to scrutinize the characteristics and evolving patterns within academic literature using various mathematical and statistical methods[10]. Through this approach, we can quantitatively assess the overall state of the literature, collaborative relationships, research areas of interest, and the development trends in a specific research field[18]. A descriptive analysis of the corpus of published research pertaining to Trichoderma formulations was conducted. This analysis entailed the examination of co-occurring terms within the body of published articles, allowing for the elucidation of evolutionary trends in scientific themes[19]. The fundamental aim of this research is to conduct an exhaustive review of the existing body of literature on Trichoderma formulations and to project the areas of highest interest and potential for future investigation[20]. One of the primary objectives of bibliometric analysis is to assess the trends in research related to Trichoderma formulations, and to identify the most influential authors and institutions in the field of Trichoderma research. Determining the impact of research in terms of citations, patents, or applications in real-world scenarios.
As a result, this study seeks to investigate the following research objectives: In the field of Trichoderma formulations, what are the key research themes and trends observed from 2016 to 2023 include:
(1) How is research on Trichoderma formulations distributed geographically, and what regions exhibit the most active contributions to the field? (2) Can bibliometric analysis predict future trends and potential innovations in Trichoderma formulations research based on historical patterns? (3) The article follows a well organised structure[21]. Initially the research methodology adopted for the study is outlined. Subsequently, a well-organized article is crucial for effectively communicating research findings to the intended audience[22].
-
Literature retrieval was performed online through the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-E) of the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC, Clarivate Analytics) from 2016 to 2023[21,22]. Scopus is a preferred data source for bibliometric analysis, and it provides comprehensive information and data from a multi-disciplinary field of literature[23]. To retrieve literature comprehensively and accurately on Trichoderma formulations, different search terms and retrieval strategies were assembled in this study. Finally, the optimal search items were set as follows: TS = ('Trichoderma formulation*') OR ('Bio formulation of Trichoderma*') OR ('Bio control') OR ('Antagonist') OR ('Rhizosphere fungus')[24]. The data range was set from 2016 to 2023, to collect all relevant publications. It is worth noting that as the Scopus database data network is constantly updated, the results may vary depending on the exact retrieval date.
A detailed literature retrieval process was performed online through Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-E) of the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC, Clarivate Analytics) from 2016 to 2023, and considered Scopus as a preferred data source for bibliometric analysis. Additionally, we outlined the search terms and retrieval strategies that are used in our study and set the range of data from 2016 to 2023 to collect all relevant publications. If we sum up our descriptions narrate on the following key points, like data sources, search terms, data range, constantly updated data base, and optimal search items[25]. The search strategy was designed to capture relevant literature on Trichoderma formulations. The search terms included Trichoderma formulation, bio-formulation of Trichoderma, biocontrol, antagonist and Rhizosphere fungus. The asterisks, in the search terms are used as wildcard characters to capture different word endings. The data range was set from 2016 to 2023 to collect all relevant publications within that timeframe. This was the period during which the literature retrieval was performed[25]. It is mentioned that as the Scopus database data network is constantly updated, and the results may vary depending on the exact retrieval date. This indicates that the study acknowledged the dynamic nature of the database and its potential impact on the results[26]. After assembling different search terms and retrieval strategies, the study determined the optimal search items, which were the selected search terms that would yield the most comprehensive and accurate results for the study's objectives. Overall, the present study took a systematic approach to literature retrieval, considering multiple data sources and employing a combination of search terms to ensure the retrieval of relevant publications on Trichoderma formulations. It is worth noting that as the Scopus database data network is constantly updated, to add upon, the results may vary depending on the exact retrieval date.
