HTML
-
Studies of fungi on Musa spp. have been conducted since the 19th century, especially in tropics and subtropics (Sawada 1959, Ellis 1971, 1976, Matsushima 1971, Ebbels & Allen 1979, Shaw 1984, Sivanesan 1984, Arnold 1986, Aptroot 1995, Heredia–Abarca et al. 1997, Photita et al. 2001a, b, 2002, 2003b, Somrithipol 2007). However, these studies were restricted to some fungal groups (e.g. hyphomycetous and endophytic fungi) and were based mostly on morphological characteristics. Hence, less novel species on Musa spp. were consequently introduced based on morphological characteristics coupled with phylogenetic analyses (Gao et al. 2014, Hernández–Restrepo et al. 2015, Liu et al. 2015, Crous et al. 2016, 2017, Samarakoon et al. 2020a, b).
Many genera of fungi have been reported as endophytes, saprobes or pathogens on Musa spp. Worldwide. The most common species are from Acremonium, Alternaria, Arthrobotryum, Bipolaris, Brevistachys, Chalara, Cladosporium, Coniothyrium, Corynespora, Cylindrocarpon, Dactylella, Diplodia, Dothiorella, Epicoccum, Helminthosporium, Lasiodiplodia, Leptosphaeria, Myrothecium, Nectria, Parapallidocercospora, Phaeodothis, Phaeosphaeria, Pseudoramularia, Pyricularia, Pyriculariopsis, Radaisiella, Scolecobasidium, Stagonospora, Torulopsis, Trichoderma, Trichothecium, Uwebraunia, Virgariella, Volutella, Wojnowicia, Zygophiala and Zasmidium (Shaw 1984, Arnold 1986, Aptroot 1995, Heredia–Abarca et al. 1997, Photita et al. 2001a, b, 2002, Cao et al. 2002, Hao et al. 2013, Gao et al. 2014, Quaedvlieg et al. 2014, Videira et al. 2017). However, few species among the latter genera have been identified based on DNA sequence data and the phylogenetic relationships of many taxa are not well investigated (Hao et al. 2013, Wikee et al. 2013, Gao et al. 2014, Liu et al. 2015, Giraldo et al. 2017).
Documentation of saprobic fungi on Musa spp. across the Asian region is also scanty (Matsushima 1975, Photita et al. 2001a, 2002, 2003b, Somrithipol 2007, Samarakoon et al. 2020a, b). Based on morphology, Photita et al. (2001a) reported 46 saprobes on Musa acuminata from Hong Kong and they belong to 40 genera in Ascomycota (Anthostomella, Bipolaris, Chloridium, Colletotrichium, Corynesporopsis, Curvularia, Dactylaria, Dactylella, Deightoniella, Diaporthe, Dictyosporium, Didymosphaeria, Diplodia, Durispora, Glomerella, Hansfordia, Hyponectria, Leptosphaeria, Massarina, Memnoniella, Mycosphaerella, Nectria, Nigrospora, Ophioceras, Periconia, Periconiella, Phaeosphaeria, Phialocephala, Phoma, Phomatospora, Phomopsis, Pyriculariopsis, Stachybotrys, Stachylidium, Stemphylium, Tetraploa, Torula, Veronaea, Verticillium and Zygosporium). In addition, Cylindrocarpon (Matsushima 1975), Dictyoarthrinium (Somrithipol 2007, Samarakoon et al. 2020b), Dictyosporium, Pseudopithomyces (Photita et al. 2002), Spegazzinia (Samarakoon et al. 2020a) and Stachybotrys (Photita et al. 2003a) were also documented as fungal saprobes on Musa spp.
Periconia (Periconiaceae) was introduced by Tode (1791) and typified by P. lichenoides Tode. Both sexual and hyphomycetous asexual morphs are recorded in Periconia (Tanaka et al. 2015, Liu et al. 2017). The sexual morph has immersed or erumpent ascomata with an ostiolar neck. The eight ascospores are biseriate, hyaline and broadly fusiform with a gelatinous sheath (Tanaka et al. 2015). The asexual morph of Periconia has pale to dark brown branched or unbranched conidiophores (referred as stipe) (Tanaka et al. 2015). The conidiogenous cells are usually monoblastic or polyblastic which form at the terminal ends or intercalary parts of the conidiophore. In addition, the conidia of Periconia are usually catenate or solitary, pale to dark brown, spherical and aseptate (Ellis 1971, 1976, Seifert & Gams 2011). Periconia has been reported as plant pathogens, endophytes and as common saprobes in terrestrial and aquatic environments worldwide (Ellis 1971, 1976, Markovskaja & Kačergius 2014, Liu et al. 2017). Currently 187 epithets are listed in Periconia (Index Fungorum 2021). In addition, there are about 2575 DNA sequence data available for Periconia in GenBank (NCBI; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/?term=Periconia, accessed on January 10, 2021), which only restricted to 36 species. This suggests more than 150 species still need correct taxonomic placements based on molecular data, especially P. lichenoides, the generic type of Periconia.
Torula (Torulaceae) was introduced by Persoon (1975) and is typified by T. herbarum (Pers.) Link. The neotype of T. herbarum was designated by Crous et al. (2015). The genus is only known by its asexual morph and is characterized by doliiform to ellipsoid or clavate, cupulate conidiogenous cells which the walls are thick and heavily melanized at the base while thin at the apex. The conidia are subcylindrical, phragmosporous, brown, smooth to verrucose, and appear as branched or unbranched chains (Ellis 1971, 1976, Crous et al. 2015, Crane & Miller 2016, Bhat 2017, Li et al. 2017, 2020). Previously, conidiogenesis was a key morphological feature used to delineate species in Torula (Mason 1941, Hughes 1953, Crane & Schoknecht 1977, Li et al. 2020). Crous et al. (2015), Su et al.(2016, 2018) and Li et al.(2017, 2020) investigated the phylogenetic relationships of Torula using DNA sequence data (ITS, LSU, SSU, TEF, and RPB2). Currently, 17 species epithets have molecular data in GenBank (Hongsanan et al. 2020, Hyde et al. 2020a, Li et al. 2020), while more than 520 species are listed in Index Fungorum (2021). Torula is common on terrestrial and aquatic habitats mainly as a saprobe across tropical and temperate regions (Crous et al. 2015, Su et al. 2018, Li et al. 2020).
Most taxonomic studies have focused mostly on fungal pathogens on Musa spp. due to their diseases and agricultural losses (Giatgong 1980, Carlier et al. 2002, Zakaria et al. 2009, Wulandari et al. 2010, Churchill 2011, Su et al. 2011, Guarnaccia et al. 2017, Dita et al. 2018, Marin–Felix et al. 2019, Maryani et al. 2019). Therefore, the hidden saprobic and endophytic fungal diversity on Musa spp. are yet to be investigated as only 8% of fungi have possibly been described from the estimated fungal number of 2.2–3.8 million (Hyde et al. 2020b). In addition, a growing number of saprobic fungi recovered from Musa spp. need modern taxonomic treatments (Marin–Felix et al. 2019, Maryani et al. 2019, Samarakoon et al. 2020a, b).
We investigated the hidden saprobic fungi associated with different tissue types of Musa spp. (i.e. dead or fallen down leaves, leaf sheaths, pseudostems and decaying fruits) from different geographical localities across Asia. Fungi were identified based on morpho–molecular data and the taxonomic relationships were evaluated. In this study, we report Periconia cortaderiae (Thailand), P. delonicis (Thailand), Torula chromolaenae (Thailand), T. fici (Yunnan, China) and T. masonii (Taiwan, China) for the first time on Musa spp. with detailed morphological illustrations and DNA sequence data.
-
Dead leaves of Musa spp. were collected from China and Thailand. Specimens were transferred to the laboratory in cardboard boxes. Samples were examined with a Motic SMZ 168 Series microscope. Powder like masses of conidia of hyphomycetous taxa on Musa samples were mounted in water for microscopic studies and photomicrography. The hyphomycetous taxa were examined using a Nikon ECLIPSE 80i compound microscope and photographed with a Canon 550D digital camera fitted to the microscope. Measurements were made with the Tarosoft (R) Image Frame Work program and images used for figures processed with Adobe Photoshop CS6 Extended version 12.0 software (Adobe, USA).
