-
Seeds are vital for angiosperm and gymnosperm survival and dispersion[1]. Seed germination is the basis for crop production. Seed germination refers to the process via which viable seeds transition from a dormant state to an active physiological one, leading subsequently to the development of a plant with normal roots, stems, and leaves under appropriate conditions[2−4]. Physiologically, seed germination is characterized by the absorption of water, which initiates the metabolism of reserves and energy in seeds. Molecularly, the expression of certain genes is activated, which instigates a series of reactions that lead to embryo growth[5].
Seed germination is influenced by internal and external factors[6, 7]. Hormones such as abscisic acid (ABA), gibberellin (GA), auxin (AUX), brassinosteroid (BR), cytokinin (CTK), ethylene (ET), and jasmonate (JA) are the key internal factors regulating seed germination[8−13]. Post-translational modifications (PTMs), such as phosphorylation[14] and ubiquitylation[15], are critical for seed germination, directly or indirectly affecting protein localization, stability, and activity[16, 17]. Meanwhile, external factors, such as light, temperature, and water, are the main signals that seeds can perceive for determining the timing of seed germination[18−22]. Here, the current knowledge relating to the regulatory roles of hormones, reactive oxygen species (ROS), small RNAs, epigenetic modifications, PTMs, and environmental cues in seed germination concentrating primarily on Arabidopsis and rice were summarized.
-
Seed dormancy is a temporary intrinsic block to germination even under favorable environmental conditions[21]. Seed dormancy is established during seed maturation[23] and seed dormancy is gradually released during after-ripening or stratification stages[24]. Seed dormancy is an effective way to regulate the optimal spatiotemporal distribution of seed germination and seedling formation[25]. The transition between dormancy and germination is mainly precisely regulated by endogenous hormones ABA and GA, in which ABA positively regulates dormancy induction and maintenance, while GA promotes seed germination[26]. Other plant hormones, such as auxin, JA, salicylic acid (SA), and CTKs, are involved in seed dormancy and germination via the ABA or GA pathways[27].
Seed germination
-
Seed germination begins with imbibition, and can be divided into three phases, namely, a rapid imbibition phase (Phase I), a lag phase (Phase II), and a phase in which active water uptake is resumed (Phase III)[28]. In Phase I of seed germination, the seed absorbs water rapidly, which immediately initiates the repair of cellular structures, such as cell organelles, and the reactivation of biochemical processes, such as enzyme activities[29]. When hydration levels exceed 60%, seeds enter the lag phase (Phase II), in which metabolism becomes active and the seed enters a new physiological state. Embryonic cells grow rapidly, and active substances, such as sugars and amino acids, accumulate in large amounts, while cell wall acidification promotes the loosening of cell wall polymers[6, 30]. Concomitantly, H+-ATPase activity is enhanced, which further promotes seed water absorption (Phase III) and weakens the restrictions on the development of embryonic tissues (such as endosperm), ultimately causing embryonic axis elongation, the breaking of radicle through the seed coat, and the completion of germination[31]. During seed germination, seed nutrients, such as lipids, proteins, and starch, are decomposed and utilized to maintain the early growth of the seedling until it reaches autotrophy[28]. Although the characteristics of seed germination have been widely investigated, the key events that determine seed germination remain unclear.
-
The hormone ABA promotes seed dormancy and inhibits germination[32,33]. Several genes regulate seed germination by influencing ABA content (Fig. 1). The RNA-binding protein RZ-1 and polycomb repressor complex 2 (PRC2) can synergistically silence the expression of ABA biosynthesis enzyme gene 9-CIS-EPOXYCAROTENOID DIOXYGENASE 6 (NCED6), thereby promoting seed germination in Arabidopsis, but promote seed dormancy in rice[34]. The bHLH transcription factors Seed Dormancy 6 (SD6) and INDUCER OF CBF EXPRESSION2 (ICE2) directly regulate the expression of the ABA degradation gene ABA8OX3, while OsbHLH048 of rice directly regulates the expression of the ABA synthesis gene NCED2 during rice seed germination[35]. Transcription factor OsGAMYB activates the expression of trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase 1 (OsTPP1), leading to an increase in trehalose content; this then enhances the expression of the ABA catabolic genes OsABA8OX3 and OsABA8OX2, resulting in the promotion of seed germination[36]. Mitogen-activated protein kinase 11 (MAPK11) negatively regulates tomato seed germination by upregulating the expression of NCED1 and affecting SNF1-RELATED PROTEIN KINASE SnRK2.2 phosphorylation, thus regulating ABA signal transduction[37].