Publication collection and exclusion criteria
-
To ensure the credibility of the research conclusions, this study gathered peer-reviewed English journal articles to summarize global research perspectives. It's important to mention that articles not aligned with this paper's purpose were manually omitted in the final phase of data collection[27]. For instance, some articles explored the relationship between plants and microorganisms on leaves. Eventually, a total of 287 articles that met all criteria were sourced from Scopus. These pieces represented almost all top-tier experimental studies on Trichoderma formulations from 2016 to 2023 worldwide. The variability among these articles could effectively indicate the trend of related research development. Therefore, these publications were prioritized for further analysis and assessment. Figure 1 illustrates the flowchart of the literature retrieved in this study[28].
-
Table 1 presents the top 10 countries/regions, institutions, authors, and journals that published the most studies on Trichoderma formulations. As indicated in Table 1, China emerged as the country making the most significant contribution, with 1,231 publications, accounting for 20.33% of the total. India and Pakistan followed closely, ranking second and third, with 1,096 (18.10%) and 618 (10.20%) publications, respectively. Among the institutions, the Chinese Academy of Sciences held the top spot, boasting 160 (2.64%) publications. Following closely was the University of Agriculture, Faisalabad (144, 2.37%), and Nanjing Agricultural University (137, 2.26%). In the realm of scholarly contributions, prolific authors often set the tone for research trends. Identifying these influential scholars can shed light on the direction of the research field[29]. The leading author in the study of rhizosphere microorganisms was Wang Y, with 102 publications. Li Y, Zhang Y, and Hkan M were also highly prolific, each publishing nearly 90 studies. These works were predominantly featured in prominent journals in Ecology and Botany, such as Frontiers in Microbiology (3.73%), Frontiers in Plant Science (2.36%), and Plant and Soil (2.03%).
Table 1. Leading journals contributing to the existing body of knowledge in the field of formulation of Trichoderma.