Single spore isolation was carried out following the method described in Senanayake et al. (2020). Germinated spores were individually transferred to potato dextrose agar (PDA) plates and grown at 25℃ in normal light. Colony characteristics were observed and measured after 3 weeks. The specimens are deposited at the Mae Fah Luang University (MFLU) Herbarium, Chiang Rai, Thailand. Living cultures are deposited at the Culture Collection of Mae Fah Luang University (MFLUCC). Faces of fungi numbers are registered as in Jayasiri et al. (2015).
DNA extraction and PCR amplification
-
Fungal isolates derived from single spore cultures were grown on potato dextrose agar (PDA) for 4 weeks at 25℃ and the axenic mycelia (50–100 mg) of each isolate were scrapped off for DNA extraction purposes. Mycelia were ground to a fine powder with liquid nitrogen and fungal DNA was extracted using the Biospin Fungus Genomic DNA Extraction Kit–BSC14S1 (BioFlux®, P.R. China) according to the instructions of the manufacturer. Five gene regions were used for the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, including partial 18S small subunit rDNA (SSU), partial 28S large subunit rDNA (LSU), internal transcribed spacer (ITS), RNA polymerase II second largest subunit (RPB2) and partial translation elongation factor 1–alpha gene (TEF) using the primers NS1/NS4 (White et al. 1990), LR0R/LR5 (Vilgalys & Hester 1990), ITS5/ITS4 (White et al. 1990), fRPB2–5f/fRPB2–7cR (Liu et al. 1999) and EF1–983F/EF1–2218R (Rehner 2001), respectively.
The final volume of the PCR reaction was 25 μl, consisting of 2 μl of DNA template, 1 μl of each forward and reverse primer, 12.5 μl of 2×Easy Taq PCR SuperMix (mixture of EasyTaqTM DNA Polymerase, dNTPs, and optimized buffer, Beijing TransGen Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing, P.R. China) and 8.5 μl of the sterilized double–distilled water (ddH2O). The thermal cycle programs were set up following the procedures described by Samarakoon et al.(2019, 2020b) for the respective genes. The amplified PCR fragments were sent to a commercial sequencing provider (TsingKe Biological Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd, China) for PCR purification and sequencing. The Sanger DNA sequences obtained from this study were deposited in GenBank (Tables 1, 2).
Table 1. Taxa used in the phylogenetic analyses of Periconiaceae with the corresponding GenBank accession numbers. Type strains are superscripted with "T" and newly generated strains are indicated in black bold.
Taxa Culture collection/Voucher no. GenBank accession numbers LSU SSU ITS TEF Flavomyces fulophazii CBS 135761T KP184040 KP184082 KP184001 NA F. fulophazii MF09 MN515261 NA MN537663 MN535259 Helminthosporium H 4628 AB807521 AB797231 LC014555 AB808497 dalbergiae Massarina cisti CBS 266.62T AB807539 AB797249 NA AB808514 Noosia banksiae CPC: 17282 JF951167 NA JF951147 NA N. banksiae CBS 129526 MH878062 NA NA NA Periconia aquatica MFLUCC 16–0912T KY794705 NA KY794701 KY814760 P. byssoides MFLUCC 17–2292 MK347968 MK347858 MK347751 MK360069 P. byssoides MFLUCC 18–1548 MK348013 MK347902 MK347794 MK360070 P. caespitosa LAMIC_110_16 MH051907 NA MH051906 NA P. cortaderiae MFLUCC 15–0457T NG_068238 NG_068373 NR_165853 KY310703 P. cortaderiae MFLUCC 15–0451 KX954403 KX986346 KX965734 KY429208 P. cortaderiae MFLUCC 20–0236 MW406971 MW406969 MW406973 MW422156 P. cyperacearum CPC: 32138T NG_064549 NA NR_160357 MH327882 P. delonicis MFLUCC 17–2584T MK347941 MK347832 NA MK360071 P. delonicis MFLUCC 20–0235 MW406970 MW406968 MW406972 MW422155 P. digitata CBS 510.77 AB807561 AB797271 NA AB808537 P. epilithographicola CBS 144017T NA NA NR_157477 NA P. epilithographicola PL5–1B NA NA MF422162 NA P. homothallica HHUF 29105 NG_059397 NG_064851 NR_153446 AB808541 P. homothallica KT 916 AB807565 AB797275 AB809645 NA P. igniaria CBS 379.86 AB807566 AB797276 LC014585 AB808542 P. igniaria CBS 845.96 AB807567 AB797277 LC014586 AB808543 P. macrospinosa CBS 135663 KP184038 KP184080 KP183999 NA P. neobrittanica CPC 37903T NG_068342 NA NR_166344 NA P. palmicola MFLUCC 14–0400T NG_068917 MN648319 NA MN821070 P. pseudobyssoides DLUCC 0850 MG333494 NA MG333491 MG438280 P. pseudobyssoides H 4151 AB807568 AB797278 LC014587 AB808544 P. pseudobyssoides H 4790 AB807560 AB797270 LC014588 AB808536 P. pseudodigitata KT 644 AB807562 AB797272 LC014589 AB808538 P. pseudodigitata KT 1195A AB807563 AB797273 LC014590 AB808539 P. pseudodigitata KT 1395 AB807564 AB797274 LC014591 AB808540 P. salina MFLU 19–1235T MN017846 MN017912 MN047086 NA P. submersa MFLUCC 16–1098T KY794706 NA KY794702 KY814761 P. thailandica MFLUCC 17–0065T KY753888 KY753889 KY753887 NA Table 2. Taxa used in the phylogenetic analyses of Torulaceae with the corresponding GenBank accession numbers. Type strains are superscripted with "T" and newly generated strains are indicated in black bold.