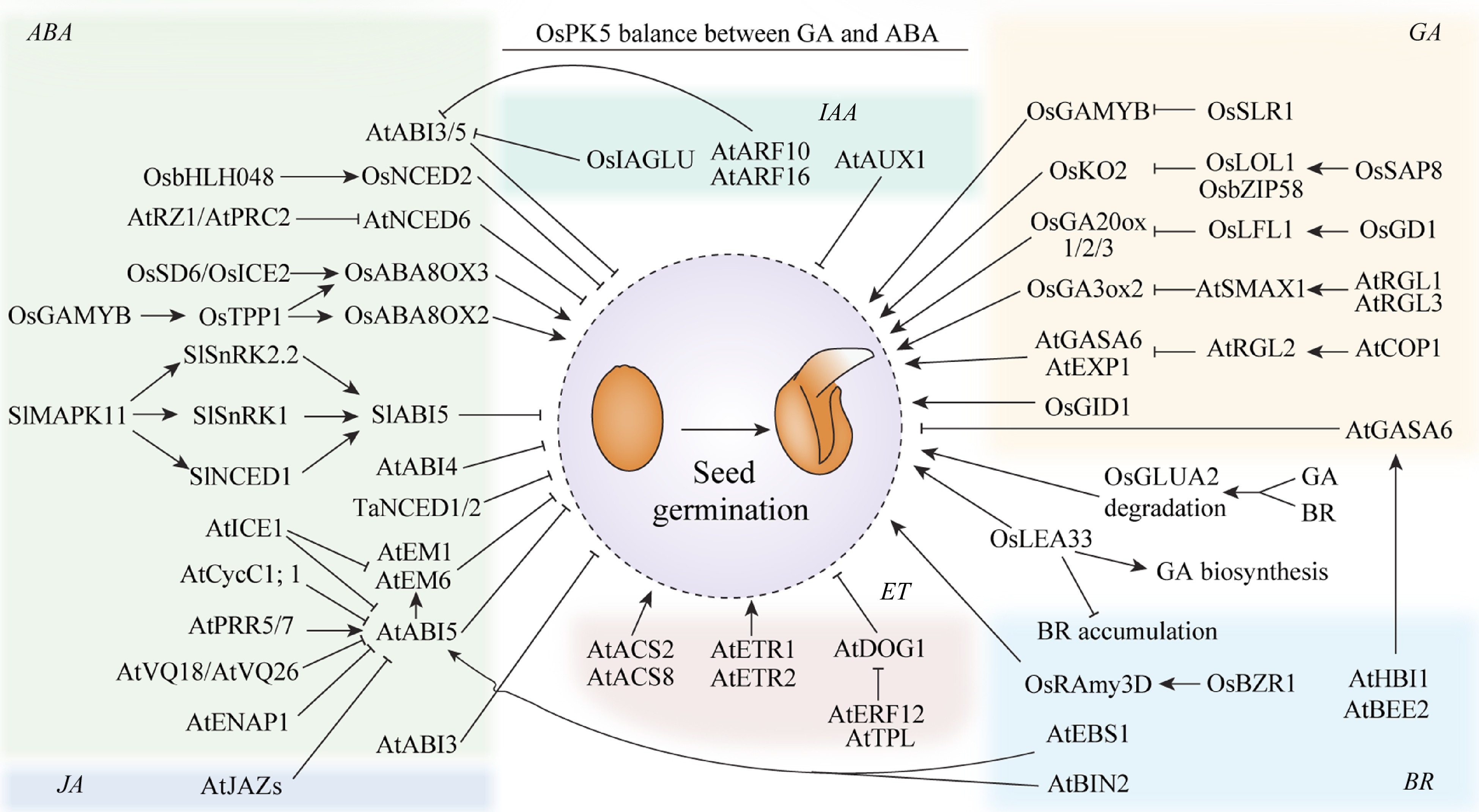
Figure 1.
Hormones regulate seed germination. ABA, abscisic acid; GA, gibberellins; ETH, Ethylene; AUX, auxins; JA, jasmonic acid. BR, brassinolid. Arrows and lines with slanted dashes indicate positive and negative effects, respectively.
ABSCISIC ACID INSENSIVE5 (ABI5) is a key component of the ABA signaling pathway during seed germination (Fig. 1). The VQ motif (FxxxVQxxTG) proteins VQ18 and VQ26 interact with ABI5 and negatively modulate its transcriptional activity, thereby promoting Arabidopsis seed germination[38]. The histone-binding protein ENAP1 regulates H3K9 acetylation, which mediates the positive feedback regulation of ABI5 and inhibits Arabidopsis seed germination[39]. INDUCER OF CBF EXPRESSION1 (ICE1) interacts with ABI5 and negatively regulates the response to ABA during seed germination in Arabidopsis; and ICE1 also interacts with and antagonizes the activities of DELLA proteins, which are positive regulators of ABA signaling. Thus, ICE1 establishes appropriate ABA signaling by counteracting ABI5 and DELLA proteins activity[40]. ABI5 also interacts with the circadian clock proteins PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR5 (PRR5) and PRR7, thereby stimulating ABA signaling and inhibiting seed germination in Arabidopsis[41]. C-type Cyclin1; 1 (CycC1; 1), another interacting partner of ABI5, inhibits the transcription-promoting activity of ABI5 by occupying the promoters of ABI5 target genes, thereby stimulating seed germination in Arabidopsis[42].