Sl. no. Name of journal No. of publication Citations 1 Journal of Applied Microbiology 2 40 2 Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2 16 3 Indian Phytopathology 3 2 4 Biological Control 2 59 5 Crop Protection 2 30 6 Frontiers in Microbiology 2 23 7 Journal of Biological Control 2 1 8 Medicinal Plants 2 5 Scientific production
-
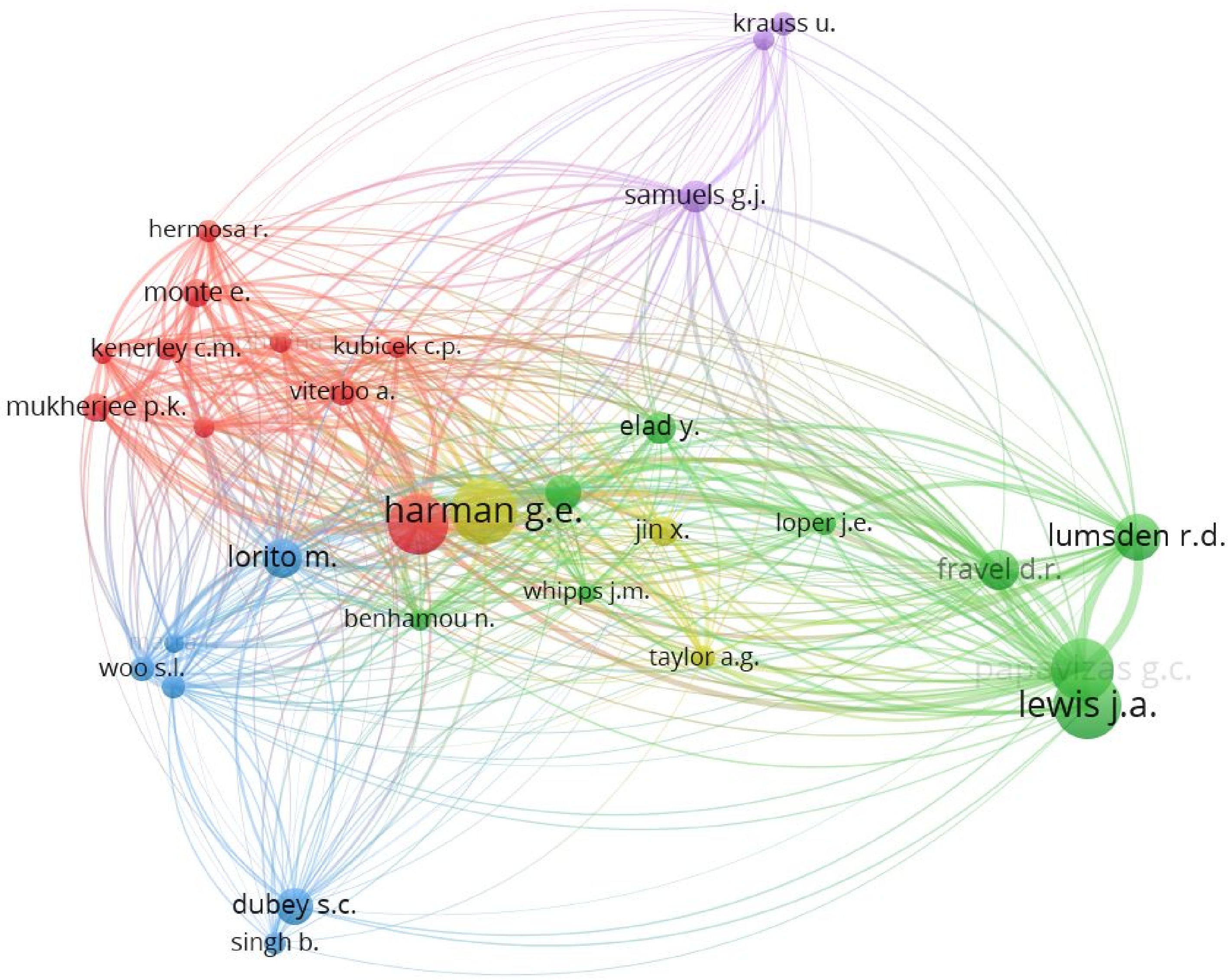
The analysis of scientific production on Trichoderma formulations demonstrated the trend of publications per year on Trichoderma formulation studies. It was observed that published research showed a significant increase of 71.24% over the last decade (2016–2023) (Fig. 1). The increasing trend is possibly related to economic support from government programs, since funding for innovative, sustainable, and ecological research is being considered to meet the demand for food and mitigate environmental pollution[30]. Figure 2 illustrates a co-citation map of authors collaborating in the field of Trichoderma formulation. The purpose of conducting this co-citation analysis is to visually portray the knowledge base of the specific area of review. The analysis identifies three distinct clusters, each represented by different colored nodes: blue, red, and green. The green cluster stands out as it is associated with Harman, who has the highest collaboration, working with nine researchers on Trichoderma formulation research. The red cluster, on the other hand, signifies the second-highest collaboration, led by Mukherjee et al.[31] with six researchers. Lastly, the pink cluster represents the lowest level of collaboration among researchers, with only two researchers working together in this area.
-
Table 2 showcases the country–wise citation analysis, and the series presented here seems to have large variability in distribution. In terms of total citations of studies dedicated to Trichoderma formulations. Citations count of articles by country as a unit of analysis represents the popularity of a field of research in a particular region. India with 20 publications having 115 citations topped the list and, therefore, is the most impactful country contributing to the existing body of knowledge in the said domain followed by Italy with four publications having 69 citations and Brazil with three publications having 51 citations. From the viewpoint of the total number of publications, India holds first position, having 20 publications, followed by Italy having four publications.
Table 2. Leading countries contributing to the existing body of knowledge in the field of formulation of Trichoderma.