Taxa Culture collection/Voucher no. ITS LSU SSU RPB2 TEF Dendryphion aquaticum MFLUCC 15–0257T KU500566 KU500573 KU500580 NA NA D. comosum CBS 208.69T MH859293 MH871026 NA NA NA D. europaeum CPC 23231 KJ869145 KJ869202 NA NA NA D. hydei KUMCC 18–0009T MN061343 MH253927 MH253929 NA NA Neotorula aquatica MFLUCC 15–0342T KU500569 KU500576 KU500583 NA NA N. submersa HKAS 92660 NR_154247 KX789217 NA NA NA Rostriconidium aquaticum KUMCC 15–0297 MG208165 MG208144 NA MG207975 MG207995 R. aquaticum MFLUCC 161113T MG208164 MG208143 NA MG207974 MG207994 R. pandanicola KUMCC 17–0176T MH275084 MH260318 MH260358 MH412759 MH412781 Roussoella nitidula MFLUCC 11–0182T KJ474835 KJ474843 NA KJ474859 KJ474852 R. scabrispora MFLUCC 11–0624T KJ474836 KJ474844 NA KJ474860 KJ474853 Roussoellopsis tosaensis KT 1659 NA AB524625 AB524484 AB539104 AB539117 Rutola graminis CPC 33267 MN313814 MN317295 NA NA NA R. graminis CPC 33695 MN313815 MN317296 NA NA NA R. graminis CPC 33715T MN313816 MN317297 NA NA NA Sporidesmioides thailandica MFLUCC 13–0840 MN061347 NG_059703 NG_061242 KX437761 KX437766 S. thailandica KUMCC 16–0012T MN061348 KX437758 KX437760 KX437762 KX437767 Thyridaria broussonetiae TB1 KX650569 NA KX650515 KX650586 KX650539 Thyridariella mahakoshae NFCCI 4215 MG020435 MG020438 MG020441 MG020446 MG023140 Th. mangrovei PUFD 17–98T MG020434 MG020437 MG020440 MG020445 MG020443 Torula acaciae CPC 29737T NR_155944 NG_059764 NA KY173594 NA T. aquatica DLUCC 0550 MG208166 MG208145 NA MG207976 MG207996 T. aquatica MFLUCC 16–1115T MG208167 MG208146 NA MG207977 NA T. breviconidiophora KUMCC 18–0130T MK071670 MK071672 MK071697 NA MK077673 T. camporesii KUMCC 19–0112T MN507400 MN507402 MN507401 MN507404 MN507403 T. chiangmaiensis KUMCC 16–0039T MN061342 KY197856 KY197863 NA KY197876 T. chromolaenae MFLUCC 20–0237 MW412524 MW412518 MW412515 MW422161 MW422158 T. fici CBS 595.96T KF443408 KF443385 KF443387 KF443395 KF443402 T. fici KUMCC 15–0428 MG208172 MG208151 NA MG207981 MG207999 T. fici KUMCC 16–0038 MN061341 KY197859 KY197866 KY197872 KY197879 T. fici MFLUCC 20–0238 MW412525 MW412519 MW412516 NA MW422159 T. gaodangensis MFLUCC 17–0234T MF034135 NG_059827 NG_063641 NA NA T. goaensis MTCC 12620T NR_159045 NG_060016 NA NA NA T. herbarum CPC 24414 KR873260 KR873288 NA NA NA T. hollandica CBS 220.69 NR_132893 NG_064274 KF443389 KF443393 KF443401 T. hydei KUMCC 16–0037T MN061346 MH253926 MH253928 NA MH253930 T. mackenziei MFLUCC 13–0839T MN061344 KY197861 KY197868 KY197874 KY197881 T. masonii CBS 245.57T NR_145193 NG_058185 NA NA NA T. masonii DLUCC 0588 MG208173 MG208152 NA MG207982 MG208000 T. masonii MFLUCC 20–0239 MW412523 MW412517 MW412514 MW422160 MW422157 T. pluriseptata MFLUCC 14–0437T MN061338 KY197855 KY197862 KY197869 KY197875 T. polyseptata KUMCC 18–0131T MK071671 MK071673 MK071698 NA MK077674 Abbreviations of culture collections: CBS: Westerdijk Fungal Biodiversity Institute, Utrecht, Netherlands. CPC: Working collection of Pedro Crous housed at CBS. DLUCC: Dali University Culture Collection, China. H: University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland. HKAS: Herbarium of Cryptogams, Kunming Institute of Botany, Academia Sinica, China. KT: K. Tanaka. LAMIC: Laboratorio Asociaciones suelo, planta microorganismos, Pontificia Universidad Javeriana, Bogotá, D.C., Colombia. MTCC: Microbial Type Culture Collection, CSIR–Institute of Microbial Technology, Sector 39–A, Chandigarh – 160036, India. KUMCC: Kunming Institute of Botany Culture Collection, China. MFLU: Mae Fah Luang University, Chiang Rai, Thailand. MFLUCC: Mae Fah Luang University Culture Collection, Chiang Rai, Thailand. NFCCI: National Fungal Culture Collection of India. NA: DNA sequence data are not available in GenBank. Sequence alignment
-
Obtained sequences were subjected to BLASTn search tool in GenBank (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) for finding the closely related taxa. BLASTn search results and initial morphological studies have supported that our isolates belong to Periconiaceae and Torulaceae. Other sequences used in the analyses were obtained from GenBank (Tables 1, 2) based on recently published data (Jayasiri et al. 2019, Hongsanan et al. 2020, Hyde et al. 2020a, Li et al. 2020). The single gene alignments were automatically analysed by MAFFT v. 7.036 (http://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/large.html; Katoh et al. 2019) using the default settings and refined where necessary, using BioEdit v. 7.0.5.2 (Hall 1999). The single gene matrixes were prior analyzed by maximum likelihood (ML) criterion for checking the congruence of the tree topologies and if the tree topologies were congruent, the concatenated sequence dataset were performed for further analyses.
Phylogenetic analyses
-
Phylogenetic analyses were preformed based on maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian inference (BI) criteria. The phylogenetic trees showing relationships of taxa in Periconiaceae and Torulaceae were generated separately. Data matrixes used in these analyses were followed as; Periconiaceae (Analysis 1): the combined SSU, LSU, ITS and TEF data matrix comprised 35 sequences of representative taxa in Periconiaceae. Helminthosporium dalbergiae (MAFF 243853) and Massarina cisti (CBS 266.62) were selected as outgroup taxa. Torulaceae (Analysis 2): the combined SSU, LSU, ITS, TEF and RPB2 matrix comprised 40 sequences of selected genera in Torulaceae. Taxa in Roussoellaceae were selected as the outgroup taxa viz. Roussoella nitidula (MFLUCC 11–0182), R. scabrispora (MFLUCC 11–0624) and Roussoellopsis tosaensis (KT 1659).
Maximum likelihood (ML) trees were generated using the RAxML–HPC2 on XSEDE (8.2.8) (Stamatakis et al. 2008, Stamatakis 2014) in the CIPRES Science Gateway platform (Miller et al. 2010) using GTR+I+G model of evolution and 1, 000 replicates of rapid bootstrap. Bayesian inference (BI) analysis was conducted with MrBayes v. 3.1.2 (Huelsenbeck & Ronquist 2001) to evaluate posterior probabilities (PP) (Rannala & Yang 1996, Zhaxybayeva & Gogarten 2002) by Markov Chain Monte Carlo sampling (BMCMC). Two parallel runs were conducted, using the default settings, but with the following adjustments: four simultaneous Markov chains were run for 2, 000, 000 generations (Analysis 1, 2) and trees were sampled every 100th generation and 20, 000 trees were obtained. The first 4, 000 trees, representing the burn–in phase of the analyses were discarded. The remaining 16, 000 trees were used for calculating PP in the 50% majority rule consensus tree.
Phylograms were visualized with FigTree v1.4.0 program (Rambaut 2011) and reorganized in Microsoft PowerPoint (2007, USA) and converted to jpeg file in Adobe Photoshop CS6 Extended version 12.0 software (Adobe, USA). The final trees and data matrixes were submitted in TreeBASE (https://www.treebase.org/), submission ID: 27468 for Periconiaceae and 27469 for Torulaceae.
Fungal collections, isolation and morphological characterization
-
Analysis 1: Periconiaceae
The best scoring RAxML tree resulted from the combined gene analysis of SSU, LSU, ITS and TEF sequence data is shown in Fig. 1 with a final ML optimization likelihood value of – 9645.86. The matrix had 561 distinct alignment patterns, with 26.15% of undetermined characters or gaps. Estimated base frequencies were as follows; A = 0.233866, C = 0.256179, G = 0.274088, T = 0.235866; substitution rates AC = 2.126081, AG = 2.703293, AT = 1.718216, CG = 1.412442, CT = 10.292987, GT = 1.000000; proportion of invariable sites I =0.624461; gamma distribution shape parameter α = 0.615919. Bayesian posterior probabilities (BYPP) from MCMC were evaluated with a final average standard deviation of split frequencies was 0.008. All trees (ML & BI) were similar in topology and did not differ significantly with respects to generic placements and this is in agreement with previous studies based on multi–gene phylogeny (Jayasiri et al. 2019, Hongsanan et al. 2020, Hyde et al. 2020a). Our MFLUCC 20–0235 strain is sister to Periconia delonicis (MFLUCC 17-2584) and grouped with P. palmicola (MFLUCC 14-0400) and P. verrucosa (MFLUCC 17-2158) with a strong statistical support (ML = 98%, BYPP =1.00; Fig. 1). The MFLUCC 20–0236 strain grouped with P. cortaderiae (MFLUCC 15-0457, MFLUCC 15-0451) with high support (ML = 100%, BYPP = 1.00), and has close phylogenetic affinity to Noosia banksiae (CPC: 17282, CBS 129526) and Periconia homothallica (KT 916, HHUF 29105). Therefore, we identify MFLUCC 20–0235 as P. delonicis and MFLUCC 20–0236 as P. cortaderiae, respectively.
