-
Wheat stands as one of the world’s most crucial staple food crops, furnishing 20% of the global population’s calorie intake and holding a pivotal role in ensuring food security worldwide. Wheat yield is mainly determined by three factors: thousand grain weight (TGW), spike number per unit area, and grain number per spike[1]. The optimization of these three components is of great significance for improving yield. Among these, increasing the grain weight emerges as a particularly significant avenue for boosting wheat productivity. Traits shaping grain morphology, including grain length, grain width, and grain thickness, directly affect grain size, which in turn affects grain weight.
The development of seeds significantly influences grain weight. The mature seeds of angiosperms are composed of the embryo, endosperm, and seed coat. The maternal and zygotic tissues jointly participate in the regulation of the growth and development of seeds as well as control of the synergistic growth of embryo, endosperm, and seed coat. As grain development advances, seed coat cells perpetually undergo division and expansion, accompanied by continuous carbohydrate accumulation in the endosperm[2]. Genes pertinent to transport, carbohydrate metabolism, and starch synthesis also become active during development. Starch is the main storage component of the wheat endosperm, and its content is a key regulator of grain weight. In addition, plant hormone contents exhibit significant changes during seed development, and genes related to metabolism participate extensively in seed development.
In this review, we summarize recent research on key regulators of wheat grain weight including transcriptional regulatory factors, post-translation modification factors, the G-protein signaling pathway, and phytohormone signalings to understand the regulatory mechanisms of wheat grain weight (Fig. 1, Table 1).
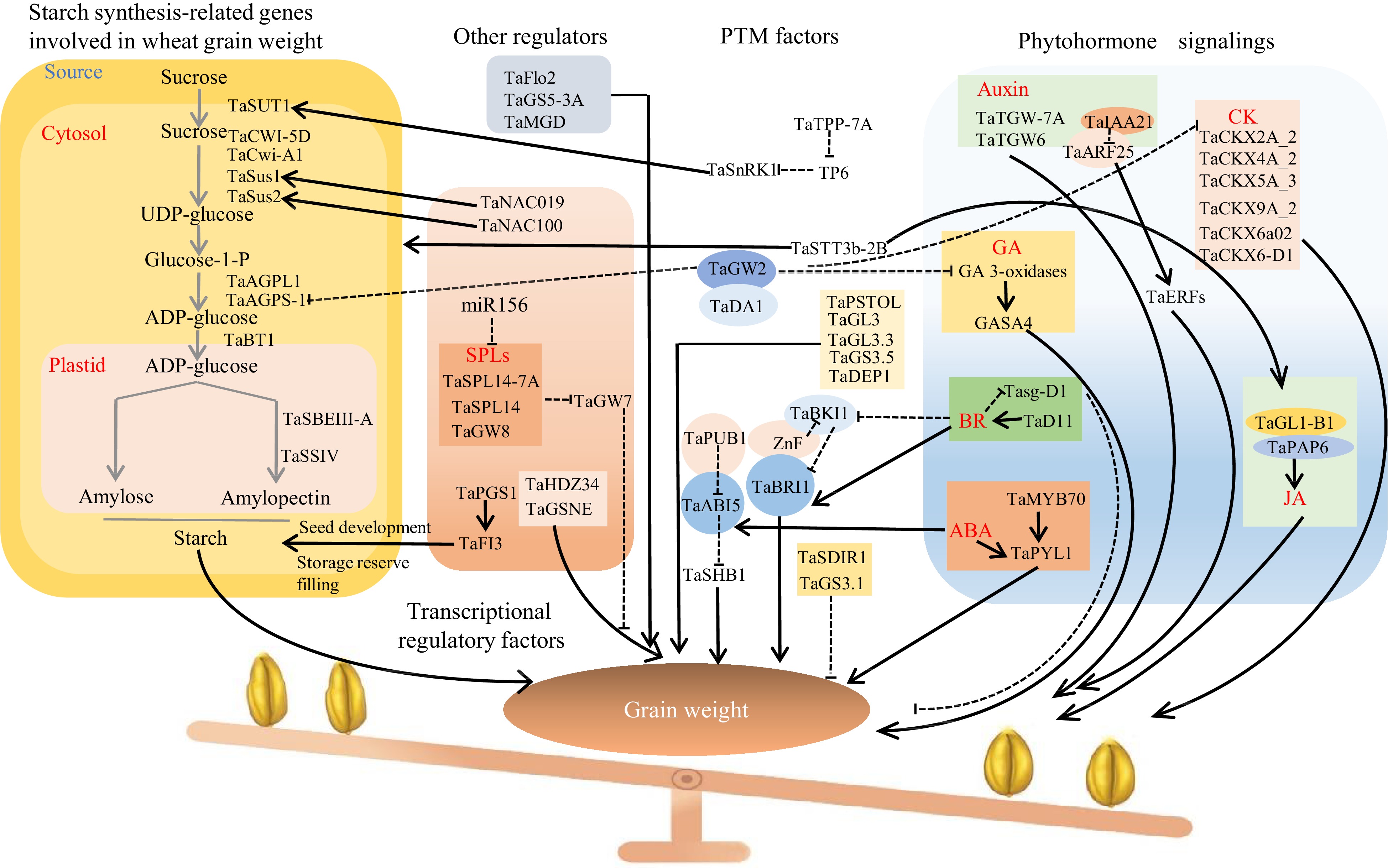
Figure 1.
Regulatory networks involved in grain weight in wheat. Several genes involved in transcriptional regulatory factors, post-translation modification factors, the G-protein signaling pathway, and phytohormone signalings participate in wheat grain weight regulation. Broken lines indicate inhibitory regulation. Arrowheads represent positive regulation. Elliptical overlaps represent interactions.
Table 1. Genes involved in wheat grain weight regulation.