GA signaling pathway
-
The components of GA signaling pathway include the GA receptor GIBBERELLIN INSENSITIVE DWARF1 (GID1), the DELLA proteins, and the F-box proteins GID2, SLEEPY 1 (SLY1) in Arabidopsis[43]. The GA-receptor GID1 perceives bioactive GA and undergoes conformational changes that enable the interaction between GID1 and DELLAs in Arabidopsis[44]. When GA is present in large quantities, GA binds to a nuclear receptor GID1A and form a complex, which promotes the ubiquitination and degradation of DELLA proteins mediated by the F-box ubiquitin ligase SLY1 and then promotes seed germination[45]. Mutations in the SLY1 lead to increased seed dormancy, and a triple knockout of AtGID1 leads to germination failure (Fig. 1)[46].
In Arabidopsis, the DELLA subfamily of GRAS regulatory genes consists of GA INSENSITIVE (GAI), REPRESSOR OF ga1-3 (RGA), RGA-LIKE1 (RGL1), RGL2, and RGL3[47]. In which, RGL2 functions as main signaling intermediate involved in GA-mediated seed germination[48]. RGL2 negatively regulates seed germination in response to GA, and that RGL1, GAI, and RGA do not[49]. However, the function of RGL2 can be enhanced by GAI, RGA, and RGL1[50]. A mutation in RGL2 can rescue the non-germinating phenotype of the gibberellin-deficient mutant[51]. CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC 1 (COP1) positively regulates seed germination by directly interacted with RGL2[48], increasing the expression of downstream regulators (such as GASA6 and EXPA1) of seed germination[51]. Meanwhile, GAI and RGA can also be degraded via the COP1/SUPPRESSOR OF PHYA-105 (SPA) complex[52]. In Arabidopsis, SMAX1 interacts with the DELLA proteins RGL1 and RGL3, thus enhances the transcriptional activity of SMAX1 and inhibits GA biosynthesis key enzyme GIBBERELLIN 3-oxidase 2 (GA3ox2) gene expression, which inhibit seed germination under weak light conditions[53].
In rice, the DELLA protein is identified as SLENDER RICE1 (SLR1), which has significant homology with RHT-1Da in wheat, D8 in maize, and GAI and RGA in Arabidopsis[54]. When GA is present, the GA-GID1-SLR1 complex is formation, which facilitates the degradation of SLR1, and then the released GAMYB from SLR1 promote the gene expression of α-amylase[27]. In addition, stress-associated protein 8 (OsSAP8) interacts with lesion simulating disease 1-like 1 (OsLOL1) and OsbZIP58 to reduce the binding of OsbZIP58 to the GA biosynthesis gene KAURENE OXIDASE 2 (KO2) promoter, which promotes the biosynthesis of GA and, consequently, the activation of amylase expression and seed germination[55]. GERMINATION DEFECTIVE 1 (OsGD1) binds to the promoter of the LEC2/FUS3-like gene OsLFL1 and activates its expression, which represses the expression of GA 2-oxidase 3 (GA2ox3) and induces that of GA20ox1, OsGA20ox2, and OsGA3ox2, thereby influencing seed germination in rice[56].
Other hormones
-
BR and ethylene pathways also promote seed germination in plants (Fig. 1)[57, 58]. It has been found that blocking BR signaling delays seed germination and inhibits embryonic growth. BRASSINAZOLE-RESISTANT 1 (BZR1), a key regulatory factor in the BR signaling pathway, upregulates α-amylase expression by binding to the promoter of alpha-Amylase 3D (RAmy3D), thus influencing starch degradation in the endosperm and subsequently promoting seed germination[59]. Similarly, seed germination is promoted by the ethylene pathway in plants[58]. The production of ethylene occurs immediately after seed imbibition and increases as germination progresses. Moreover, the peak of ethylene release coincides with the emergence of the radicle through the seed coat[60−62]. The direct precursor of ethylene, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC), promotes seed germination in many species, such as lettuce, sunflower, chrysanthemum, chickpea, amaranth, and beet (Fig. 1)[63−67]. Low temperature, GA, nitric oxide, and hydrogen cyanide (HCN) treatments can all increase ethylene production and promote seed germination[47, 50, 51]. In Arabidopsis, the ethylene-insensitive mutants Atetr1 and Atein2 show delayed seed germination[64]. The Arabidopsis ethylene-responsive factor ERF12 can bind to the promoter of the key dormancy gene DELAY OF GERMINATION1 (DOG1) and recruit the transcriptional co-repressor TOPLESS (TPL), which inhibits DOG1 expression and promotes seed germination[68].