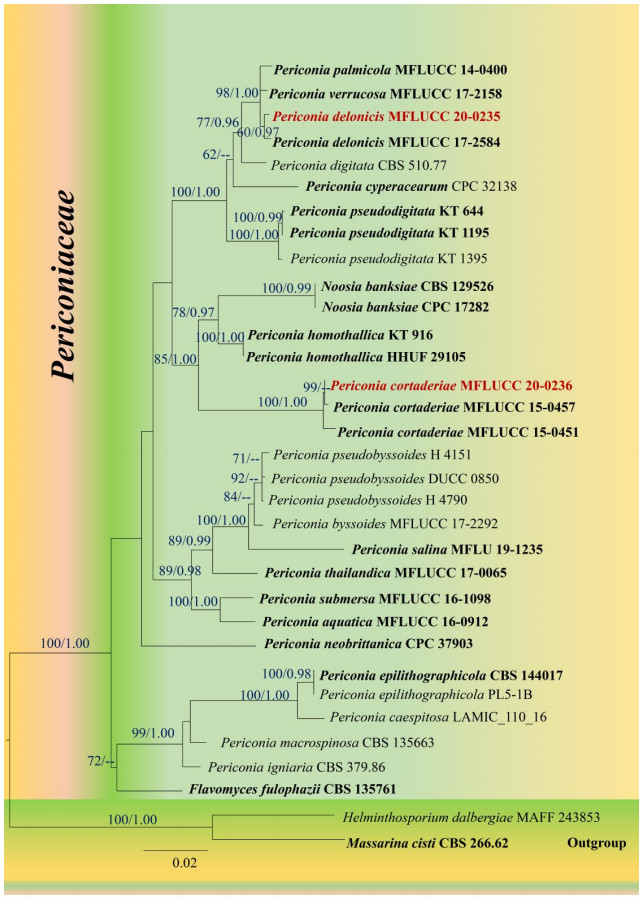
Figure 1.
Maximum likelihood tree revealed by RAxML from an analysis of a concatenated SSU, LSU, ITS and TEF sequence dataset of the species in Periconiaceae, showing the phylogenetic position of Periconia delonicis (MFLUCC 20–0235) and P. cortaderiae (MFLUCC 20–0236). ML bootstrap supports (≥ 60%) and Bayesian posterior probabilities (≥ 0.95 BYPP) are given above the branches as ML/BYPP. The tree is rooted with Helminthosporium dalbergiae (MAFF 243853) and Massarina cisti (CBS 266.62). Strains generated in this study are indicated in red bold. Ex–type strains are indicated in black bold. The scale bar 0.02 represents the expected number of nucleotide substitutions per site.
Analysis 2: Torulaceae
The best scoring RAxML tree (Fig. 2) has a final ML optimization likelihood value of – 19754.05. The matrix had 1189 distinct alignment patterns, with 31.37% of undetermined characters or gaps. Estimated base frequencies were as follows; A = 0.241559, C = 0.263242, G = 0.273563, T = 0.221637; substitution rates AC = 1.375308, AG = 2.974871, AT = 1.345285, CG = 0.922655, CT = 6.841524, GT = 1.000000; proportion of invariable sites I = 0.486989; gamma distribution shape parameter α = 0.482115. Bayesian posterior probabilities (BYPP) from MCMC were evaluated with a final average standard deviation of split frequencies was 0.005. All the phylogenetic trees (ML & BI) were similar in topology and no considerable difference at the generic level and similar with the phylogenetic analyses of Li et al.(2017, 2020), Su et al. (2018) and Hyde et al. (2020a). Our isolate (MFLUCC 20–0237) formed a clade with Torula chromolaenae (KUMCC 16–0036) with high support (ML = 100%, BYPP = 1.00), and clustered with T. breviconidiophora (KUMCC 18–0130) and T. mackenziei (MFLUCC 13-0839). The MFLUCC 20–0238 strain clustered with T. fici (CBS 595.96, KUMCC 15–0428, KUMCC 16–0038) with moderate support in ML analysis (ML = 80%) and not significant support in BI analysis and has a close relationship with T. hydei (KUMCC 16–0037; ML 98%, BYPP = 1.00). The MFLUCC 20–0239 strain clustered with T. masonii (CBS 245.57, DLUCC 0588, KUMCC 16–0033) with high support (ML = 100%, BYPP = 1.00), and also close to T. acaciae (CPC 29737). We therefore identify MFLUCC 20–0237 as T. chromolaenae, MFLUCC 20–0238 as T. fici and MFLUCC 20–0239 as T. masonii, respectively.

Figure 2.
Maximum likelihood tree (RAxML) revealed by an analysis of a concatenated SSU, LSU, ITS, TEF and RPB2 sequence dataset of the species in Torulaceae, showing the phylogenetic position of Torula chromolaenae (MFLUCC 20–0237), T. fici (MFLUCC 20–0238) and T. masonii (MFLUCC 20–0239). ML bootstrap supports (≥ 60%) and Bayesian posterior probabilities (≥ 0.95 BYPP) are given above the branches as ML/BYPP. The tree is rooted with Roussoella nitidula (MFLUCC 11–0182), R. scabrispora (MFLUCC 11–0624) and Roussoellopsis tosaensis (KT 1659). Strains generated in this study are indicated in red bold. Ex–type strains are indicated in black bold. The scale bar 0.04 represents the expected number of nucleotide substitutions per site.
Taxonomy
-
Periconia delonicisJayasiri, E.B.G. Jones & K.D. Hyde, in Jayasiri et al., Mycosphere 10(1): 9 (2019) Fig. 3

Figure 3.
Periconia delonicis (MFLU 20-0696). a-c Conidiophores bearing conidia on host. d-f Conidia and conidiophores. g, h Conidiogenous cells bearing conidia. i Base of the conidiophore. j-s Mature and immature conidia. t Colonies on PDA after 14 days. Scale bars: a, b = 500 μm, c, d = 100 μm, e, f, i = 20 μm, g, h = 10 μm, j-s = 5 μm.
Index Fungorum number: IF555562; Facesoffungi number: FoF 05268
Saprobic on a dead leaf of Musa sp. Sexual morph: Undetermined. Asexual morph: hyphomycetous. Conidiophores 320-400 × 8-12 μm (x = 365 × 9.5 μm, n = 10) macronematous, rarely micronematous. Macronematous conidiophores and conidia resembled a stipe and a globular head. Stipe of the Conidiophores unbranched, straight or flexuous from the middle, septate, pale to dark brown, often appearing black, smooth, globular heads shining by reflected light. Conidiogenous cells 4-7.5 × 3.4-7.4 μm (x = 5.5 × 5.3 μm, n = 15) monoblastic or polyblastic, discrete on the stipe, determinate, ellipsoidal, pale brown to brown. Conidia 4-8 × 4-6 μm (x = 5.6 × 5.4 μm, n =15), catenate, in chains, arising at one or more points on the curved surface of the conidiogenous cell, simple, usually spherical or subspherical, pale to dark brown, smooth to minutely veruculose, aseptate.
Culture characteristics – Conidia germinated on PDA within 48 hrs, reaching 40 mm diam. in 2 weeks at 25℃. Colonies on PDA with sparse, pinkish white mycelia on the surface, circular and flattened. Surface is smooth, with small, brown granular–like, powdery masses at maturity. The reverse of the colony is dark brown and yellow in the center with a white margin. Conidia and conidiophores are not observed in mature colonies.
Material examined – THAILAND, Chiang Mai Province, Mae Taeng District, on a dead leaf of Musa sp. (Musaceae), 22 September 2018, B.C. Samarakoon, BNS012 (MFLU 20–0696), living culture MFLUCC 20–0235.
Known hosts & distribution – on pods of Delonix regia (Fabaceae, Dicotyledon) from Thailand (Jayasiri et al. 2019); on dead leaf of Musa sp. (Musaceae, Monocotyledon) from Thailand (this study).