Protein name Gene ID Protein category Positive(+)/negative(−)
regulatorElite haplotype for
high grain weightReference Starch synthesis-related genes reported to be involved in wheat grain weight TaCwi-A1 TraesCS2A03G0736600 Cell wall invertase + TaCwi-A1a [3] TaCWI-5D TraesCS5D03G1216700 Cell wall invertase + Hap-5D-C [4] TaSUT1-A TraesCS4A03G0027400 Sucrose transporters + TaSUT1 in Kauz [5] TaSUT1-B TraesCS4B03G0758500 Sucrose transporters + TaSUT1 in Kauz [5] TaSUT1-D TraesCS4D03G0679400 Sucrose transporters + TaSUT1 in Kauz [5] TaSus1-A TraesCS7A03G0375000 Sucrose synthase + TaSus1-7A-Hap-1 [6, 7] TaSus1-B TraesCS7B03G0171900 Sucrose synthase + TaSus1-7B-Hap-T [6, 7] TaSus1-D TraesCS7D03G0358200 Sucrose synthase + − [6, 7] TaSus2-A TraesCS2A03G0349200 Sucrose synthase + TaSus2-2A-Hap-A [6, 8] TaSus2-B TraesCS2B03G0468900 Sucrose synthase + TaSus2-2B-Hap-H [6, 8] TaSus2-D TraesCS2D03G0366700 Sucrose synthase + − [6, 8] TaBT1-A TraesCS6A03G0433200 Sucrose transporter + − [9] TaBT1-B TraesCS6B03G0559700 Sucrose transporter + Hap1 and Hap2 [9] TaBT1-D TraesCS6D03G0376900 Sucrose transporter + − [9] TaAGPL1-B TraesCS1B03G1206000 Large subunit gene of the AGPase + TaAGP-L-1B-Hap-I [10, 11] TaAGPS-1 TraesCS7A03G0682600 Small subunit gene of the AGPase + TaAGP-S1-7A-Hap-I [10] TaSBEIII-A TraesCS7A03G0826800 Starch-branching enzyme + Allele-T [12] TaSSIV-A TraesCS1A03G0866200 Starch synthases + Hap-2-1A [13, 14] TaSSIV-B TraesCS1B03G1004700 Starch synthases + Hap-3-1B [13, 14] TaSSIV-D TraesCS1D03G0838700 Starch synthases + − [13, 14] GWD-A TraesCS6A03G0662800 Glucan, water dikinase − − [15] GWD-B TraesCS6B03G0813900 Glucan, water dikinase − − [15] GWD-D TraesCS6D03G0552200 Glucan, water dikinase − − [15] Transcriptional regulatory factors TaNAC019-A TraesCS3A03G0172000 NAC transcription factor + − [16] TaNAC019-B TraesCS3B03G0216600 NAC transcription factor + TaNAC019-BI [16] TaNAC019-D TraesCS3D03G0154500 NAC transcription factor + − [16] TaNAC100-A TraesCS2A03G0808100 NAC transcription factor + TaNAC100-2A-H1 [17] TaNAC100-B TraesCS2B03G0891700 NAC transcription factor + − [17] TaNAC100-D TraesCS2D03G0746900 NAC transcription factor + − [17] TaPGS1 TraesCS1D03G0219000 bHLH transcription factor + − [18] TaPGS1 TraesCS1D03G0219700 bHLH transcription factor + − [18] TaFI3 TraesCS3A03G1169900 PLATZ transcription factor + − [18] TaGSNE TraesCS5B03G0668000 WRKY transcription factor + TaGSNE-Hap-2 [19] TaHDZ-A34 TraesCS7A03G0760400 HD-Zip transcription factor + Hap-ABD [20] TaHDZ-B34 TraesCS7B03G0590000 HD-Zip transcription factor + Hap-ABD [20] TaHDZ-D34 TraesCS7D03G0729900 HD-Zip transcription factor + Hap-ABD [20] TaGW8-B1 TraesCS7B03G0430500 SPL transcription factor + TaGW8-B1a [21] TaSPL14-A TraesCS5A03G0658100 SPL transcription factor + − [22] TaSPL14-B TraesCS5B03G0692900 SPL transcription factor + − [22] TaSPL14-D TraesCS5D03G0627900 SPL transcription factor + − [22] TaSPL14-7A TraesCS7A03G0567100 SPL transcription factor + TaSPL14-7A-Hap1/2 [23] TaSPL14-7B TraesCS7B03G0393600 SPL transcription factor + − [23] TaSPL14-7D TraesCS7D03G0548900 SPL transcription factor + − [23] Post-Translational Modifications (PTMs)
Ubiquitin–proteasome pathwayTaGW2-6A TraesCS6A03G0480200 RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase − Hap-A [24, 25] TaGW2-6B TraesCS6B03G0578500 RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase − TaGW2-B-HapI/II [24, 25] TaGW2-6D TraesCS6D03G0404800 RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase − − [24, 25] TaDA1-A TraesCSU03G0004100LC Ubiquitin receptor − TaDA1-A-HapI [26] TaDA1-B TraesCS2B03G0048000 Ubiquitin receptor − − [26] TaDA1-D TraesCS2D03G0031900 Ubiquitin receptor − − [26] TaSDIR1-4A TraesCS4A03G0197400 RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase − TaSDIR1-4A-2 [27] TaPUB1-A TraesCS5A03G1197700 U-box E3 ligase + − [28] TaPUB1-B TraesCS4B03G0885300 U-box E3 ligase + − [28] TaPUB1-D TraesCS4D03G0783100 U-box E3 ligase + − [28] ZnF-A TraesCS4A03G0701600 RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase + − [29] ZnF-B TraesCS4B03G0092600 RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase + − [29] ZnF-D TraesCS4D03G0066800 RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase + − [29] SnRK and phosphatase pathways TaSnRK2.3-A TraesCS1A03G0569000 Sucrose non-fermenting 1 (SNF1)-related protein kinase Hap-1A-1 [30] TaSnRK2.3-B TraesCS1B03G0660500 Sucrose non-fermenting 1 (SNF1)-related protein kinase Hap-1B-1 [30] TaSnRK2.9-A TraesCS5A03G0177100 Sucrose non-fermenting 1 (SNF1)-related protein kinase Hap-5A-1/2 [31] TaSnRK2.9-B TraesCS5B03G0188000 Sucrose non-fermenting 1 (SNF1)-related protein kinase − [31] TaSnRK2.9-D TraesCS5D03G0195600 Sucrose non-fermenting 1 (SNF1)-related protein kinase − [31] TaSnRK2.10-A