In contrast to BR and ethylene, seed germination is inhibited by jasmonic acid (JA) and its derivates[69, 70]. The application of exogenous JA or methyl jasmonate (MeJA) can inhibit seed germination, as can their precursor 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid (OPDA)[71]. Interestingly, auxin both stimulates and inhibits seed germination in plants, depending on its concentration[72]. For instance, at high concentrations (0.3 to 1 μM indole-3-acetic acid (IAA)), auxin inhibits seed germination in Arabidopsis[73, 74], whereas at low concentrations (0.03 to 3 nM IAA), the opposite is observed[75]. Recent research has shown that exogenous auxin and JA synergistically enhance the ABA-induced delay in seed germination. Auxin Response Factor10 (ARF10) and ARF16 positively mediate JA-increased ABA responses, and this process is mainly dependent on ABI5 (Fig. 1)[76]. In general, the regulatory roles of signaling pathways associated with other hormones except ABA and GA, such as ETH, BR, JA, and auxin, on seed germination remains unclear.
Hormone interactions
-
The crosstalk among hormones plays an important role in seed germination in plants (Fig. 1). For example, in wheat, JA can suppress the ABA biosynthesis genes, TaNCED1 and TaNCED2, and thereby promote seed germination[77]. Several JAZ repressors stimulate seed germination by interacting with ABI3 and inhibit its transcription as well as that of ABI5[13]. OsPK5 improves seed germination by increasing the GA/ABA ratio[78]. Similarly, BR promotes seed germination by antagonizing ABA signaling through a feedback loop mediated by MOTHER OF FT AND TFL1 (MFT)[79]. BRINSENSITIVE1 (BRI1)-EMS-SUPRESSOR1 (BES1), a BR signaling component, interacts with ABI5 and inhibits its binding to the promoter region of target genes, resulting in a decrease in their expression levels and the promotion of seed germination in Arabidopsis[80]. In the presence of ABA, the protein kinase BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE2 (BIN2), another constituent of the BR signaling pathway, interacts with ABI5 and stabilizes it through phosphorylation, thus positively regulating ABA signaling and inhibiting seed germination[9]. Ethylene can antagonize the effect of ABA on endosperm weakening and seed coat rupture, which consequently stimulates seed germination without affecting ABA levels[81]. ABI4 can directly bind to the promoters of the ethylene biosynthesis genes ACC SYNTHASE2 (ACS2) and ACS8, resulting in reduced ethylene production and the suppression of seed germination[82]. The indole-3-acetic acid glucosyltransferase gene of rice (OsIAGLU) positively regulates seed germination by reducing IAA and ABA contents and OsABI3/5 expression[83]. AUXIN RESISTANT 1 (AUX1) is required for ABA-mediated inhibition of seed germination and AtAUX1 loss-of-function mutants display an enhanced ABA-resistant phenotype[84].
Studies have also shown that BR and auxin regulate seed germination in a manner involving GA metabolism or the GA signaling pathway (Fig. 1). For example, GA and BR can synergistically induce the degradation of the key gluten protein-encoding gene GLUA2, thereby promoting seed germination in rice[85]. Rice LATE EMBRYOGENESIS ABUNDANT 33 (LEA33) affects seed germination possibly by reducing BR accumulation and enhancing GA biosynthesis[86]. Two components of the BR signaling pathway, the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors HBI1 and BEE2, can directly regulate the gene expression of GA-stimulated Arabidopsis 6 (GASA6), which promotes seed coat and endosperm breakage for seed germination[87]. Moreover, exogenous auxin treatment represses soybean seed germination by positively mediating ABA and negatively regulating GA biosynthesis[88]. The expression of the auxin transporters AUX1, PIN-FORMED 2 (PIN2), and PIN7 are highly upregulated in ga1 mutant seeds following treatment with GA[89]. These findings underscore the importance of hormone crosstalk on seed germination in plants. However, an in-depth understanding of the crosstalk among JA, BR, ethylene, and auxin is still lacking.