Notes – Based on BLASTn search results of SSU, LSU, ITS, TEF sequence data, our strain (MFLUCC 20-0235) showed high identity to the taxa in GenBank as follows; SSU = 99.75% similarity to Periconia palmicola (MFLUCC 14-0400), LSU = 99.88% similarity to P. delonicis (MFLUCC 17-2584), ITS = 99.20% similarity to P. palmicola (MFLUCC 14-0400). Multi–loci phylogenetic analysis (Fig. 1) showed that the new strain MFLUCC 20–0235 forms a clade together with P. palmicola (MFLUCC 14-0400) and P. verrucosa (MFLUCC 17-2158) with high statistical support (ML = 98%, BYPP = 1.00).
Our strain (MFLUCC 20–0235) shares similar morphology to the type of Periconia delonicis in having macronematous, unbranched conidiophores, with monoblastic, terminal conidiogenous cells and brown, globose to subglobose, aseptate, veruculose conidia (Jayasiri et al. 2019). Our strain (MFLUCC 20-0235) also shares similar size range of conidiophores (320-400 × 8-12 μm vs. 360-420 × 8-12 μm) and conidia (4-8 × 4-6 μm vs. 5.5-7 μm diam.). Based on recommendations by Jeewon & Hyde (2016), we also compare the nucleotide bases of TEF region for our new strain and the type strain of P. delonicis. MFLUCC 20-0235 differs from P. delonicis (MFLUCC 17-2584) in 5/746 bp (0.67%).
In our phylogenetic analyses, MFLUCC 20-0235 and ex–type stain of Periconia delonicis (MFLUCC 17-2584) showed a close phylogenetic affinity to P. palmicola (MFLUCC 14-0400) and P. verrucosa (MFLUCC 17-2158). The conidiophores, conidiogenous cells and the conidia of MFLUCC 20-0235 shares similar morphology with the holotype illustration of P. palmicola in Hyde et al. (2020a) (i.e. dark brown to black conidiophores, hyaline conidiogenous cells, subglobose to globose conidia). However, P. palmicola differs from MFLUCC 20-0235 in having comparatively short conidiophores (151–188 × 5.6–8 μm vs. 320-400 × 8-12 μm) which were branched at apex. The conidiophores of MFLUCC 20-0235 are unbranched and comparatively long with respect to P. palmicola. A nucleotide base pair comparison of TEF region showed that MFLUCC 20-0235 differs from P. palmicola (MFLUCC 14-0400) in 4/746 (0.53%). MFLUCC 20-0235 also has similar morphology to P. verrucosa (MFLUCC 17-2158) but differs in having longer conidiophores (320-400 × 8-12 μm vs. 170–296 × 10–12 μm) and smaller conidia (4-8 × 4-6 μm. vs. 7–15 μm diam.) (Phukhamsakda et al. 2020). A nucleotide base comparison of ITS and TEF regions showed that MFLUCC 20-0235 differs from P. verrucosa (MFLUCC 17-2158) in 7/501 bp (1.39%) of ITS and 4/746 bp (0.53%) of TEF. Based on morphological comparison with the types of P. delonicis, P. palmicola and P. verrucosa, a nucleotide base comparison of ITS and TEF regions and phylogenetic evidence, we thus identify our new collection as P. delonicis. In this study, we report P. delonicis on Musa sp. (Musaceae, monocotyledon) for the first time.
Periconia cortaderiaeThambugala & K.D. Hyde, in Thambugala et al., Mycosphere 8(4): 734 (2017) Fig. 4
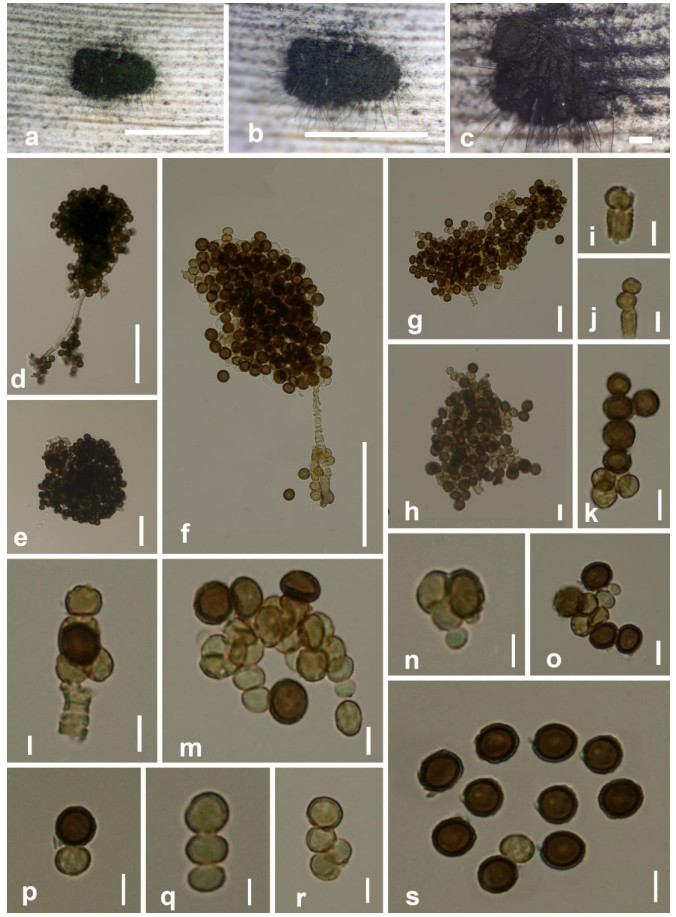

Figure 4.
Periconia cortaderiae (MFLU 20-0697). a-c Colonies on host substrate. d, f Conidiophores bearing conidia. e, g, h Conidial masses. i, j, m-o Conidiogenesis from terminal mother cells. l Monoblastic, annellidic conidiogenous cells bearing conidial chains. k, p, q, r Conidial chains. s Conidia. Scale bars: a = 3 mm, b = 3.5 mm, c = 50 μm, d, f = 50 μm, e, g = 20 μm, h-s = 5 μm.
Index Fungorum number: IF553165; Facesoffungi number: FoF 03226
Saprobic on a dead leaf of Musa sp. Sexual morph: Undetermined. Asexual morph: hyphomycetous. Colonies on host effuse, powdery, gregarious, with a black, conidial masses on the host. Mycelium composed of cottony, branched, hyphae forming dark clusters with conidia scattered on the host surface. Conidiophores 40–120 × 1-6 μm (x = 58.5 × 3.5 μm, n = 15), macronematous, mononematous, single or rarely 2–3 together, erect, thick–walled, brown to dark brown, septate, rough, 4–5 μm wide at base, and 1–2 μm wide at apex; base shoe–shaped, distinct. Conidiogenous cells 2.5–4.5 μm × 2.5–3.5 μm (x = 3.5 × 2.8 μm, n = 10), annellidic, monoblastic, discrete on stipe, percurrent proliferations present as scars at the apex of conidiophore. Conidia 4–7.6 × 4–6.5 μm (x = 6.5 × 5.9 μm, n = 40), catenate, globose, one–celled, hyaline to pale brown when immature, becoming brown to dark brown, smooth or minutely verruculose.
Culture characteristics – Conidia germinating on PDA within 48 hrs. Colonies growing on MEA, reaching a diameter of 20 mm after 14 days at 25℃, flat when immature, raised at maturity with unevenly distributed radial furrows or linear marks, surface is smooth at immature stage and notably rough at maturity with crenulate to crenate margin. Colony is initially white, moderately dense and completely black at maturity with the sporulation, reverse white to black.
Material examined – THAILAND, Nan Province, Nai Wiang, on a dead leaf of Musa sp. (Musaceae), 1 March 2019, B.C. Samarakoon, BNS100 (MFLU 20-0697), living culture MFLUCC 20-0236.
Known hosts & distribution – on Cortaderia sp. (Poaceae, Monocotyledon) from Thailand (Thambugala et al. 2017); on Caragana arborescens (Fabaceae, Dicotyledon) from Yunnan, China (Phookamsak et al. 2019); on Musa sp. (Musaceae, Monocotyledon) from Thailand (this study).
