-
According to the 'Notice on the Administrative Measures for the Set-aside and Use of Enterprise Work Safety Expenses Issuance' (No. 136 [2022], Financial Resources), the enterprise's work safety expenses refers to the funds that the enterprise set-asides according to the prescribed standards and is charged in the cost (expense), which is specially used to improve and perfect the safety production conditions of the enterprise or project. Since the release of the policy on the set-aside and use of work safety expenses, it has played a positive role in ensuring the basic work of production safety and enhancing the emergency rescue capability of enterprises[1,2]. However, enterprises have many problems in the actual management process of work safety expenses, such as not having a thorough understanding of the relevant policies of work safety expenses, accounting treatment usually replacing accounting with statistics, and the lack of effective communication between the safety department and the financial department[3, 4]. To further standardize the set-aside and use of work safety expenses in enterprises and promote the establishment of a long-term mechanisms of work safety input, it is urgent to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the history, set-aside and use, supervision and management of work safety expenses.
-
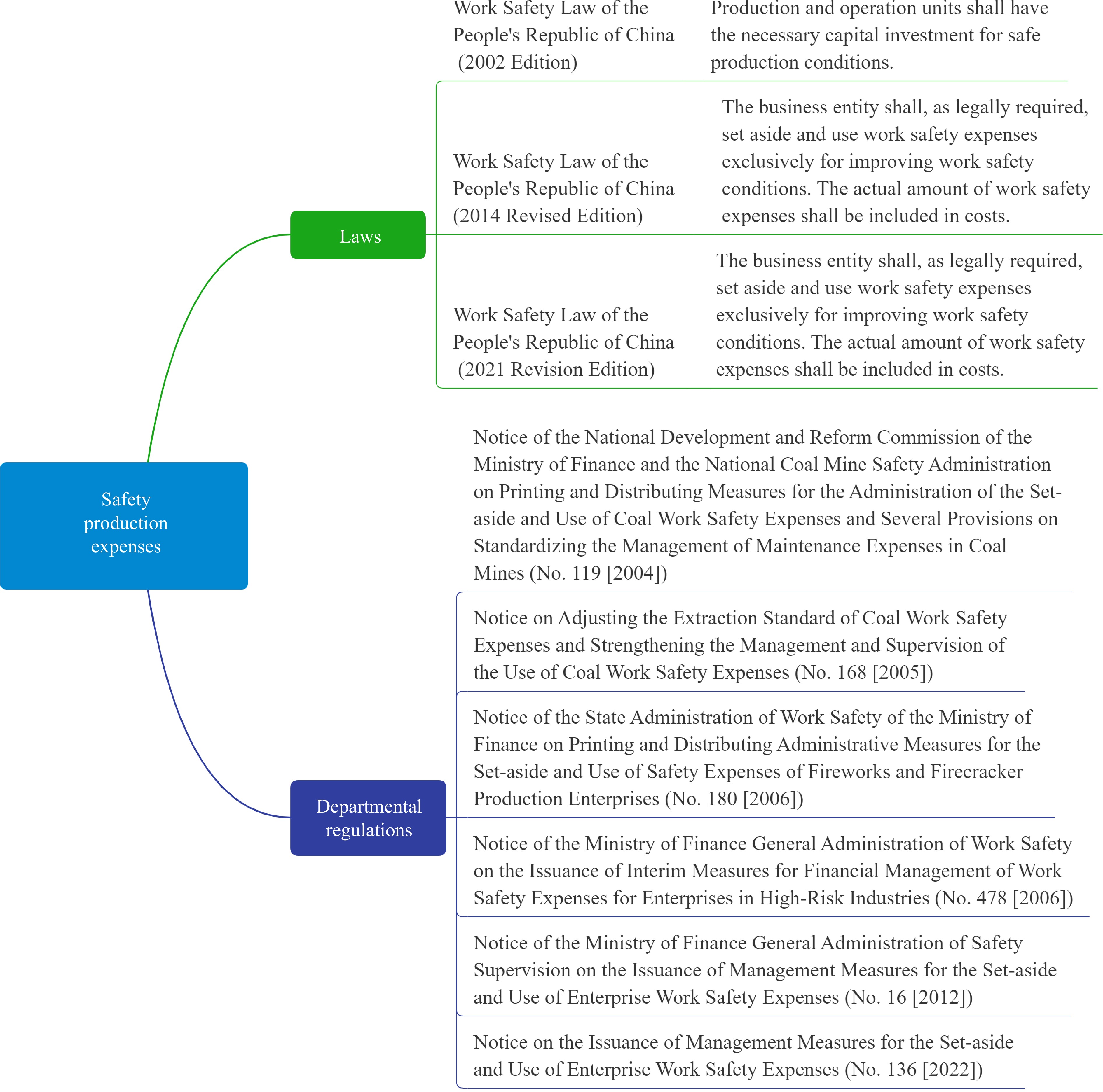
The earliest approximate definition of work safety expenses in enterprises comes from Article 18 of 'The Work Safety Law of the People's Republic of China' (Order No. 70 of the President of the People's Republic of China), which was first implemented on November 1st, 2002, namely: The investment of funds necessary for the conditions of production safety that a production or business operation unit should have shall be guaranteed by the decision-making body, the principal person in charge of the investor in the individual operation of the production or business operation unit, and it shall be liable for the consequences resulting from the insufficient investment of funds necessary for production safety. Later, 'the Decision of The State Council on Further Strengthening the Work of Safety Production' (No. 2 [2004]) proposed