-
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are a class of highly active oxygen-containing molecules or ions that mainly include superoxide anions (O2•−), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), singlet oxygen (1O2), and hydroxyl radicals (•OH)[90, 91]. In dry seeds, ROS are mainly generated by lipid autooxidation, whereas following imbibition, they are primarily produced by enzymatic reaction[92]. ROS have a dual role in seed physiology. Low levels of ROS stimulate seed germination, while excessive ROS accumulation causes oxidative damage and inhibits seed germination[93]. ROS promote seed germination by contributing to cell wall loosening, endosperm weakening, and radicle and root elongation[94−97]. Rice polyamine oxidase 5 (OsPAO5) oxidizes spermine and generates H2O2, which promotes mesocotyl cell elongation during seed germination[98, 99]. Cotton HSP24.7 enhances the release of ROS from mitochondria, which leads to the degradation of key components within the endosperm membrane and reduces its strength for seed germination[100]. Generally, within a certain concentration range, known as the 'oxidative window', ROS promote seed germination, while the opposite is observed at concentrations that deviate from this window[101]. Although the appropriate ROS concentrations that contribute to seed germination have been reported for camphor, wheat, soybean, barley, and pea[101−103], the oxidative window for the promotion of seed germination remains unclear for most crops.
Interactions between ROS and hormones regulate seed germination
-
Interactions between ROS and hormones such as GA and ABA play important roles in seed germination in plants. Exogenous GA treatment can induce ROS production and promote seed germination in wild oat (Avena fatua) and Chinese flowering cabbage (Brassica parachinensis)[104, 105]. Exogenous H2O2 can enhance the expression of kaurenoic acid oxidase 1 (KAO1) and HvGA3ox1, thereby promoting GA synthesis and seed germination in barley[106]. Similarly, H2O2 can enhance the GA-induced expression of the expansin gene HvExpA11 and the GA biosynthesis gene HvGA20ox1, as well as inhibit the expression of the GA catabolic gene HvGA2ox3, thereby promoting GA accumulation and, consequently, seed germination in barley[92]. In Arabidopsis, exogenous H2O2 treatment can activate the expression of the GA synthesis-related genes GA3ox and GA20ox and the ABA metabolism-related gene CYP707A, which enhances GA synthesis and ABA metabolism and improves seed germination[107]. In tomato, H2O2 enhances germination capacity by upregulating the expression of the GA biosynthesis gene GA3ox1 as well as that of the ABA catabolism gene ABA 8'-hydroxylase (ABA8ox)[108]. H2O2 regulates barley seed germination by influencing the activity of an ABA catabolic enzyme, and consequently, ABA content in seed embryos[109]. Meanwhile, H2O2 can suppress the phosphatase activity of ABI1 and ABI2, thus inhibiting seed germination in Arabidopsis[110, 111]. ABI4, another major constituent in ABA signaling, modulates ROS metabolism during seed germination under salt stress by directly combining with RbohD and Vitamin C Defective 2 (VTC2), key genes in ROS production and scavenging[112]. Similarly, ABI5 can modify ROS homeostasis by inducing CATALASE 1 (CAT1) expression and, consequently, catalase activity[113]. Furthermore, exogenous H2O2 can induce ethylene biosynthesis, which promotes seed germination in soybean[102]. Exogenous ethylene positively regulates seed germination in sunflower by activating NADPH oxidase, which leads to ROS accumulation in the embryonic axis[60]. However, whether crosstalk between ROS and other hormones such as JA, BR, or auxin also exerts regulatory effects on seed germination requires further investigation.
-
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small, non-coding RNAs, approximately 20 to 24 nucleotides in length[114, 115]. They can influence gene expression at the transcriptional level via the methylation of target genes or at the post-transcriptional level by promoting target mRNA degradation or inhibiting target mRNA translation[116]. Several hormone-related signaling pathways are controlled by miRNAs during seed germination in plants (Fig. 2)[74]. In Arabidopsis, the overexpression of miR159 can inhibit the transcription of the ABA response factors MYB33 and MYB101, resulting in reduced sensitivity to ABA during seed germination. MiR159 has also been reported to regulate seed germination by regulating the mRNA level of GAMYB, and thus modulating GA signaling[117]. MiR9678 regulates seed germination via its effects on ABA/GA signaling pathways in wheat[118]. Meanwhile, miR160 was shown to participate in seed germination by negatively regulating the auxin response factor ARF10 in Arabidopsis[74]. In addition, rice miR393 negatively mediates coleoptile elongation under flooded conditions by regulating the expression of the auxin receptor-encoding genes OsTIR1 and OsAFB2[119]. MiRNAs have also been found to affect seed germination by regulating epigenetic factors. For example, miR402 regulates seed germination under stress conditions by targeting the mRNA of DML3, a DNA demethylase, and promoting its degradation[120]. Overall, only a few small RNAs that participate in seed germination in crops have been identified to date. However, given their biological importance, the application of small RNAs for the improvement of seed germination deserves further investigation.