Notes – Based on BLASTn search results of SSU, LSU, ITS sequence data, our strain (MFLUCC 20-0236) showed high identity to the taxa in GenBank as follows; SSU = 99.76%, LSU = 99.88%, ITS = 99.80% similarities to Periconia cortaderiae (MFLUCC 15-0457). The morphology of our strain is similar to the holotype of P. cortaderiae (Thambugala et al. 2017), except the length of the conidiophores. Our strain has short conidiophores with respect to the holotype (40–120 × 1-6 μm vs. 400–800 × 4–9.4 μm). A nucleotide base comparison of ITS and TEF regions showed that MFLUCC 20-0236 differs from P. cortaderiae (MFLUCC 15-0457) in 1/493 bp (0.2%) of ITS and 1/829 bp (0.12%) of TEF. In addition, our MFLUCC 20-0236 strain differs from P. cortaderiae (MFLUCC 15-0451) in 2/493 bp (0.4%) of ITS and 2/872 bp (0.2%) of TEF. Therefore, we identify our new collection as P. cortaderiae, and this is reported from Musa sp. (monocotyledon) from Thailand for the first time.
Torula chromolaenaeJun F. Li, Phook., Mapook & K.D. Hyde, in Li et al., Mycol. Progr. 16(4): 454 (2017) Fig. 5

Figure 5.
Torula chromolaenae (MFLU 20–0698). a-c Colonies on leaf vein of Musa sp. d, e Conidia arranged in multi planes. f Conidiophore and conidiogenous cell. g-p Conidia and the formation of immature conidia. q Colonies on PDA after 21 days. Scale bars a = 1000 μm, b = 500 μm, c = 50 μm, d-h, k, o, p = 10 μm, l-n, i, j = 5 μm.
Index Fungorum number: IF819536; Facesoffungi number: FoF 02713
Saprobic on a dead leaf vein of Musa sp. (Musaceae). Sexual morph: Undetermined. Asexual morph: hyphomycetous. Colonies effuse, black, powdery, thread–like on host. Mycelium slightly immersed, septate, unbranched, smooth, pale brown hyphae. Conidiophores 2–5 × 2–4 μm (x = 3.8 × 3.3 μm, n = 10), micronematous or semi–macronematous, unbranched, straight or flexuous, subhyaline or pale brown, smooth or minutely verruculose. Conidiogenous cells 2–6 × 2–4.5 μm (x = 4.5 × 3.7 μm, n =10), polyblastic or sometimes monoblastic, integrated, terminal, discrete, determinate, usually spherical, smooth, distal fertile part thin–walled, subhyaline to pale brown, proximal sterile part dark brown, thick–walled, produced conidia in multiple planes. Conidia 10–15 × 5–7 μm (x = 11.4 × 6.2 μm, n = 40) dry, in simple or branched chains arising from the surface of the upper half of the characteristic conidiogenous cells, cylindrical with rounded ends, ellipsoidal or subspherical, brown or dark brown, minutely verruculose, 1–3 transverse septa, usually strongly constricted at the septa; conidial chains arranged in multiple planes.
Culture characteristics – Conidia germinating on PDA within 18 hrs and germ tubes produced from the tip cell. Colonies growing on PDA, reaching 50 mm diam. in 14 days at 25℃. Mycelium partly immersed to superficial, slightly effuse, and hairy, with dentate margin, pale pink at periphery golden brown in the middle with whitish hairy mycelial clumps. Sporulation was not observed in mature cultures.
Material examined – THAILAND, Chiang Mai Province, Mae Taeng District, on a dead leaf vein of Musa sp. (Musaceae), 15 February 2019, B.C. Samarakoon, BNS083 (MFLU 20-0698), living culture MFLUCC 20-0237.
Known hosts & distribution – on Chromolaena odorata (Asteraceae, Dicotyledon) from Thailand (Li et al. 2017, Mapook et al. 2020); on Clematis fulvicoma, (Ranunculaceae, Dicotyledon) from Thailand (Phukhamsakda et al. 2020); on Pandanus tectorius (Pandanaceae, Monocotyledon) from Yunnan, China (Tibpromma et al. 2018); on herbaceous litter (Dicotyledon) from Yunnan, China (Hyde et al. 2020a); Musa sp. (Monocotyledon) from Thailand (this study).
Notes – The BLASTn search results of SSU, LSU, ITS and TEF sequence data, indicated that our strain (MFLUCC 20-0237), showed a high identity to Torula chromolaenae (KUMCC 16–0036) as follows; SSU = 100.00%, LSU = 100.00%, ITS = 100.00%, TEF = 99.5% similarities. Morphological comparison with the type specimen of T. chromolaenae showed that our new collection (MFLU 20-0698/ MFLUCC 20-0237) is typical to T. chromolaenae in having brown or dark brown, minutely verruculose, 1–3–septate conidia. However, our collection (MFLU 20-0698) has slightly smaller conidiophores (2–5 × 2–4 μm vs. 5–6.3 × 3.5–4.6 μm) and conidia (10–15 × 5–7 μm vs. 2.1–16.5 × (3.6–) 4.1–5 μm) with respect to Li et al. (2017). A nucleotide base comparison of ITS, TEF and RPB2 regions also showed that MFLUCC 20–0237 is conspecific with T. chromolaenae (KUMCC 16–0036) (0/502 bp of ITS, 0/787 bp of TEF, and 0/817 bp of RPB2). We thus identify our new collection (MFLU 20–0698) as T. chromolaenae. Previously, T. chromolaenae was reported as a saprobe on dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous hosts from China and Thailand, indicating that the species is not specific on hosts and normally found in tropical region.
Torula ficiCrous [as 'ficus'], in Crous et al., IMA Fungus 6(1): 192 (2015) Fig. 6

Figure 6.
Torula fici (MFLU 20-0699). a-c Colonies on dead leaf of Musa sp. d-n Conidiogenesis. o, p Conidial masses. q Conidia (in chain). r-u Disposed conidia. v Colonies on PDA after 28 days. Scale bars: a = 500 μm, b = 100 μm, c = 20 μm, d-u = 5 μm.
Index Fungorum number: IF816154; Facesoffungi number: FoF 02712
Saprobic on dead leaf vein of Musa sp. (Musaceae). Sexual morph: Undetermined. Asexual morph: hyphomycetous. Colonies superficial, black, appearing as powdery masses on the host. Mycelium slightly immersed, septate, smooth, pale brown. Conidiophores 1–6 × 1.5–3 μm (x = 4.8 × 1.8 μm, n = 10), micronematous or semi–macronematous, unbranched, straight or slightly flexuous, subhyaline or pale grayish brown, verruculose. Conidiogenous cells 3.5–4 × 2.5–3.5 μm (x = 3.2 × 2.7 μm, n = 10) polyblastic or sometimes monoblastic, terminal, discrete, determinate, brown to dark brown, usually spherical, thin–walled, veruculose, having rough distal fertile part and a notably thick–walled, proximal sterile part. Base of sterile part of the conidiogenous cells that arise from mycelium is notably flat. Conidia (4–) 10–25(–75) × 3.5–4.5 μm (x = 24.8 × 3.8 μm, n = 40) dry, in simple or branched chains arising from the surface of the upper half of the characteristic conidiogenous cells, cylindrical with rounded ends, ellipsoidal or subspherical, brown or dark brown, notably verruculose, 1–3 transverse septa, slightly constricted at the septa, immature conidia hyaline to subhyaline, comparatively thin–walled, mature conidia notably thick–walled.
Culture characteristics – Conidia germinating on PDA within 20 hrs and germ tubes produced from the tip cell. Colonies growing on PDA, reaching 50 mm diam. in 14 days at 25℃, mycelium partly immersed to superficial, slightly effuse, hairy, with dentate to irregular margin, pinkish white.
Material examined – CHINA, Yunnan, Xishuangbanna, on a dead leaf vein of Musa sp. (Musaceae), 20 December 2018, D.N Wanasinghe, BNSWN5 (MFLU 20–0699), living culture MFLUCC 20–0238.