the establishment of a safety expense set-aside system for enterprises, requiring that the experience of mine safety expense set-aside should be learned, and a safety expense set-aside system should be gradually established for production enterprises in high-risk industries after the conditions are mature. And the set-aside of enterprise safety costs, according to the characteristics of the region and industry, to determine the set-aside standards, by the enterprise's set-aside, special account storage, special for safety production. At the same time, the relevant regulations on work safety expenses mostly involved coal production, fireworks and firecracker production and other industries with high risk. For example, 'Notice of the National Development and Reform Commission of the Ministry of Finance and the National Coal Mine Safety Administration on Printing and Distributing Measures for the Administration of the Set-aside and Use of Coal Production Safety Expenses and Several Provisions on Standardizing the Management of Maintenance and Testing Expenses in Coal Mines' (No. 119 [2004]) issued on 21 May 2004, 'Notice on Adjusting the Set-aside Standard of Coal Production Safety Expenses and Strengthening the Management and Supervision of the Use of Coal Production Safety Expenses' (No. 168 [2005])[5] issued on April 8th, 2005 , 'Notice of the State Administration of Work Safety of the Ministry of Finance on Printing and Distributing Administrative Measures for the Set-aside and Use of Safety Expenses of Fireworks and Firecracker Production Enterprises' (No. 180 [2006])[6], issued on March 24th, 2006. Until December 8th, 2006, the Ministry of Finance and the State Administration of Work Safety jointly issued 'The Interim Measures for the Financial Management of Work Safety Expenses of Enterprises in High-risk Industries'[7], in which enterprises in high-risk industries specifically refer to enterprises engaged in mining, construction, production of dangerous goods and road transportation and other economic organizations within the territory of the People's Republic of China. Making it the first departmental regulation of work safety expenses across multiple hazardous industries.