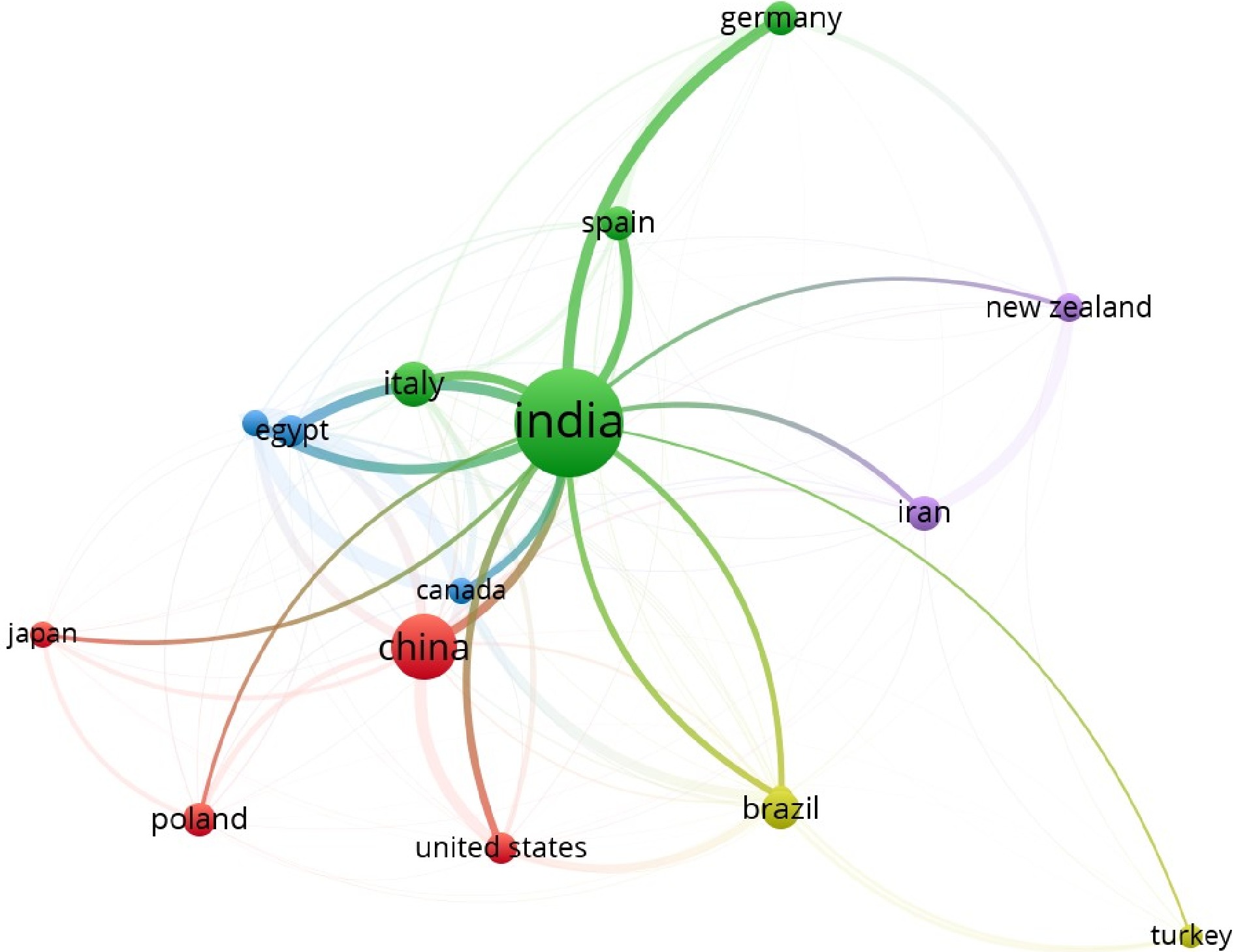
Sl. no. Country No. of publication Citations 1 Argentina 1 20 2 Belgium 2 30 3 Brazil 3 51 4 China 2 82 5 Croatia 1 30 6 Finland 1 37 7 India 20 115 8 Italy 4 69 9 New Zealand 2 21 10 Portugal 1 67 11 South korea 1 54 The top researchers working in the field of Trichoderma formulation are presented in Table 2. The authors' citation count represents the recognition of their research work in a particular field of research. It is quite clear from the list of 13 author's citations that all the authors have at least 10 citations to their name based on the total citation count. Among the 13 authors Park et al.[32] has the highest number of citations of 57 followed by Herrera-Téllez et al.[33] having 47 and Hewedy et al.[34] having 44 citations. The analysis of bibliographic coupling in the Trichoderma formulation domain is represented in Fig. 3. This technique utilizes references from existing publications to elucidate the relevant literature[35]. For this study, five thematic clusters have been identified, labeled green, red, blue, yellow, and purple. Among these interconnected groups, India stands out as the country with the most extensive collaboration network, linked with 15 other countries. Given that India also holds the highest number of published documents (115), it was anticipated to be the central node in this cooperation network. The findings demonstrate the strong relationships between researchers and their respective institutional affiliations, emphasizing the scientific cooperation aimed at developing sustainable and ecologically sound strategies for crop protection in a competitive manner[36].