Known hosts & distribution – on Chromolaena odorata (Asteraceae, Dicotyledon) from Thailand (Li et al. 2017, Mapook et al. 2020); on Ficus religiosa (Moraceae, Dicotyledon) from Cuba (Crous et al. 2015); on Garcinia sp. (Clusiaceae, Dicotyledon) from Thailand (Jayasiri et al. 2019); on Magnolia grandiflora (Magnoliaceae, Dicotyledon) from Yunnan, China (Jayasiri et al. 2019); on Olea europaea (Oleaceae, Dicotyledon) from South Africa (Spies et al. 2020); on Pandanus sp. (Pandanaceae, Monocotyledon) from Thailand (Tibpromma et al. 2018); on submerged decaying wood in Yunnan, China (Su et al. 2018); on Musa sp. (Musaceae, Monocotyledon) from Yunnan, China (this study).
Notes – The BLASTn search results of SSU, LSU, ITS and TEF sequence data, indicated that our strain (MFLUCC 20–0238), has a high identity to Torula fici (KUMCC 16–0038) as follows; SSU = 99.88%, LSU = 100.00%, ITS = 98.99%, TEF = 98.53% similarities. Our new collection (MFLU 20–0699) is morphologically similar to T. fici in having short conidiophores, or reduced to conidiogenous cells, mono– to polyblastic, brown, verruculose conidiogenous cells and brown or dark brown, 1–3–septate conidia (Crous et al. 2015). However, our collection has slightly smaller conidiogenous cells (3.5–4 × 2.5–3.5 μm vs. (5–) 6(–8) × 5(–7) μm) and overlapped size of conidia (4–16 × 3.5–4.5 μm vs. (12–) 13–14(–15) (–19) × 5(–6) μm; Crous et al. 2015). A nucleotide base comparison of ITS and TEF regions also showed that MFLUCC 20–0238 differs from T. fici (CBS 595.96, type strain) in 7/467 bp (1.49%) of ITS and 16/776 bp (2.06%) of TEF. In addition, our strain MFLUCC 20–0238 differs from the strains KUMCC 15–0428 and KUMCC 16–0038 in 3/429 bp (0.69%) and 5/494 bp (1.01%) of ITS, and 15/808 bp (1.8%) and 11/813 bp (1.35%) of TEF, respectively. Nevertheless, our new strain (MFLUCC 20–0238) shows a high variation of TEF sequence with the type strain of T. fici (CBS 595.96; 2.06%) and strain KUMCC 15–0428 (1.8%). Based on current phylogenetic results (Fig. 2), we thus identify our new collection (MFLU 20–0699/ MFLUCC 20–0238) as T. fici. The conspecific of these strains is needed to be clarified in further studies. In this study, we report T. fici on Musa sp. (Monocotyledon) from Yunnan, China for the first time.
Torula masoniiCrous, in Crous et al., IMA Fungus 6(1): 195 (2015) Fig. 7
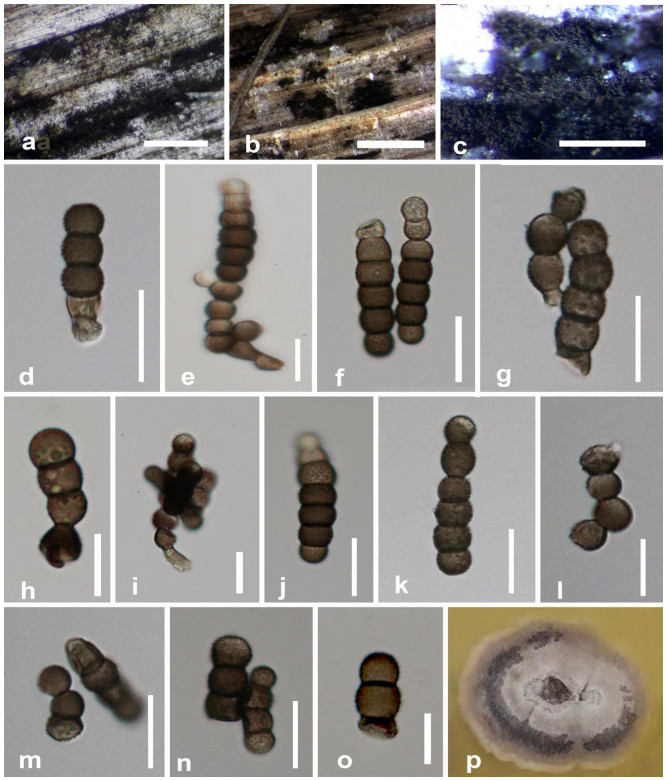

Figure 7.
Torula masonii (MFLU 20–0700). a Colonies on dead leaf of Musa sp. b, c Masses of conidia on host surface. d–h, j–o Conidia. i Conidiophore, conidiogenous cell and budding of conidia. p Colonies on PDA after 28 days. Scale bars: a = 50 μm, b = 500 μm, c = 1000 μm, d, f–o = 10 μm, e = 5 μm.
Index Fungorum number: IF812806; Facesoffungi number: FoF 02711
Saprobic on a dead leaf of Musa sp. (Musaceae). Sexual morph: Undetermined. Asexual morph: hyphomycetous. Colonies superficial, appearing as black, powdery masses on the host. Mycelium slightly immersed, septate, smooth, grayish brown. Conidiophores 3–6.5 × 4–5 μm (x = 5.4 × 4.3 μm, n = 10), micronematous or semi–macronematous, unbranched, straight or slightly flexuous, pale grayish brown to brown, subcylindrical, septate, or reduced to conidiogenous cells. Conidiogenous cells 5.5–6.5 × 4.5–6 μm (x = 6.3 × 5.3 μm, n = 10) polyblastic or sometimes monoblastic, terminal, discrete, determinate, grayish brown to dark brown, darker than the conidiophores or conidia, spherical, cup–shaped, or inverted cup–shaped, thin–walled, smooth, pale brown of distal fertile part and subhyaline or pale grayish brown of proximal sterile part. Conidia 8–25 × 4–6.5 μm (x = 18.3 × 5.6 μm, n = 40), dry, in simple or branched chains arising from the surface of the upper half of the characteristic conidiogenous cells, cylindrical with rounded ends, ellipsoidal or subspherical in each cell, grayish brown to dark brown, (2–) 3–5(–12) transverse septa, notably constricted at the septa, verruculose, arranged in different planes with respect to the main axis.
Culture characteristics – Conidia germinating on PDA within 14 hrs and germ tubes produced from the apex. Colonies growing on PDA, reaching 50 mm diam. in 15 days at 25℃, mycelium partly immersed to superficial, slightly effuse and hairy. Colonies medium dense, circular, flattened, slightly raise, surface smooth, with edge entire to sinuate margin, hairy at the center and margin, with dense, floccose to cottony at the middle, three distinct colour zones present in the culture. Periphery pinkish white, middle gray and grayish white next.
Material examined – Taiwan (China), Alishan, on a dead leaf of Musa sp. (Musaceae), 20 September 2018, D.S. Tennakoon, BNS023 (MFLU 20–0700), living culture MFLUCC 20–0239.
Known host & distribution – on Brassica sp. (Brassicaceae, Dicotyledon) from United Kingdom (Crous et al. 2015); Iris germanica (Iridaceae, Monocotyledon) from Italy (Li et al. 2017); on submerged decaying wood (Dicotyledon) from Yunnan, China (Su et al. 2018); on Musa sp. (Musaceae, Monocotyledon) from Taiwan (China, this study).