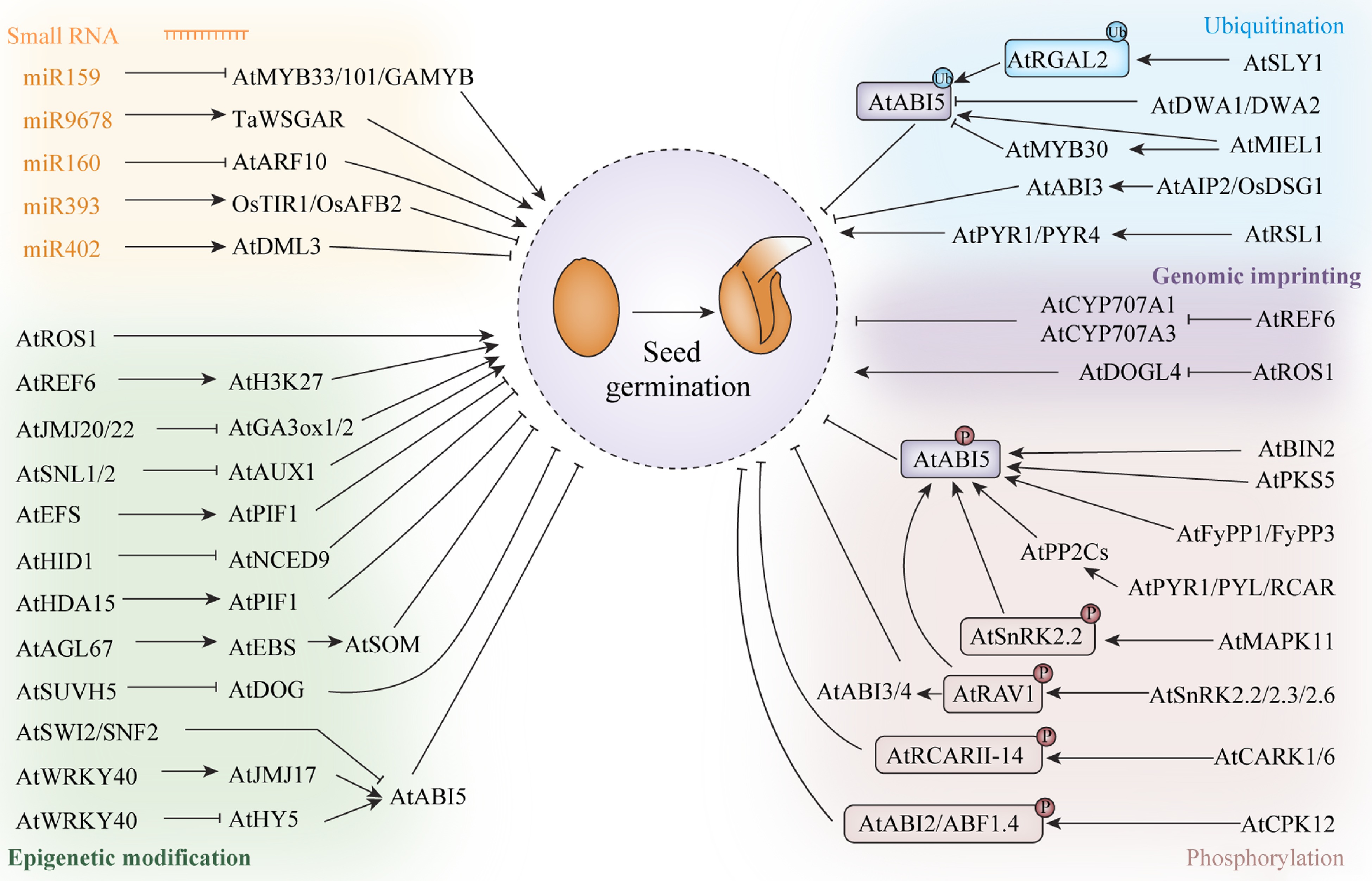
Figure 2.
Internal regulatory factors regulate seed germination. Arrows and lines with slanted dashes indicate positive and negative effects, respectively.
Genomic imprinting
-
Genomic imprinting refers that one parent allele is silenced while the other parent allele remains active, which caused by the asymmetric DNA methylation between parental alleles, including maternally expressed genes (MEGs), or paternally expressed genes (PEGs)[121]. In Arabidopsis, DNA methylation is an important imprinting for many MEGs[122]. Trimethylation of histone H3 on lysine 27 (H3K27me3), catalyzed by the PRC2, is an important epigenetic mark involved in the regulation of some imprinted genes in the endosperm[123]. Many genes marked by single H3K27me3 have been found to be induced during seed germination[124]. In Arabidopsis, H3K27me3 is catalyzed by histone methyltransferases[125]. Arabidopsis endosperms are targeted by the H3K27me3 demethylase REF6 and became activated during germination[124]. Additionally, AtREF6 can directly targets ABA catabolizing enzymes CYP707A1 and CYP707A3, which contributes to suppress seed dormancy (Fig. 2)[126]. DOGL4 is an imprinted gene in Arabidopsis endosperm, and it negatively affects seed dormancy. DNA demethylase ROS1 negatively regulates DOGL4 imprinting via demethylation of the DOGL4 promoter on the paternal allele, and ROS1 regulates seed dormancy by controlling DOGL4 expression[127]. In castor bean, imprinted genes showed dynamic expression characteristics at different stages of endosperm, mainly involved in endosperm development and storage material accumulation, and MEGs and PEGs had obvious functional differentiation. It showed that imprinted genes persisted in germinated endosperm and participated in seed germination[128]. Overall, only a few genomic imprinting genes that participate in seed germination in crops have been identified to date.