On July 19th, 2010, 'The Notice of The State Council on Further Strengthening the Work of Production Safety in Enterprises' (No. 23 [2010]) further clearly required strengthening the supervision and inspection of the set-aside and use of work safety expenses of enterprises in high-risk industries, and further improve the financial management system of work safety expenses of enterprises in high-risk industries. We will study raising the lower limit of work safety expenses and appropriately expanding their scope of application. In this context, the Ministry of Finance and the State Administration of Work Safety jointly formulated and issued the first departmental regulation applicable to the comprehensive management of work safety expenses in multiple industries − 'Administrative Measures for the Set-aside and Use of Work Safety Expenses in Enterprises' (No. 16 [2012]). The measures define the requirements on the set-aside standard, use, supervision and management of work safety expenses for enterprises and other economic organizations in coal production, mining of non-coal mines, construction engineering construction, production and storage of dangerous goods, transportation, production of fireworks and firecrackers, metallurgy, machinery manufacturing, development, production and test of weapons and equipment (including civil aviation and nuclear fuel)[8,9]. Subsequently, 'The Production Safety Law of the People's Republic of China' amended in 2014 stipulates from a legal level that relevant production and business units shall, in accordance with regulations, set-aside and use work safety expenses for the purpose of improving production safety conditions, and the work safety expenses shall be included in the cost according to the facts. On November 21st, 2022, the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Emergency Management revised the above measures, adding civil explosive products production and the power industry (enterprises), adjusting the scope of the transportation industry, metallurgy industry and machinery manufacturing industry (enterprises), including oil and natural gas set-aside enterprises, and adjusting the standards for drawing safety costs. The scope of security expenses is further expanded[10,11]. The relevant laws and regulations on work safety expenses of enterprises are shown in Fig. 1.
Set-aside of work safety expenses in developed countries
-
The Korean government has developed an Occupational Safety and Health Costs Act to ensure that companies receive a minimum safety management budget, the size of which depends on the size and type of project. Taking the construction industry as an example, the safety cost budget of general construction projects must be equal to or exceed 1.86% of the total material and labor costs. The regulation requires construction companies to spend more than half of their budget before completing 70% of construction projects[12]. The Occupational Safety and Health Organization (OSHA) in the United States forces employers to provide a fall protection system that can prevent falls when the working surface is more than 1.82 meters (6 feet) from the ground. The Korean government legislates on occupational safety and health costs in accordance with the law, and requires appropriate budgets for safety management activities. The amount of safety costs required is determined according to the type and scale of related construction projects. Specifically, the safety budget is part of the total labor and material costs. The setting of legal liability in foreign countries is generally strict. Even if the early laws and regulations are weak, they have been revised many times, and the punishment has been increased to a certain extent. In comparison, in addition to setting principles, China's safety production legal responsibility is not sufficient to combine with specific illegal acts, and there is still a widespread problem of insufficient punishment, which is difficult to effectively curb illegal and criminal acts. In recent years, many laws and regulations have gradually exceeded the maximum limit of 200,000 Chinese yuan. Therefore, in order to improve the legal system of production safety and establish a strong and efficient law enforcement system, it is urgent to set up a more scientific and rational punishment range.
Current situation and problems of work safety expense management
-
As work safety expenses belong to the enterprise operating cost expenditure item, the investment in work safety expenses is long-term, but there is no obvious immediate income. The extraction amount for some industries has been greatly improved compared with previous, which has a certain impact on the operating profit of the enterprise. Therefore, some enterprises, especially the owners of small and medium-sized enterprises, do not have enough understanding of this part of the investment, have limited understanding of the content of the policy, and treat the work safety expenses in a provincial manner. It has increased the difficulty of set-aside and use of work safety expenses, and it is inevitable that the behavior of not setting aside work safety expenses according to the regulations will occur. At the same time, the level of corporate financial management is uneven, increasing the difficulty of supervision. The lack of detailed rules for financial taxation and accounting has also created a regulatory gap. The lack of relevant laws and system construction has increased the difficulty of supervision, and there is also a lack of effective joint communication mechanisms between multiple departments.
Enterprises do not pay enough attention to the use of work safety expenses and the enthusiasm of enterprises in the process of participating in safety management is low. The state does not pay attention to the relevant supervision work, which leads to the failure of enterprises to meet the requirements in the level of safety production, resulting in accidents. Although the current construction sites and enterprises pay more attention to safety management and control, compared with some foreign fire protection industries, China's foundation in safety production is still relatively weak, and its production investment is still insufficient. At the macro level, the state formulates the enterprise work safety expenses extraction system in order to establish the consciousness of work safety expense management, and through the extraction of costs, it forces enterprises to improve their own safety production capacity and improve their financial security ability, so as to prevent and reduce the impact of safety production accidents on the production and operation of enterprises. However, from the perspective of enterprises, the goal of survival and development of enterprises is to obtain more benefits. In their own production process, some enterprises tend to reduce the probability of risk occurrence through safety production management mechanism and standardized operation process, rather than extracting part of the cost and increasing the production cost of enterprises. Moreover, the current cost extraction lacks incentives for enterprise development. After the enterprise extracts the cost, it does not see the return but increases the input in vain, and naturally lacks the motivation to set-aside these funds. In addition, the lack of regulatory systems for set-aside and use has also led to the status quo.