In Fig. 4, a co-occurrence analysis of keywords with a minimum threshold of five occurrences is displayed. The network illustrates the most frequently utilized terms within the 'Trichoderma formulation' research domain, capturing the essence of the article's core content. The prevalence of these keywords can be indicative of the research direction and content within this specific field[37]. This analysis allows for the identification of developmental trends within a field and a comprehensive understanding of its current research status[38]. The co-occurrence graph of keywords reveals a total of four co-occurrence clusters (Fig. 4), encompassing themes like biocontrol, formulation, Trichoderma, and shelf life. Each cluster is further examined below, providing an in-depth portrayal of the prominent topics within the Trichoderma formulations landscape during the research period. Annual publication number leading years contributing to the existing body of knowledge in the field of formulation of Trichoderma is presented in Table 3.
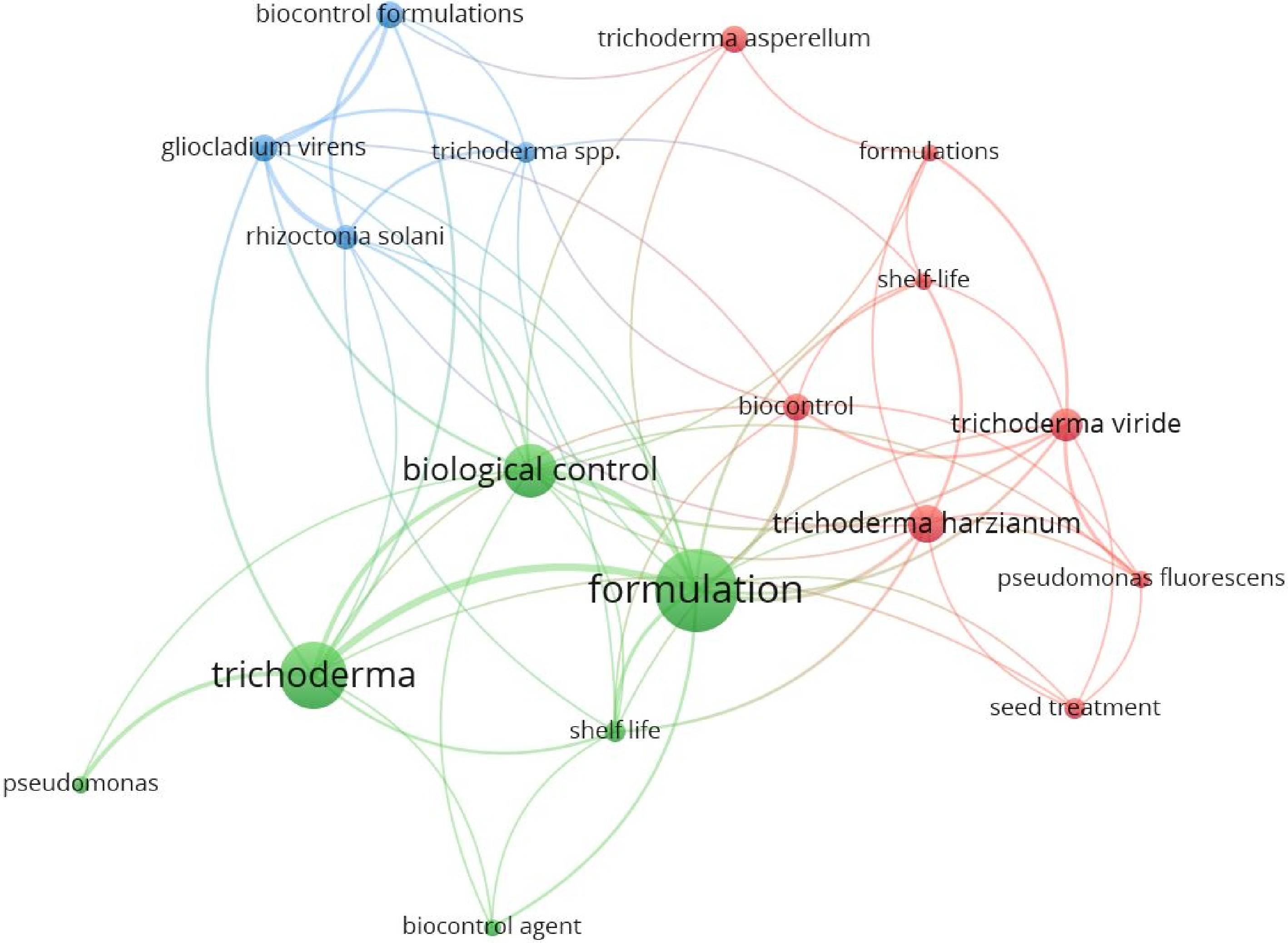
Figure 4.
Co-occurrence analysis based upon keywords from articles in the field of Trichoderma formulation.
Table 3. Annual publication number leading years contributing to the existing body of knowledge in the field of formulation of Trichoderma.
Sl. no. Year No. of publication 1 2016 8 2 2017 13 3 2018 21 4 2019 16 5 2020 20 6 2021 17 7 2022 15 8 2023 8 The shift in annual publication counts serves as a vital benchmark for gauging the progress of a research field, lending insights into potential development trends[28]. Figure 4 provides a clear portrayal of the publication distribution in Trichoderma formulation from 2016 to 2023, illustrating a noticeable increase in annual article output. This surge suggests a