TraesCS4A03G0621500 Sucrose non-fermenting 1 (SNF1)-related protein kinase Hap-4A-H [32] TaSnRK2.10-B TraesCS4B03G0179500 Sucrose non-fermenting 1 (SNF1)-related protein kinase − [32] TaSnRK2.10-D TraesCS4D03G0149100 Sucrose non-fermenting 1 (SNF1)-related protein kinase − [32] TaPSTOL TraesCS5A03G0115500LC Phosphate Starvation Tolerance 1 + − [33] TaGL3-5A TraesCS5A03G0897900 PPKL family—Ser/Thr phosphatase + TaGL3-5A-G [1] TaGL3-5B TraesCS5B03G0943200 PPKL family—Ser/Thr phosphatase + − [1] TaGL3-5D TraesCS5D03G0859400 PPKL family—Ser/Thr phosphatase + − [1] TaGL3.3-A TraesCS5A03G0073900 PPKL family—Ser/Thr phosphatase + − [34] TaGL3.3-B TraesCS5B03G0068000 PPKL family—Ser/Thr phosphatase + TaGL3.3-5B-C [34] TaGL3.3-D TraesCS5D03G0098300 PPKL family—Ser/Thr phosphatase + − [34] TaTPP-7A TraesCS7A03G0422300 Trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase + TaTPP-7A-HapI [35] TaTPP-7B TraesCS7B03G0228800 Trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase + − [35] TaTPP-7D TraesCS7D03G0410500 Trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase + − [35] Asparagine N-glycosylation pathway TaSTT3b-2A TraesCS2A03G1282700 Catalytic subunit of oligosaccharyltransferase + − [36] TaSTT3b-2B TraesCS2B03G1473200 Catalytic subunit of oligosaccharyltransferase + − [36] TaSTT3b-2D TraesCS2D03G1245300 Catalytic subunit of oligosaccharyltransferase + − [36] G-protein signaling pathway TaGS3-4A TraesCS4A03G1194500 Gγ subunit − [37, 38] TaGS3-7A TraesCS7A03G0037700 Gγ subunit − [37, 38] TaGS3-7D TraesCS7D03G0033100 Gγ subunit − [37, 38] TaDEP1-A TraesCS5A03G0545300 Gγ subunit + TaDEP1-Hap1 [39] TaDEP1-B TraesCS5B03G0555000 Gγ subunit + − [39] TaDEP1-D TraesCS5D03G0509000 Gγ subunit + − [39] Phytohormone signalings CK TaCKX2 TraesCS3A03G0298200 Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKX) enzymes + TaCKX2A-2 [40] TaCKX4 TraesCS3A03G1128900 Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKX) enzymes + TaCKX4A-2 [40] TaCKX5 TraesCS3A03G0763900 Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKX) enzymes + TaCKX5A-3 [40] TaCKX9 TraesCS1A03G0609600 Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKX) enzymes + TaCKX9A-2 [40] TaCKX6a02 TraesCS3D03G0306000 Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKX) enzymes + TaCKX6a02-D1a [41] TaCKX6-D1 TraesCS3D03G0305400 Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKX) enzymes − TaCKX6-D1-a [42] GA TaGASR7-A TraesCS7A03G0485700 Gibberellin-regulated protein − H1c [43, 44] TaGASR7-B TraesCS7B02G115300 Gibberellin-regulated protein − − [43, 44] TaGASR7-D TraesCS7D02G210500 Gibberellin-regulated protein − − [43, 44] Auxin TaTGW-7A TraesCS7A03G0542800 Involved in the tryptophan biosynthetic pathway + TaTGW-7Aa [45] TaTGW-7B TraesCS7B03G0358400 Involved in the tryptophan biosynthetic pathway + − [45] TaTGW-7D TraesCS7D03G0520200 Involved in the tryptophan biosynthetic pathway + − [45] TaTGW6 TraesCS7D03G0173900 IAA–glucose (IAA-Glc) hydrolase activity + − [46] TaIAA21-A TraesCS7A03G0816300 Auxin/indole acetic acid repressor − Hap2, Hap3, Hap5 TaIAA21-B TraesCS7B03G0674700 Auxin/indole acetic acid repressor − − TaIAA21-D TraesCS7D03G0801000 Auxin/indole acetic acid repressor − − TaARF25-A TraesCS5A03G0098100 Auxin response factor (ARF) protein + TaARF25-B TraesCS5B03G0104300 Auxin response factor (ARF) protein + TaARF25-D TraesCS5D03G0114800 Auxin response factor (ARF) protein + BR TaD11-2A TraesCS2A03G0818100 BR biosynthesis enzymes + TaD11-2A-HapI [47] TaD11-2B TraesCS2B03G0904700 BR biosynthesis enzymes + − [47] TaD11-2D TraesCS2D03G0759600 BR biosynthesis enzymes + − [47] Tasg-D1 TraesCS3D03G0288900 STKc_GSK3 Kinase − − [48] ABA TaPYL1-1A TraesCS1A03G0514200 Abscisic acid (ABA) receptor PYL + − [49] TaPYL1-1B TraesCS1B03G0603200 Abscisic acid (ABA) receptor PYL + TaPYL1-1BIn-442 [49] TaPYL1-1D TraesCS1D03G0499200 Abscisic acid (ABA) receptor PYL + − [49] TaMYB70-A TraesCS5A03G0432900 MYB transcription factor + − [49] TaMYB70-B TraesCS5B03G0428700 MYB transcription factor + − [49] TaMYB70-D TraesCS5D03G0401500 MYB transcription factor + − [49] TaABI5-A TraesCS3A03G0880400 Basic/region leucine zipper transcription factor − − [28] TaABI5-B TraesCS3B03G1006600 Basic/region leucine zipper transcription factor − − [28] TaABI5-D TraesCS3D03G0808000 Basic/region leucine zipper transcription factor − − [28] JA KAT-2B TraesCS6B03G1211100 Keto-acyl thiolase 2B + − [50] TaPAP6-A TraesCS2A03G0298800 Fibrillin family member + − [51] TaPAP6-B TraesCS2B03G0419200 Fibrillin family member + − [51] TaPAP6-D TraesCS2D03G0317100 Fibrillin family member + − [51] TaGL1-B1 TraesCS1B03G0239600 Carotenoid isomerase gene + TaGL1-B1b [51] Other regulators TaCYP78A3-A TraesCS7A03G0630800 Cytochrome P450(CYP) 78A3 protein + − [52] TaCYP78A3-B