-
The set-aside of enterprise work safety expenses shall follow the principle of financing with regulations, that is, overall development and safety, the implementation of the main responsibility of enterprise safety input in accordance with the law, and the full set-aside of 12 kinds of enterprise by referring to the 'Measures for the Administration of the Set-aside and Use of Enterprise Work Safety Expenses'. The set-aside basis and set-aside time of work safety expenses of different types of enterprises are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Set-aside standard and time of work safety expenses of different types of enterprises.
No. Type of enterprise Set-aside basis Set-aside time Remarks 1 Coal production enterprises Output of raw coal mined for the month End of month 2 Non-coal mining enterprises Production of raw ore mined during the month End of month 3 Oil and gas exploitation enterprises Amount of oil and natural gas produced in the month End of month Onshore oil (gas) or offshore oil (gas) production enterprises Direct engineering cost in the cost of a project or project Monthly set-aside Drilling, geophysical exploration, logging, logging, down hole operations, oil construction, offshore engineering and other enterprises 4 Construction project construction enterprises Construction and installation cost End of month Calculated according to the progress of the project 5 Dangerous goods production and storage enterprises Operating income of the previous year Average withdrawals month by month Amount payable for the current year shall be determined using excess regressive 6 Transportation enterprise Operating income of the previous year Average withdrawals month by month Determine the amount payable for the current year 7 Metallurgical enterprise Operating income of the previous year Average withdrawals month by month Amount payable for the current year shall be determined using excess regression 8 Machinery manufacturing enterprise Operating income of the previous year Average withdrawals month by month Amount payable for the current year shall be determined using excess regressiion 9 Fireworks and firecracker production enterprises Operating income of the previous year Average withdrawals month by month Amount payable for the current year shall be determined using excess regression 10 Civil explosive products production enterprises Operating income of the previous year Average withdrawals month by month Amount payable for the current year shall be determined using excess regression 11 Weapon equipment development, production and testing enterprises Military sales revenue for the previous year Average withdrawals month by month Amount payable for the current year shall be determined using excess regression 12 Electric power production and supply enterprises Operating income of the previous year Average withdrawals month by month Amount payable for the current year shall be determined using excess regression Taking dangerous goods production and storage enterprises[10,11] as an example, the set-aside of work safety expenses is explained. According to the provisions of 'The Administrative Measures on the Set-aside and Use of Enterprise Work Safety Expenses', the production and storage enterprises of dangerous goods shall, based on of the operating income of the previous year, determine the amount payable for the current year in the way of excess regression, and make an average monthly set-aside. Among them, the business income of an enterprise includes the main business income and other business income. Main business income refers to the regular income generated by an enterprise's main business, such as the sales of products and semi-finished products of the manufacturing industry; Ticket income and catering income of the tourism service industry; Other business income refers to other business income except for the above main business income, such as sales of purchased commodities, real estate development income, consulting income, guaranteed income and other business income. For example, if the operating income of a dangerous goods production and storage enterprise in 2022 is 1.2 billion Chinese yuan, the amount payable in 2023 is 1000 × 0.045 + 9000 × 0.0225 + 90000 × 0.0055 + 20000 × 0.002 = 45 + 202.5 + 49.5 + 40 = 337 (ten thousand Chinese yuan), and the average monthly withdrawal amount is 337/12 = 28.08 (ten thousand Chinese yuan). In particular, for the production and storage enterprises of dangerous goods that are newly built and put into operation in less than one year, the safety production expenses of the current year shall be itemized according to the actual expenses. At the end of the year, the work safety expenses of the enterprise shall be deducted according to the operating income of the current year.