heightened interest in the field over the past few years. Scientific research fields typically undergo a four-stage evolution[39] ; (1) the inception phase, characterized by the introduction of novel research areas or directions by notable scientists; (2) the expansion phase, where scientists gravitate toward the emerging research direction, leading to a proliferation of discussion topics; (3) the stabilization phase, marked by the amalgamation of new knowledge to form a distinct research context; and (4) the contraction phase, in which the number of new publications diminishes. Notably, the research on Trichoderma formulation seems to be currently in the expansion phase[40].
-
The publication pattern reveals a growing research interest in Trichoderma formulations, a relatively new field that is attracting increasing enthusiasm among scholars. Notably, the top contributors to this area, as identified through VOS viewer analysis, include key individuals, organizations, sources, and countries. Park emerges as the leading author based on citation count, followed by Herrera-Téllez and Hewedy. China, Portugal, Italy, and South Korea are recognized as major contributors to research in this field, as reflected in their citation counts. Conversely, India leads in terms of document count, demonstrating a significant contribution to the literature.
Co-citation and bibliographic coupling analyses have identified three distinct thematic clusters. In the co-citation analysis, these clusters relate to application methods, types of Trichoderma formulations, and their biocontrol efficacy. Additionally, insights from the bibliometric analysis of biopesticide formulations have facilitated the integration of methods and strategies aimed at enhancing the effectiveness of Trichoderma formulations.