Other modifications
-
Epigenetic modifications, including methylation, demethylation, deacetylase have also been reported to be involved in the regulation of seed germination in plants[129] (Fig. 2). H3K27me3 plays a key role in regulating gene repression and cell fate specification. Relative of Early Flowering 6 (REF6) mediates the demethylation of H3K27, which helps to activate gene transcription and promote seed germination in Arabidopsis[130]. The EARLY FLOWERING IN SHORT DAYS (EFS) gene encodes a H3K4 and H3K36 methyltransferase that inhibits seed germination in Arabidopsis by directly binding to the promoter of PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR 1 (PIF1) and increasing the levels of H3K36me2 and H3K36me3 at the binding sites, thus upregulating PIF1 expression[131]. The histone mark reader Early Bolting in Short Days (EBS) is recruited by the transcription factor Agamous-Like67 (AGL67) to H3K4me3 at the promoter of the gene encoding the zinc-finger protein SOMNUS (SOM), thereby epigenetically activating SOM expression and suppressing seed germination under high-temperature conditions[132]. The histone deacetylase HDA15 is recruited by the bHLH transcription factor PIF1 to the promoters of hormone signaling-related genes and inhibits their expression by reducing H3 acetylation levels. Additionally, HDA15 was shown to negatively regulate phytochrome B (PhyB)-dependent seed germination under dark conditions[133].
Several studies have demonstrated that epigenetic factors regulate seed germination via their effects on hormone-related metabolism and signaling pathways (Fig. 2). The non-coding RNA HIDDEN TREASURE 1 (HID1) promotes PhyB-dependent seed germination by directly inhibiting the expression of NCED9, which encodes the rate-limiting enzyme in ABA biosynthesis in Arabidopsis[134]. Switch/sucrose non-fermentable (SWI2/SNF2) chromatin remodeling ATPase BRAHMA (BRM) directly represses the expression of ABI5 and the loss of function of BRM results in ABA hypersensitivity during seed germination[135]. The JmjC domain-containing demethylase JMJ17 participates in the response to ABA during seed germination in Arabidopsis by co-regulating WRKY DNA-BINDING PROTEIN 40 (WRKY40), HYPOCOTYL5 (HY5), and ABI5[136]. The histone methylase SUVH5 regulates light-dependent seed germination by suppressing the ABA signal and reducing the expression of DOG genes via H3K9 dimethylation[137]. The lack of DNA demethylation by the plant-specific REPRESSOR OF SILENCING 1 (ROS1) gene impairs seed germination by activating the ABA pathway and impacting germination-related gene expression under heat stress in Arabidopsis[138]. The histone arginine demethylases JMJ20 and JMJ22 act redundantly as positive regulators of seed germination through the removal of repressive histone arginine methylations at GA3ox1/GA3ox2 in Arabidopsis[139]. Also in Arabidopsis, the loss of function of two histone deacetylase-binding factors, SWI-INDEPENDENT3 (SIN3)-LIKE1 (SNL1) and SNL2, results in accelerated radicle protrusion and growth during seed germination via the regulation of AUX1 expression, IAA levels, and signal transduction in Arabidopsis[72]. The roles of epigenetic modifications in the regulation of plant phenotypes and environmental adaptability have been widely investigated[140, 141]. Nonetheless, how epigenetic modifications influence seed germination under environmental stress conditions remains unclear.