Use of work safety expenses
-
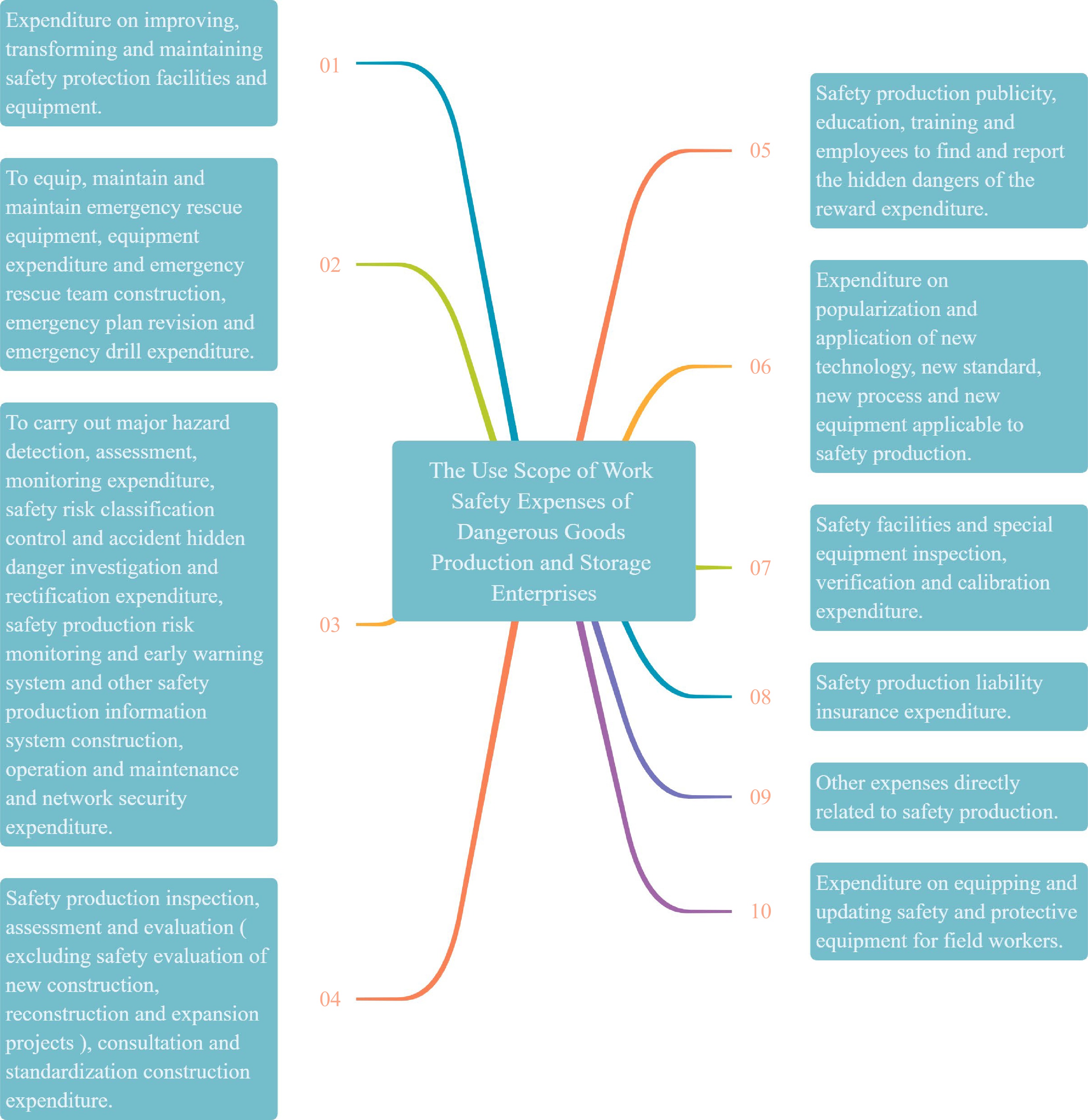
The use of work safety expenses of enterprises follows the principle of evidence-based expenditure, that is, according to the actual needs of production and operation, enterprises carry out special accounting from the cost (expense) of work safety expenses in accordance with the provisions, and refer to 'The Administrative Measures for the Set-aside and Use of Work Safety Expenses of Enterprises' within the scope of 12 kinds of expenses[13,14]. Taking the production and storage of dangerous goods as an example, the application scope of work safety expenses is shown in Fig. 2. Compared with 'The Administrative Measures on the Set-aside and Use of Work Safety Expenses in Enterprises' (No. 16 [2012]), the use of work safety expenses increases the construction of emergency rescue teams, major hazard detection, safety risk grading management, hidden trouble checking, construction of work safety information, and operation and maintenance, production safety liability insurance and employees' reward for finding and reporting safety hidden dangers, which are closely combined with the production safety status and needs of enterprises.