Notes – The BLASTn search results of SSU, LSU, ITS, TEF and RPB2 sequence data, showed that our strain (MFLUCC 20-0239), is similar to taxa in GenBank as follows; SSU = 99.87% similarity to Torula chromolaenae (MFLUCC 17-1514), LSU = 100.00% similarity to T. masonii (CBS 245.57), ITS = 99.88% similarity to T. masonii (KUMCC 16–0033), TEF = 100% and RPB2 = 99.75% similarities to T. masonii (DLUCC 0588). Comparing with the type specimen, our new isolate (MFLU 20–0700) is morphologically similar to T. masonii; however, the type of T. masonii has slightly larger size of conidiophores and conidia. The conidia of the type of T. masonii are predominantly 6–septate, but also vary in conidial septation from 2– to 12–septate (Crous et al. 2015), whereas the conidia of our new isolate are predominantly 3–5–sepate, occasionally 2– to 12–septate. A nucleotide base pair comparison of ITS showed that our strain (MFLUCC 20-0239) differs from other T. masonii strains (CBS 245.57, DLUCC 0588 and KUMCC 16–0033) in 8/509 (1.57%), 2/441 (0.45%) and 1/508 (0.19%). Our strain MFLUCC 20-0239 also differs from the strains DLUCC 0588 and KUMCC 16–0033 in 2/798 bp (0.25%) and 2/830 (0.34%) of RPB2 but has no different nucleotide base in TEF gene region. We identify our new isolate as T. masonii, based on phylogenetic evidence, although there is more than 1.5% variation in the ITS DNA regions as compared to the type strain (CBS 245.57). We document T. masonii on Musa sp. for the first time. This is the first geographical record of T. masonii from Taiwan (China).
Phylogenetic analyses
-
Many Torula and Periconia species have been reported on Musa spp. worldwide. Torula herbarum has been reported on Musa spp. from Papua New Guinea, Somalia, Taiwan (China), Thailand, and Zambia (Castellani & Ciferri 1937, Riley 1956, Matsushima 1971, 1980, Photita et al. 2001a, 2003b). Periconia byssoides (Venezuela, Cuba, and Somalia) (Matsushima 1971, Urtiaga 1986, Delgado–Rodriguez & Mena–Portales 2004), P. digitata (Thailand, Malaysia) (Williams & Liu 1976, Photita et al. 2001b), P. lateralis (Thailand) (Photita et al. 2001b) and P. minutissima (Ghana) (Hughes 1953) have also been reported on Musa spp. The identification of the latter taxa on Musa spp. was solely based on morphology and molecular data were not integrated. Therefore, more taxon sampling of saprobic and endophytic fungi on Musa spp. should be carried out by integrating morpho–molecular data in taxonomy.
Some Periconia species have been reported as plant pathogens (i.e., P. cicirnata, P. digitata and P. macrospinosa) on leaves, roots and stems of economically important crops such as maize, sorghum and pointed gourd (Stojkov et al. 1996, Sarkar et al. 2019). In addition, P. keratitis has been reported as a human pathogen from India (Gunasekaran et al. 2020). Periconia produce some economically important bioactive compounds with antimicrobial activities (Kim et al. 2004, Bhilabutra et al. 2007, Hongsanan et al. 2020). It is interesting to note that P. delonicis and P. cortaderiae may also produce bioactive compounds which were discovered from taxa in the same genus. In addition, some species of Torula also produce chemically active compounds (i.e., Dichlorinated Aromatic Lactones and erythritol) which have a wide range of applications in the food industry (Chunyu et al. 2018). Mapook et al. (2020) also reported that T. chromolaenae, T. fici and T. polyseptata showed antimicrobial activity against Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli and Mucor plumbeus on their preliminary screening of antimicrobial activity of fungi on Chromolaena odorata. Therefore, it will be interesting to know whether T. chromolaenae and T. fici from Musa spp. will have the same biological ability.
Recent taxonomic studies integrated DNA sequence data on the introduction of novel taxa in Periconia and Torula (Crous et al. 2015, Su et al. 2016, 2018, Li et al. 2017, 2020, Liu et al. 2017, Jayasiri et al. 2019, Hyde et al. 2020a, Mapook et al. 2020, Phukhamsakda et al. 2020). Protein– coding genes revealed to be good phylogenetic markers in species delineation of Periconia and Torula (Su et al. 2016, 2018, Li et al. 2017, 2020, Jayasiri et al. 2019, Hyde et al. 2020a, Mapook et al. 2020, Phukhamsakda et al. 2020). Corresponding protein–coding sequences (RPB2 and TEF) with ribosomal DNA (SSU, LSU and ITS) sequence dataset can provide well–resolved tree topologies for the taxa in Periconiaceae and Torulaceae. However, several taxa of Periconiaceae and Torulaceae lack protein–coding DNA sequences in GenBank. Therefore, many Periconia and Torula taxa need to be recollected so that valid sequence data are provided to GenBank for better taxonomic resolutions.
Phylogenetic tree of Periconiaceae (Fig. 1) showed that Periconia delonicis does not form a well–separated clade with P. palmicola (MFLUCC 14-0400) and P. verrucosa (MFLUCC 17-2158). The tree topology showed that they are conspecific, and this result is also supported by a nucleotide base comparison of ITS and TEF regions. However, P. delonicis is phylogenetically well–resolved and is distinct from P. verrucosa in Phukhamsakda et al. (2020), indicating that ITS and TEF regions are not good phylogenetic markers for some species in Periconiaceae. Periconia delonicis was not included in phylogenetic analyses of Periconiaceae when Hyde et al. (2020a) introduced P. palmicola as a new species. The conspecific of P. delonicis and P. palmicola is therefore questionable and should be reinvestigated in future studies.
Phylogenetic tree of Torulaceae (Fig. 2) showed that Torula chromolaenae, T. fici and T. masonii form well–resolved subclades within Torulaceae. However, the four strains (including type strain) of T. fici and T. masonii formed insignificantly separated branch lengths in this analysis and this phylogenetic result is also supported by Hongsanan et al. (2020), Hyde et al. (2020a), Li et al. (2020), Mapook et al. (2020) and Phukhamsakda et al. (2020). This may be the result of a high variation (> 1.5%) in the TEF region (see notes under T. fici and T. masonii). Further studies on the conspecific or complexity of these species are needed for their clarification based on the reliable protein coding genes.
Documentation of fungi from new hosts and geographical locations supports the accurate estimates and taxonomic establishments of fungal diversity and distribution. In addition, new occurrences of fungi from various hosts and habitats further provide insights to determine host jumping patterns, host shift speciation and the adaptations of fungi during their life cycle (Hyde et al. 2020c). Taxonomy and phylogeny of fungal pathogens on Musa spp. (i.e., Colletotrichum, Fusarium, Mycosphaerella, Neocordana and Phyllosticta) have been well–studied worldwide (Giatgong 1980, Wulandari et al. 2010, Churchill 2011, Guarnaccia et al. 2017, Marin–Felix et al. 2019, Maryani et al. 2019). The detailed taxonomic works on endophytic fungi in Musa spp. were previously conducted by Brown et al. (1998), Photita et al.(2001b, 2004), Zakaria & Aziz (2018) and Samarakoon et al. (2019). Still the saprobic fungal niches on Musa spp. remain unrevealed and many more taxa are yet to be discovered. Hence the morpho–molecular data of this study will be further useful in future taxonomic works of fungi.
This study is supported by Key Research Project "Agroforestry Systems for restoration and bio–industry technology development (grant no. 2017YFC0505101)". We also thank Biology Experimental Center, Germplasm Bank of Wild Species, Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences for providing the facilities of molecular laboratory. Binu C. Samarakoon is grateful to Danushka Tennakoon for collecting the specimens from Taiwan (China), Dr. Dhanushka N. Wanasinghe and Junfu Li for the valuable comments and suggestions on the morphological studies of Periconia and Torula. Rungtiwa Phookamsak thanks CAS President's International Fellowship Initiative (PIFI) for young staff (grant no. Y9215811Q1), the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) project code 31850410489 (grant no. Y81I982211) and Chiang Mai University for financial support. Samantha C. Karunarathna thanks CAS President's International Fellowship Initiative (PIFI) young staff under the grant number: 2020FYC0002 and the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) for funding this work under the project code 31851110759. Jianchu Xu thanks Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant no. QYZDY–SSW–SMC014) and the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences for supporting this research.
- This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 4.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
| BC Samarakoon, R Phookamsak, SC Karunarathna, R Jeewon, P Chomnunti, JC Xu, YJ Li. 2021. New host and geographic records of five pleosporalean hyphomycetes associated with Musa spp. (Banana). Studies in Fungi 6(1):92−115 doi: 10.5943/sif/6/1/5 |