TraesCS7B03G0455800 Cytochrome P450(CYP) 78A3 protein + − [52] TaCYP78A3-D TraesCS7D03G0611800 Cytochrome P450(CYP) 78A3 protein + − [52] TaGW7-A TraesCS2A03G0367000 TONNEAU1-recruiting motif (TRM1) protein − H1a [53] TaGW7-B TraesCS2B03G0488200 TONNEAU1-recruiting motif (TRM1) protein − H1b [53] TaGW7-D TraesCS2D03G0384600 TONNEAU1-recruiting motif (TRM1) protein − H1d [53] TaFlo2-A1 TraesCS2A03G1201700 FLOURY ENDOSPERM2 (Flo2) gene + TaFlo2-A1b [54, 55] TaGS5-3A TraesCS3A03G0396700LC Serine carboxypeptidases + TaGS5-3A-T [56] TaMGD-A TraesCS6A03G0937800 Monogalactosyl diacylglycerol + − [57] TaMGD-B TraesCS6B03G1143600 Monogalactosyl diacylglycerol + − [57] TaMGD-D TraesCS6D03G0814200 Monogalactosyl diacylglycerol + − [57] -
Grain weight hinges on both grain size and endosperm constituents. Within monocot plants, the endosperm has a pivotal role in determining seed size and weight. This prominence arises because the endosperm occupies most of the volume of a mature grain. Consequently, endosperm components exert defining influences on grain weight. In general, among seeds of comparable size, those with higher oil contents have lower seed weights, and those with higher starch contents have higher seed weights. Notably, starch is an important component of wheat grains, accounting for approximately 70% of the dry weight[58]. Starch synthesis and accumulation are related to the development of wheat endosperm and contribute directly to grain weight[59]. Furthermore, the starch content within grains of the same variety exhibits a significantly positive correlation with grain size. The filling process and endosperm development also affect the accumulation, conversion, and starch synthesis of photosynthetic products. Several starch synthesis-related genes have important roles in controlling size and weight in wheat grains. These include the cell wall invertase genes TaCwi-A1 and TaCWI-5D, the sucrose transporter gene TaSUT1, sucrose synthase genes TaSus1 and TaSus2, ADP-Glc pyrophosphorylase genes TaAGPL1/ TaLSU1, BRITTLE1 (BT1), and TaBT16B, starch synthase TaSSIV, starch branching enzyme TaSBEIII-A, and Glucan, Water-Dikinase gene GWD; these genes play vital roles in starch accumulation and are all associated with TGW ( Table 1)[3−12,15].
The division and elongation of seed coat cells affect the volume of the cavity wherein both the embryo and the endosperm develop, and they determine traits related to the final grain size, including grain length, width, and thickness. Several signaling pathways have been shown to control seed size by regulating the growth of maternal tissues in wheat. We summarize the grain weight regulatory pathways in wheat from the following aspects: transcriptional regulatory factors, post-translation modification factors, the G-protein signaling pathway, and phytohormone signalings.
-
Transcription factors (TFs) are general regulators of functional genes that bind to specific motifs of target gene promoters, thereby activating or suppressing transcription. Numerous TFs have been identified as participants in the intricate orchestration of wheat grain weight.
Notably, several SQUAMOSA PROMOTER-BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE (SPL) family TFs are associated with grain weight. OsSPL16 positively regulates grain weight by enhancing cell proliferation and grain filling in rice[60]. Its ortholog, TaSPL16, also known as TaGW8, is reported to have a similar function to OsSPL16 in wheat grain weight regulation and is regulated by miR156[21,53]. Correlation analysis between TaGW8-B1a, TaGW8-B1b alleles and agronomic traits showed that wheat cultivars with the allele TaGW8-B1a exhibit a significantly larger grain size and higher TGW compared to those with TaGW8-B1b, because TaGW8-B1b possesses a 276-bp indel in its first intron[21]. Knockdown lines of TaGW7, the ortholog of GRAIN WIDTH7 (OsGW7), showed increases in grain width and weight but reductions in grain length by regulating cell division and organ growth[53]. OsSPL16 directly interacts with the promoter of OsGW7, and represses OsGW7’s expression[61]. Therefore, it is possible that TaSPL16 could bind directly to the promoter of TaGW7 to regulate wheat grain weight. MiR156 cleaves TaSPL14 mRNA, with knockout lines exhibiting a reduced TGW[22]. Another SPL TF, TaSPL14-7A, has a similar function, and its elite alleles, TaSPL14-7A-Hap1/2, are significantly correlated with a higher TGW; expression levels are higher for TaSPL14-7A-Hap1/2 than for TaSPL14-7A-Hap3 and the locus underwent positive selection during global wheat breeding over the last century[23]. Given the conservation of SPL family TF binding motifs and miR156-regulated SPLs, the miR156-SPLs-TaGW7 pathway emerges as a potential regulator of wheat grain weight.