As the funds are directly used to improve the production safety conditions of enterprises, work safety expenses should not include the salaries of full-time safety management personnel, security guards, guards and other personnel, the cost of cold and heat protection items for employees, the fine imposed by the competent authorities on enterprises, work-related injury insurance, medical insurance, the cost of COVID-19 prevention and control, the prevention and treatment of occupational diseases, the cost of occupational health examination, and the operation cost of production equipment. The expenses of group personal accident insurance or individual accident insurance for enterprises engaged in high-altitude, high-pressure, flammable, explosive, highly toxic, radioactive, high-speed transportation, field, mine and other high-risk operations are directly included in the cost (expense) and are not included in the safety expenses.
If there is a certain amount of surplus in work safety expenses of the enterprise, it can be normalized according to Table 2. If the balance at the beginning of the month reaches three times or more of the amount accrued from the previous year, the set-aside of enterprise work safety expenses shall be suspended from the current month until the balance of enterprise work safety expenses is less than three times of the amount accrued from the previous year. If there is a deficit in the enterprise's work safety expenses (that is, the enterprise's work safety expenses and the balance at the beginning of the year are less than the actual annual expenses), the enterprise's work safety expenses shall be made up at the end of the year.
Table 2. Work safety expense balance processing.
No. Relationship between the amount withdrawn (x) and the amount used (y) Methods of handling work safety expenses 1 y < 0.6x 1) Information disclosure in accordance with regulations;
2) Before the end of April of the next year, in accordance with the territorial supervision authority, it shall submit a written explanation to the department responsible for supervision and administration of production safety under the people's government at or above the county level for deliberation by the board of directors, shareholders' meetings and other organs of the enterprise.2 0.6x ≤ y < x Carried forward to the next year. -