Conclusions
-
This paper conducts a bibliometric analysis to critically examine articles related to biological control, focusing specifically on those published in various indexed journals, and offers a comprehensive overview of the evolution of Trichoderma formulations over time. The primary objective of this research is to investigate and characterize the key literature on this topic, covering historical, current, and emerging developments in this dynamic field. Bibliometric techniques are employed to visualize the Trichoderma formulation landscape.
To achieve this goal, the study analyses a dataset of articles obtained from the core collection databases of Scopus and Web of Science. Within the scope of this study, significant publications on Trichoderma formulations are meticulously reviewed to highlight the potential trajectory of Trichoderma's role in biological disease control in plants. The study identifies and examines the various developmental phases of Trichoderma formulations, offering a comprehensive analysis that can shape the future of this critical research area. Given the scarcity of comprehensive bibliometric studies on Trichoderma formulation research, this study seeks to fill this gap, making a significant contribution to the extensive readership interested in Trichoderma.
-
This study has several limitations and challenges that must be considered by future researchers. First, the study relies on a single database, which could restrict the amount of available data. Additionally, the search criteria were limited to research articles, and only those with specific phrases in the title were included, which may not represent the complete dataset. However, Trichoderma's biological control mechanisms against plant fungal and nematode diseases involve various strategies, including competition, antibiosis, antagonism, and mycoparasitism. In addition to these, Trichoderma enhances plant growth and induces systemic resistance in plants, making it effective in controlling a wide range of plant fungal and nematode diseases[41]. Although biological control is effective, it generally requires time to become established in the environment, making it a slower process. Therefore, optimizing the formulation of Trichoderma-based products is essential to ensure their stability and efficacy. It is important to ensure that these formulations are compatible with other agricultural treatments, such as chemical fertilizers and pesticides, to maximize their overall effectiveness. Proper formulation can improve the shelf life, ease of application, and survival of Trichoderma under varying environmental conditions. Ongoing research is necessary to refine these formulations for broader application in integrated pest management programs[42]. This is a significant limitation as the analysis was restricted to articles published in journals, excluding other valuable sources like reviews, conferences, books, and book chapters. To overcome this limitation, future researchers should consider utilizing additional databases such as Scopus and Science Direct, which can provide more comprehensive data. This limitation may have impacted the study's ability to provide a comprehensive overview of the field.
-
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: conceptualization: Kumar V, Mishra KK, Panda SR; writing − original draft preparation: Kumar V, Wagh AK, Mishra KK; writing − review and editing: Panda SR, Kumar V, Wagh AK; supervision: Kumar V, Panda SR, All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
-
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
- Copyright: © 2024 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press, Fayetteville, GA. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra KK, Kumar V, Wagh AK, Panda SR. 2024. The promise of Trichoderma formulations: insight from bibliometric analysis. Studies in Fungi 9: e014 doi: 10.48130/sif-0024-0014
The promise of Trichoderma formulations: insight from bibliometric analysis
- Received: 05 August 2024
- Revised: 04 September 2024
- Accepted: 06 September 2024
- Published online: 24 September 2024
Abstract: Trichoderma formulations have garnered significant attention in agricultural practices owing to their multifaceted roles in promoting plant growth, enhancing disease resistance, and improving soil health. However, despite extensive research in this field, a comprehensive bibliometric analysis elucidating the trends, patterns, and advancements remains scarce. This study aims to fill this gap by conducting a bibliometric analysis of publications about Trichoderma formulations. Leveraging data from prominent scholarly databases, the analysis examines publication trends, authorship patterns, citation networks, and thematic evolution over time. By identifying key research clusters and influential works, this study offers insights into the current state of Trichoderma research, as well as potential avenues for future exploration. Understanding the landscape of Trichoderma formulations through bibliometric analysis is crucial for unlocking their full potential in sustainable agriculture and fostering innovation in biocontrol strategies.
-
Key words:
- Bibliometric /
- Trichoderma /
- Formulation /
- Agriculture /
- Biological control