NAC TFs belong to a plant-specific TF family. As one of the largest TF families, its members are widely involved in the regulation of many biological processes in plants, including stress responses, seed development, and nutrient accumulation. Recently, NAC TFs have been reported to participate in grain weight regulation. For example alterations in TaNAC019 and TaNAC100 could affect TaSus expression, thereby affecting grain starch content and grain size[16,17]. Remarkably, OsNAC20 and OsNAC26 in rice and ZmNAC128 and ZmNAC130 in maize have been recently reported to regulate starch synthesis-related genes to impact grain size and weight[62,63]. Notably, these NAC genes are specifically expressed in endosperm tissue, except for TaNAC100.
Ectopic overexpression of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) TF TaPGS1 (T. aestivum Positive Regulator of Grain Size 1) within the wheat endosperm yields increases carbohydrate and total protein levels, thereby increasing grain weight[18]. The plant AT-rich zinc-binding proteins (PLATZ), OsFI3 and ZmFI3, which are orthologs of TaFI3 in wheat, are associated with a high TGW, grain width, and grain length in rice and maize[18,64]. TaPGS1 regulates TaFI3 expression in wheat and the PGS1-Fl3 regulatory system is conserved in different cereals[18].
Grain Size and Number Enhancer (TaGSNE) encodes a WRKY TF and has the highest expression in young roots at the flowering stage[19]. TaGSNE not only governs root length but also adeptly balances the trade-off between grain size and number in wheat[19]. Further, TaGSNE displays responsive behavior to abscisic acid (ABA) and environmental cues. As evaluated using a generalized linear model, the TaGSNE-Hap-2 allele exhibits a significant positive correlation with TGW in three environments[19]. TaGSNE is a candidate gene for breeding high-yield, abiotic-stress-resistant wheat varieties.
The homeodomain-leucine zipper (HD-Zip) TF, TaHDZ34, plays an important role in modulating wheat TGW. TaHDZ34 can be classified into eight haplotype combinations: Hap-ABD, Hap-Abd, Hap-aBd, Hap-AbD, Hap-aBD, Hap-abD, Hap-ABd, and Hap-abd. A correlation analysis based on two populations (172 lines and162 lines) and eight haplotype combinations of TaHDZ34 showed that the Hap-ABD allele is associated with a higher TGW than those of the other seven haplotype combinations, revealing that it is a superior haplotype for wheat breeding[20]. The regulatory mechanism of TaHDZ34 warrants comprehensive exploration in future studies.
-
Post-translation modifications (PTMs) constitute a cornerstone in plant development’s regulatory landscape, and are flexibly responsive to plant signals through protein ubiquitination, phosphorylation, glycosylation, and methylation. These modifications exert influence over gene expression and protein stabilization. Within this intricate framework, the OST pathway, and sucrose non-fermentation-1-related protein kinases (SnRKs) pathway, PPKL family Ser/Thr phosphatase protein phosphatases pathway, collectively contribute to grain weight regulation.
Grain weight regulation via the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway
-
The ubiquitin–proteasome pathway plays a critical role in seed development by ubiquitinating and degrading proteins. This ubiquitination reaction requires a series of special enzymes: ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s)[65]. Notably, the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway assumes a conserved role in crop grain weight regulation. We summarize some new recently reported genes involved in this pathway in wheat and regulatory networks that differ from those of other crops.
TaGW2, a well-known negative regulator of grain weight, encodes an E3 RING ubiquitin ligase and has a similar function to that of its ortholog OsGW2 in rice. In Arabidopsis, rice, and wheat, the ubiquitin receptor DA1, a conserved component of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway, restricts the proliferation of maternal pericarp cells and in wheat, TaDA1 has an additive effect on TaGW2 by physically interacting with TaGW2, which shares significant sequence similarity with DA2 in Arabidopsis[26,66]. TaDA1 and TaGW2 function in partially overlapping but relatively independent regulatory networks because the abundance of downstream proteins in lines with TaGW2 silencing and lines with TaDA1 silencing differ[26]. In wheat, TaGW2 ubiquitinates TaAGPS via the 26S proteasome pathway and is a negative regulator of TGW[24,25]. Meanwhile, TaGW2-6A has a negative correlation with cytokinin (CK) and gibberellin (GA) synthesis genes, thereby leading to negative control of endosperm cell elongation and division during grain filling[59,67].
The RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase TaSDIR1-4A also negatively regulates grain size in common wheat, and Hap-4A-2, a elite allele of TaSDIR1-4A, is associated with a higher TGW because its expression is repressed by the ethylene response factor TaERF3[27]. Overexpression of the E3 ligase TaPUB1 results in a larger seed size and higher TGW than those of WT lines[28]. A recent report published in Nature showed that ZnF-B, a zinc-finger RING-type E3 ligase, ubiquitinates the brassinosteroid (BR) signaling repressor BRI1 kinase inhibitor 1 (TaBKI1), and degrade it to affect wheat plant height and yield. The loss of ZnF stabilizes TaBKI1 to block BR signal transduction to reduce plant height and improve grain size and weight[29].
Grain weight regulation via the SnRK pathway
-
Protein phosphorylation, mediated by protein kinases, is one of the most important post-translational modifications and is critically involved in almost every biological process, including defense responses, sugar synthesis, seed dormancy, and germination. Reported functions of protein kinases are mainly focus on their responses to biotic and abiotic stresses, while few studies have focused on seed traits in wheat. A notable exception lies in the SnRKs, which have been reported to be associated with wheat grain traits. Whereas mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) have been reported to play important roles in regulating the grain size in other plants.
The SnRK family is a class of Ser/Thr protein kinases; according to sequence homology and protein structural characteristics, it can be divided into three families: SnRK1, SnRK2, and SnRK3[68]. SnRK1 exhibits an important role in carbon metabolism regulation, and SnRK2 and SnRK3 are related to ABA-mediated signaling pathways[69].