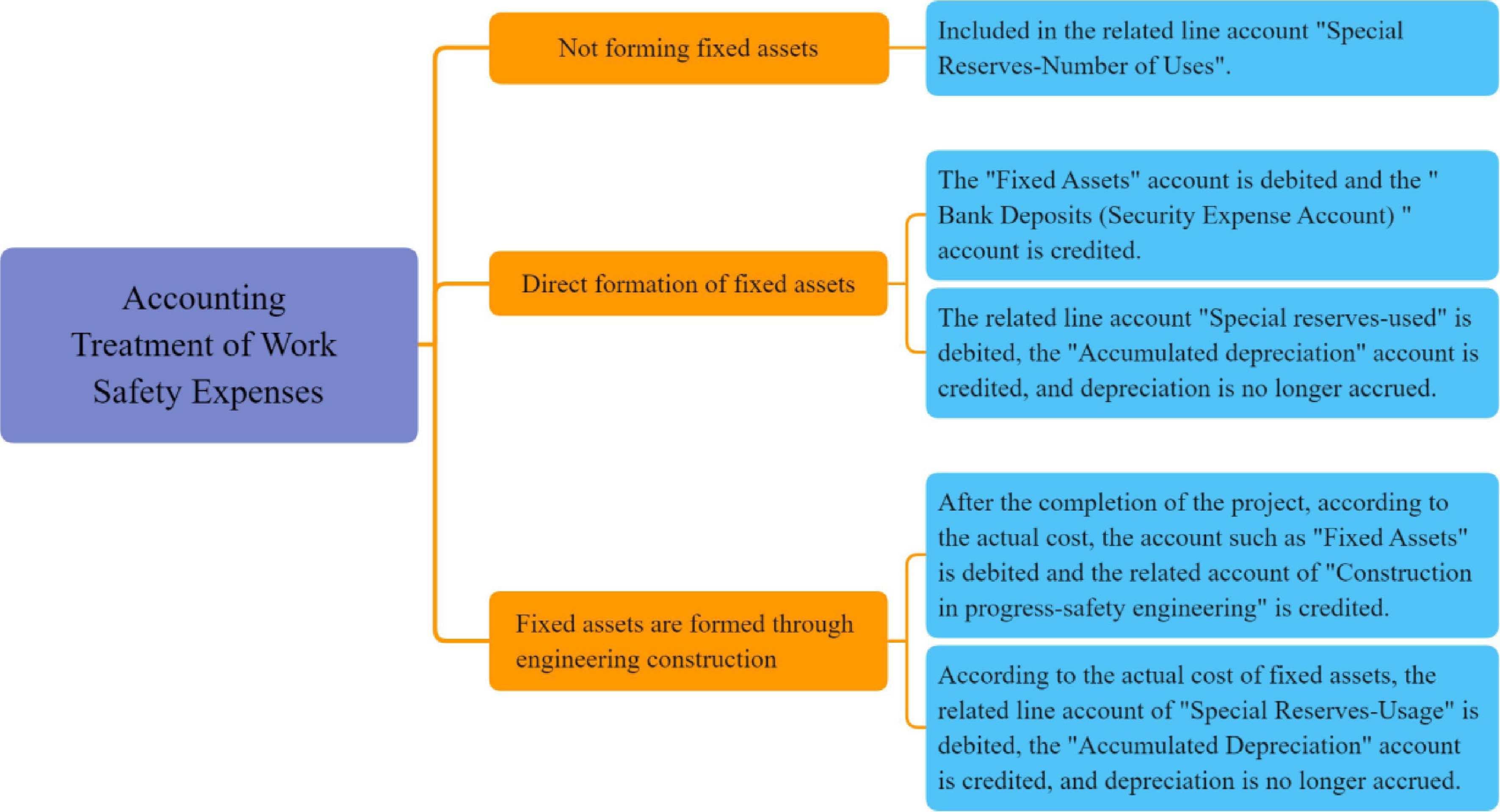
The accounting treatment of work safety expenses of enterprises shall conform to the provisions of the unified state accounting system. "The Ministry of Finance on the issuance of on the implementation of 'the Enterprise Accounting System' and related accounting standards related questions Answer (4)" (No. 3 [2004], Finance and Accounting) for the first coal production enterprises work safety expenses accounting treatment provisions, that is, debit 'manufacturing expenses (safety expenses)' account, credit 'long-term payable (safety expenses payable)' account, to calculate the set-aside, use and balance of work safety expenses. On August 21st, 2006, 'Jiangsu Provincial Department of Finance Jiangsu Provincial Work Safety Supervision Administration on Printing and Distributing the Enterprise Safety Expense Accounting Method Notice' (No. 46 [2006], Jiangsu Finance and Accounting) in the setting of accounting items requires that all kinds of enterprises in Jiangsu Province should set up a 'set-aside number' and 'use number' levels of accounts. For the coal production enterprises that need to use the safety expenses in accordance with the provisions of the state, continue to set 'ventilation equipment and discharge', 'gas monitoring and drainage system expenditure', 'coal and gas outburst prevention expenditure', 'fire prevention expenditure', 'water prevention expenditure', 'electromechanical equipment safety protection expenditure', 'power supply and distribution system safety protection expenditure', 'transportation (upgrading) system safety protection expenditure', 'dust proof system expenditure', 'ventilation equipment and discharge system expenditure' under the three-level accounting of 'usage number' and 'other production safety expenditures' (10 four-level subjects); According to the formation of fixed assets and the formation process of the provision of security costs of three accounting methods, and provides the main accounting items entry examples.