Trehalose-6-phosphate (T6P), a signal hub for sucrose abundance and carbon availability, is important in the regulation of plant growth, development, and yield in major cereal crops[70]. During early grain development stages, T6P directly inhibits SnRK1 activity in response to sucrose availability and promots carbon biosynthesis in wheat grains[71,72]. With a dramatic decrease in T6P levels, SnRK1 activity is activated, and many genes dependent on SnRK1 and related to starch synthesis are triggered to initiate grain filling and maturation[35]. Additionally, ABA is involved in SnRK-related sugar signaling and promotes starch accumulation during grain development. TaTPP-7A encodes the functional T6P dephosphorylation enzyme[35]. In TaTPP-7A overexpression lines, SnRK1-dependent gene (PYL3-7D, PP2C-7D, and SnRK2-1B) expression levels, as well as the expression levels of NCED, a key rate-limiting enzyme coding gene in the ABA biosynthetic pathway, were higher than those in WT[35]. Thus, TaTPP-7A enhances starch synthesis and grain filling mainly through the T6P–SnRK1 pathway and sugar–ABA interaction[35]. A haplotype association analysis show that varieties with HapI of TaTPP-7A have a high TGW and long grain length, whereas those with HapII show a low TKW and short grains. Therefore, HapI is the elite allele for TGW[35].
SnRK2 is a plant-specific protein kinase family, and is instrumental in the regulation of carbon metabolism[73]. TaSnRK2.3-1A and TaSnRK2.3-1B affect TGW in different environments[30]. Hap-1A-1 and Hap-1B-1, which are associated with a higher TGW, are considered elite haplotypes. Hap-5A-1/2 of TaSnRK2.9-5A and Hap-4A-H of TaSnRK2.10-4A are significantly associated with a higher TGW[31,32]. Regulatory relationships between these SnRK2 haplotypes and TGW were found by association analyses. However, studies on the TGW regulatory mechanisms of SnRK2s are lacking. These regulatory mechanisms are worthy of further exploration.
The SnRK pathway is a new pathway that regulates grain weight in wheat. Other protein kinases are also involved in regulating grain weight. TaPSTOL (Phosphate Starvation Tolerance 1) is a putative kinase gene that promotes flowering time and seed size, and these traits are correlated with the expression of TaPSTOL under different P concentrations in wheat[33]. However, the regulatory mechanism linking TaPSTOL to grain weight is still unclear. Owing to the functional versatility of protein kinases, the regulation of these genes on grain weight may have indirect or secondary effects. Precise regulatory mechanisms need to be determined.
Grain weight regulation via the PPKL family Ser/Thr phosphatase pathway
-
Protein phosphatases and kinases have opposing functions and regulate the reversible phosphorylation of proteins[74]. The qGL3 gene encodes the phosphatase kelch (PPKL) family Ser/Thr phosphatase and is associated with a higher grain size and yield in rice[75,76]. GL3.1 directly dephosphorylates Cyclin-T1;3 in rice and results in a shorter grain[75]. TaGL3-5A, an ortholog of GL3.1 in wheat, and the other PPKL-related gene TaGL3.3 are significantly associated with a higher TGW in common wheat[1,34]. These regulatory mechanisms may be conserved, but still need to be verified.
Grain weight regulation via the OST pathway
-
Asparagine N-glycosylation is one of the most abundant post-translational protein modifications in eukaryotic cells. This biochemical process is catalyzed by the oligosaccharyltransferase (OST) complex and plays a pivotal role in various biological processes in plant development[77,78]. The STAUROSPORINE AND TEMPERATURE SENSITIVE3 (STT3) subunit is a subunit of the OST complex and is important for the catalytic activity of OST[79]. Overexpression of TaSTT3b-2B significantly increases wheat grain weight by affecting the expression of a series of starch synthase, sucrose synthase, and jasmonate (JA) biosynthesis related genes[36]. These recent findings support the role of the OST pathway in the regulation of grain weight in wheat.
-
The G-protein signaling pathway is one of the most crucial pathways for grain weight regulation in rice[80]. And this regulatory mechanism is also conserved in wheat. Heterotrimeric G-proteins, comprising Gα, Gβ, and Gγ subunits, could transmit signals from transmembrane receptors to target proteins[37]. A plant-specific organ size regulation (OSR) domain exists at the N-terminus of the G-protein γ-subunit[81]. OsGS3, a Gγ subunit in rice, is identified as a negative regulator of grain weight and length[82]. Correspondingly, in wheat, TaGS3, an ortholog of OsGS3, negatively regulates grain weight and size[38]. However, TaGS3 has five splicing variants, among which GS3.1 is a negative regulator and GS3.5 is a positive regulator because of their different OSR domains[37]. The TaGS3.1 variant can bind to WGB1 to form a functional Gβγ heterodimer and regulate grain weight and size, while TaGS3.5 with an incomplete OSR domain does not interact with WGB1[37].
DENSE AND ERECT PANICLE 1 (DEP1) was identified a genomic loci associated with grain thickness by genome-wide association study (GWAS)[39]. TaDEP1, which encodes the G-protein γ-subunit, is essential for wheat grain development, and its knockout lines exhibit decreased grain size and TGW[39]. HapI is the elite allele of TaDEP1 and manifests as a major factor with a grain-weight-improving effect of 32%[39]. The SKP1 gene encodes a critical component of the DELLA protein degradation complex within the GA pathway, and it is downregulated in TaDEP1 mutants[39]. This observation hints at an interaction between the G-protein pathway and the GA pathway. This finding provides a novel insight intowheat grain weight regulation, even though the G-protein signaling pathway is conserved in wheat and rice. Nonetheless, the mechanisms by which TaDEP1 regulates grain weight and the interaction between the G-protein pathway and GA pathway are still unclear and should be elucidated in further studies.
-
Plant hormones play significant roles in seed development[83,84]. The concentrations of many hormones show large transient changes during grain filling and development. CK, GA, auxin, BR, ABA, and JA are involved in wheat grain weight regulation.
CK
-
CK is a classic plant hormone with crucial roles in plant growth and development. Recent studies in model plants have unveiled its pivotal role in regulating the number of endosperm cells and grain-filling patterns by modulating CK metabolic genes' expression; this affects the size and weight of wheat grains and significantly affects the wheat grain yield[85,86]. Cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKX) enzymes impact plant growth and development by catalyzing the irreversible degradation of CKs[87]. The TaCKX gene family is linked to TGW and plant height in common wheat. Haplotype variants such as TaCKX2A_2, TaCKX4A_2, TaCKX5A_3, and TaCKX9A_2 show significantly associated with a higher TGW and shorter plant height in both Chinese wheat micro-core collection and GWAS open population[40]. Haplotype variants TaCKX6a02-D1a of TaCKX6a02 (TaCKX2.1)and TaCKX6-D1-a of TaCKX6-D1 (TaCKX2.2) are associated with higher filling rates and grain sizes[41,42]. While numerous CKXs regulators have been reported in rice, relatively little is known about their roles in wheat, necessitating further exploration.
GA
-
GA plays a crucial role in plant growth and is associated with seed development. TaGW2-6A negatively regulates GA synthesis and GA response genes. TaGW2-6A allelic variant TaGW2-6ANIL31 regulates GA synthesis via regulating GA 3-oxidases, thereby leading to higher expression of GASA4 and promoting endosperm cell elongation and division during grain filling[67]. TaGASR7, a gibberellin-regulated gene, is identified as a negative regulator of wheat grain weight[44]. However, the regulatory mechanism has not been studied yet in both rice and wheat.
Auxin
-
Auxin, the first plant hormone discovered, contributes substantially to plant growth and development. Auxins exhibit polar transport characteristics, and their concentrations have important effects on plant morphogenesis. Auxin/INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID (Aux/IAA) repressors and the AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR (ARF) TFs are two core components of the auxin signaling pathway[88]. Aux/IAA repressors negatively regulate auxin signal transduction and often form dimers with ARF TFs to prevent their transcriptional activation functions of ARFs to their targets[89]. TaIAA21 encodes an Aux/IAA repressor, and mutation in this gene increases grain length, grain width, and grain weight significantly by restricting maternal cell elongation in wheat grains[90]. TaIAA21 interacts with TaARF25, which can directly regulate TaERF3, thereby regulating grain size and weight[90]. The Aux/IA-ARF-ERF regulatory module is relatively conserved in rice and wheat, but target genes of ARFs are different between rice and wheat[90].
Grain carbohydrates primarily arise from pre-heading and post-heading photosynthesis-derived carbohydrates[91]. In rice, THOUSAND-GRAIN WEIGHT 6 (TGW6) encodes a protein with IAA-glucose hydrolase activity[91]. Loss of function of TGW6 can increase the grain length and grain weight by controlling the IAA supply and increasing the accumulation of carbohydrates before heading[91]. In contrast, Kabir & Nonhebel[46] gave a different viewpoint, declaring that TaTGW6 and OsTGW6 do not regulate grain size via the hydrolysis of IAA-glucose because developing wheat grains do not express an IAA-glucose synthase and have undetectable levels of TaTGW6 and OsTGW6[46]. This is a controversial result and requires further study.
TaTGW-7A has an N-terminal domain of sigma 54-dependent transcriptional activators[45]. TaTGW-7A is positively correlated with TGW because it encodes a key enzyme in auxin biosynthesis[45,46].TaTGW-7Aa is associated with a high TGW and is the predominant allele[45].
BR
-
BRs are a class of plant steroid hormones. Despite their low content, they have high activity and play key roles in the growth and development of plants[92]. BR content is positively correlated with grain weight. Genetic networks of BR level or BR sensitivity to improve rice yield has established in rice, but BR’s impact on wheat remains less understood.
TaGS5-3A encodes a putative serine carboxypeptidase and is a positive regulator of grain size[56]. TaGS5-3A-T is an elite haplotype and is significantly correlated with a larger grain size and higher TGW[56]. In rice, GS5 regulates grain width by interacting with OsBAK1-7 to affect endocytosis and enhance BR signaling, thereby promoting cell proliferation and palea/lemma expansion[93]. GS5’s role in grain weight regulation of crop might be conserved, because ZmGS5 in maize has similar function with GS5 in rice.
TaD11, the ortholog of D11 in rice, encodes a enzyme involved in BR biosynthesis, and the expression of TaD11 is significantly suppressed by exogenous BR (24-epiBL)[47]. Overexpressing TaD11-2A in rice could increase endogenous BR levels and improve grain weight. The tad11-2a-1 mutant exhibited a lower grain size than that of the WT. TaD11-2A-HapI is the elite allele and positively selected with wheat breeding development[47]. Tasg-D1, an ortholog of OsGSK2, encodes a Ser/Thr protein kinase glycogen synthase kinase3 and negatively regulates BR signaling, resulting in a reduced TGW[48]. As mentioned above, ZnF-B is a BR signaling activator that regulates the BR signaling pathway to affect wheat grain size[29].
ABA
-
ABA plays a pivotal role in plant growth, development, and other processes, like grain development, seed dormancy, germination, and seedling establishment. The ABA signal transduction pathway is regulated by a variety of factors. In the presence of ABA, soluble pyrabactin resistance 1 (PYR1)/PYR1-like (PYL)/regulatory components of ABA receptors bind ABA and undergo conformational changes[94]. They can then interact with clade A type 2C protein phosphatases (PP2Cs) and release SnRK2s, which are inhibited by PP2Cs[95,96]. SnRK2s could phosphorylate the downstream ABA-responsive proteins AREB/ABFs[97,98]. TaPYL1-1B encodes an ABA receptor[49]. TaPYL1-1B overexpression lines show higher ABA sensitivity, larger grain sizes, and higher grain yields, water-use efficiency, and drought tolerance than those of WT lines[49]. The TaPYL1-1BIn-442 allele is targeted by TaMYB70 and associated with larger kernel size and higher TGW[49]. The wheat E3 ligase TaPUB1 acts as a negative regulator of the ABA signaling pathway by mediating TaABI5 degradation and positively controlling seed TGW in wheat[28].