'The Notice of the Ministry of Finance on Issuing Accounting Standards for Enterprises No. 3' (No. 8 [2009], Finance and Accounting) has made the latest provisions on the accounting treatment of the set-aside of work safety expenses in high-risk industries, requiring that the work safety expenses should be included in the cost of related products or current profit and loss, and included in the '4301 special reserves' item. According to the latest requirements of the Ministry of Finance, the Jiangsu Provincial Department of Finance and Jiangsu Provincial Administration of Work Safety revised the above 'Accounting Methods of Enterprise Safety Expense' in the next year and jointly issued 'The Notice on Adjusting the Accounting Treatment of Enterprises in high-risk Industries Set-aside Safety Production Expense' (No. 6 [2010], Jiangsu Finance and Accounting). Enterprises are required to conduct standardized management of safety expenses according to 'The Statement of Set-aside, Use and Balance of Enterprise Work Safety Expenses'. Since then, the accounting account has been changed from the four-level account of 'long-term payable-security expenses payable-number of the uses-specific scope of use' to the three-level accounting of 'special reserve-number of the use-specific scope of use', and the three accounting treatment methods of safety expenses have also been updated (Fig. 3)[15−18].
-
The set-aside, use and management of work safety expenses of enterprises is a professional task of comprehensive accounting and safety science, which plays an irreplaceable fundamental role in ensuring the production safety of enterprises and promoting the stable development of the social economy[19−21]. In order to further strengthen and standardize the set-aside and use of enterprise safety costs, it is necessary to establish a three-level linkage of government supervision, enterprise implementation, and third-party agency services. From the government level, we should strengthen publicity, improve corporate awareness, improve top-level design and incentive and restraint mechanisms. From the enterprise level, the main responsibility of work safety expenses set-aside and use should be well implemented, knowledge training of financial personnel and safety personnel should be strengthened, and relevant business capabilities should be effectively improved. From the level of third-party agencies, the theoretical and practical research on financial knowledge and security practices should be steadily promoted, and the working bond between government departments and enterprises should be done well.
-
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: study conception and design: Ma C, Ma P; data collection: Ma C; analysis and interpretation of results: Ma C, Ma P; draft manuscript preparation: Ma C, Xu J. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
University-Industry Collaborative Education Program (202002177004).
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
- Copyright: © 2023 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press on behalf of Nanjing Tech University. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Ma C, Xu J, Ma P. 2023. Research on the set-aside, use and administration for work safety expenses of the business entity in China. Emergency Management Science and Technology 3:12 doi: 10.48130/EMST-2023-0012
Research on the set-aside, use and administration for work safety expenses of the business entity in China
- Received: 24 May 2023
- Accepted: 11 October 2023
- Published online: 27 October 2023
Abstract: Work safety expenses, as legally required, should be used to meet and improve the prescribed work safety conditions of the business entity specifically. The standardized set-aside, use and management of work safety expenses can ensure the normal development of work safety activities and the safety of employees' lives and property. The historical evolution of work safety expenses in China is described in detail, from the department rules of work safety expenses set-aside for coal production enterprises, fireworks and firecracker production enterprises, and other single enterprise types to the comprehensive department rules, applicable to the management of work safety expenses in multiple industries. The set-aside standard and time of work safety expenses of different types of enterprises are comprehensively compared, and the standardized set-aside of work safety expenses is explained by taking the production and storage enterprises of dangerous chemicals as an example. It is analyzed that the scope of use of work safety expenses includes the construction of emergency rescue teams, major hazard detection, safety risk grading management, hidden trouble checking, construction of work safety information, etc. Through the establishment of a three-level linkage of government supervision, enterprise implementation, and third-party agency services, the standardized management of work safety expenses will be realized.
-
Key words:
- Work safety expenses /
- Historical evolution /
- Set-aside and use /
- Accounting treatment