JA
-
JA has a significant impact on crop growth and defense. Overexpression of the ketoacyl thiolase 2B gene (KAT-2B), which is involved in oxidation during JA synthesis, increases grain weight, thereby enhancing yield[50]. TaPAP6 could promote the accumulation of JA contents by suppressing the jasmonic acid-amino synthetase (JAR) gene[51]. TaGL1-B1 encodes a carotenoid isomerase[51]. The interaction relationship between TaGL1-B1 and TaPAP6 could increase JA accumulation, carotenoid contents, and photosynthesis, thereby increasing wheat grain weight[51]. TaSTT3b-2B impacts grain weight through regulating the expression of JA biosynthesis genes[36].
-
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 78A protein (CYP78A) belongs to a plant-specific gene family. Several cytochrome P450s have been reported to be involved in seed weight regulation in in rice and Arapidopsis. In wheat, the activity of TaCYP78A3 is positively correlated with the final seed size by affecting the cell number in the seed coat[52].
The function of FLOURY ENDOSPERM2 (Flo2) is conserved across plants. OsFlo2 is positively correlated with the amylose content and grain weight by influencing the expression of starch synthesis-related genes in rice[55,99]. In wheat, TaFlo2-A1, an ortholog of rice OsFlo2, exhibits the same function; furthermore the haplotype TaFlo2-A1b, which is highly expressed levels, is an elite haplotype associated with a high TGW[54].
Monogalactosyl diacylglycerol (MGDG) is the major glycolipid of the amyloplast membrane and is essential for chloroplast photosynthesis[57]. Overexpressing MGDG synthase gene TaMGD could increase the expression of most starch synthesis-related genes, therefore increasing starch accumulation and grain weight[57].
-
Wheat grain weight is regulated by multiple signaling pathways. These signaling pathways are relatively conserved across crops and involve the transcriptional regulation, post-translational modifications, G-protein signaling pathway, and phytohormone signalings. Due to the large and complex genome of wheat, the moleculer basis of wheat grain weight cannot be directly compared with that of rice grain weight. For example, while a number of rice genes has been studied to regulate grain weight through the BR signaling pathway, wheat research has only revealed two such genes. The regulation pathways of grain weight are conserved among different crops. Many grain weight regulatory genes in wheat are orthologous to genes identified in rice. For example, TaGS3, a Gγ subunit identified as a negative regulator of grain weight and length in wheat, is the ortholog of OsGS3. The huge genome and redundant gene functions in wheat make it difficult to explore functions of such orthologous genes. With the development of biotechnology, it is becoming easier to knock out multiple genes simultaneously and explore function of genes in wheat. Moreover, wheat-specific genes, like those in the OST pathway, important candidates for functional studies. The wheat genome is hexaploid with high heterozygosity, presenting substantial opportunities for discovering new grain weight-regulated genes, and for overcoming yield bottlenecks.
Despite numerous studies on wheat grain weight, the regulatory mechanisms of wheat gain weight genes have not been systematically analyzed. Starch synthesis-related genes are regulated by lots of factors in many pathways related to grain weight. Plant hormones vary substantially across time and post-translational modifications are often involved in hormone signal transduction. SKP1 is downregulated in the TaDEP1 mutant, and this observation suggests that there is an interaction between the G-protein pathway and GA pathway. Pathways contributing to the regulation grain weight are related. However, the interrelationships between regulatory pathways still need to be systematically studied. Most genes affect not only grain weight but also other functional traits. Future challenges in wheat grain weight research involve unraveling the molecular mechanisms of identified regulators, identifying novel regulators, and enhancing grain weight without compromising other traits by establishing appropriate genetic frameworks. The work described in this review provide an important basis for enhancing grain weight through multi-gene-based breeding strategies.
-
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: Gao Y, Li Y wrote the article; Dai D and Xia W collected the data; Dai Y, Wang Y, Ma Haigang and Ma Hongxiang modified the manuscript. All authors have reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during current study.
This work was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20220568), Jiangsu Key Project for the Research and Development (BE2022346), Natural Science Fund for Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province (22KJB210018), National Natural Science Foundation of China (32201772).
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
-
# These authors contributed equally: Yujiao Gao, Yongsheng Li
- Copyright: © 2023 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press on behalf of Hainan Yazhou Bay Seed Laboratory. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Gao Y, Li Y, Xia W, Dai M, Dai Y, et al. 2023. The regulation of grain weight in wheat. Seed Biology 2:17 doi: 10.48130/SeedBio-2023-0017
The regulation of grain weight in wheat
- Received: 27 May 2023
- Accepted: 11 October 2023
- Published online: 06 November 2023
Abstract: Wheat (Triticum aestivum L., AABBDD) is one of the world's most extensively cultivated crops, furnishing vital nutrients and energy for human consumption. Wheat seeds are the primary sustenance source. Given the mounting global population and dwindling arable land, enhancing wheat grain yield has implications for global dood security. A pivotal agronomic trait influencing grain yield is grain weight, which is predominantly contingent on seed size and endosperm components and is regulated by complex and precise molecular networks. Endogenous factors, such as transcriptional and post-translational regulators, exert pivotal influence over seed development. Notably, starch is the main storage component of wheat endosperm, and starch synthesis-related genes exert an important effect on grain weight. Prior reviews on wheat grain traits have mostly focused on the regulation of grain size, and the contents of such reviews are almost entirely written based on the regulatory network of rice seed size. Although many regulatory mechanisms for various traits are similar in rice and wheat, there are lots of differences in wheat due to its large and intricate genome. An all-encompassing panorama of the grain weight regulatory network has not yet been comprehensive. This review summarizes the catalog of reported genes, discusses the emerging molecular mechanisms, and delves into regulatory networks to foster a more holistic understanding of the intricate regulation of wheat seed weight.
-
Key words:
- Grain weight /
- Starch /
- Plant hormones /
- Post-translation modification factors