Post-translational modifications
Phosphorylation
-
Protein phosphorylation, which refers to the transfer of a phosphate group from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to a specific amino acid residue in a substrate protein by protein kinases (PKs)[14], is widely involved in the regulation of seed germination[142]. Four types of kinases—sucrose non-fermentation 1-related protein kinases (SnRKs)[143], mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs)[37, 144], calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs)[145], and receptor-like kinases (RLKs)[146] have been widely shown to play significant roles in seed dormancy and germination. Studies have reported that phosphorylation related to seed germination mainly affects the ABA signaling pathway (Fig. 2). For example, the binding of ABA to its receptors PYR1/PYL/RCAR activates SnRK2s by inhibiting the phosphatase activity of PP2Cs. The activated SnRK2s subsequently phosphorylate ABI5 and promote its stability, thereby inhibiting seed germination[147]. The Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3-like kinase BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE2 (BIN2) enhances ABA signaling by phosphorylating ABI5 during seed germination in Arabidopsis[9]. The Arabidopsis RAV (Related to ABI3/VP1) transcription factor RAV1 is phosphorylated by SnRK2.2, SnRK2.3, and SnRK2.6, leading to an increase in the expression levels of ABI3, ABI4, and ABI5 during seed germination and early seedling development[143]. SOS2-LIKE PROTEIN KINASE5 (PKS5) phosphorylates ABI5, which activates the expression of downstream genes involved in seed germination in Arabidopsis[148]. Similarly, the protein phosphatases FyPP1 and FyPP2 directly dephosphorylate ABI5 and act antagonistically with SnRK2 to regulate ABA responses in seed germination[149]. The receptor-like protein kinases CARK1 and CARK6 interact with and phosphorylate the ABA receptors RCAR11–14, which enhances the ABA signal and inhibits seed germination in Arabidopsis[150]. The calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK12 of Arabidopsis phosphorylates and stimulates the type 2C protein phosphatase ABI2, a negative regulator of ABA signaling, while also phosphorylating two ABA-responsive transcription factors, ABF1 and ABF4, during seed germination[145]. In addition, MAPK11 positively influences ABA signaling by upregulating both NCED1 expression and ABA biosynthesis, and also negatively regulates seed germination by influencing the phosphorylation status of SnRK2.2 in tomato[37]. Totally, most relevant studies have reported that phosphorylation plays an important role in the ABA signaling pathway-mediated regulation of seed germination. However, whether phosphorylation is also involved in the regulation of seed germination in other signaling pathways needs to be further investigated.
Ubiquitination
-
Protein ubiquitination is a multi-stage enzyme-linked reaction involving the concerted activity of ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2, and ubiquitin ligase E3, which results in the transfer of ubiquitin molecules to lysine residues in target proteins[151, 152]. Ubiquitination modification regulates seed germination involving ABA and GA signaling pathways (Fig. 2)[16]. CUL4-based E3 ligases (DWA1 and DWA2) directly interact with each other and negatively regulate ABA signal transduction during seed germination[153]. The Arabidopsis ubiquitin E3 ligase MYB30-INTERACTING E3 LIGASE 1 (MIEL1) directly mediates the proteasomal degradation of ABI5 and inhibits its activity during seed germination[154]. The single-subunit RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase RSL1 can ubiquitinate the ABA receptors PYRABACTIN RESISTANCE1 (PYR1) and PYR1-LIKE 4 (PYL4), which weakens ABA signaling and, consequently, promotes seed germination[155]. Arabidopsis ABI3-interacting protein (AIP2) and its rice homolog Delayed Seed Germination 1 (OsDSG1), a RING ubiquitin ligase, can ubiquitinate the core transcription factor ABI3, thereby diluting the ABA signal and promoting seed germination[156, 157]. GA promotes seed germination by binding to the GA receptor and subsequently forming a complex with the DELLA protein REPRESSOR OF GA1–3 (RGA). This leads to RGA ubiquitination and its degradation through the 26S proteasome pathway, which relieves the inhibitory effect of DELLA on GA signal transduction[158, 159]. Similarly, RGA-like2 (RGAL2) is degraded via F-box protein SLY1 E3 ubiquitin ligase-mediated ubiquitination during seed germination[160, 161]. Phosphorylation and ubiquitination are widely reported involving seed germination via influencing protein activities and gene expression levels[16]. However, the regulatory roles of the other above-mentioned post-translational modifications in seed germination require further exploration.
-
Light is an important environmental factor that regulates seed germination[19,21,162]. Phytochromes (Prs) are key photoreceptors that regulate responses to light and are responsible for initiating between 10% and 30% of the transcriptional cascades of the entire transcriptome[163]. Under red light illumination, the inactive form, Pr, is transformed into the biologically active form, Pfr, thus promoting seed germination; however, Pfr is converted into Pr under far-red light conditions, leading to the inhibition of seed germination[164]. In Arabidopsis, there are five phytochrome proteins — PhyA, PhyB, PhyC, PhyD, and PhyE — with PhyB playing a dominant role in light-mediated seed germination (Fig. 3)[21,165]. The bHLH transcription factor PIF1 plays an important role in phytochrome-mediated seed germination[20,166]. The F-Box protein Cold Temperature-Germinating 10 (CTG10) of Arabidopsis can sense light signals. PIF1 and CTG10 coexist under dark conditions; however, after exposure to light, CTG10 helps reduce PIF1 levels, thereby promoting seed germination[167].
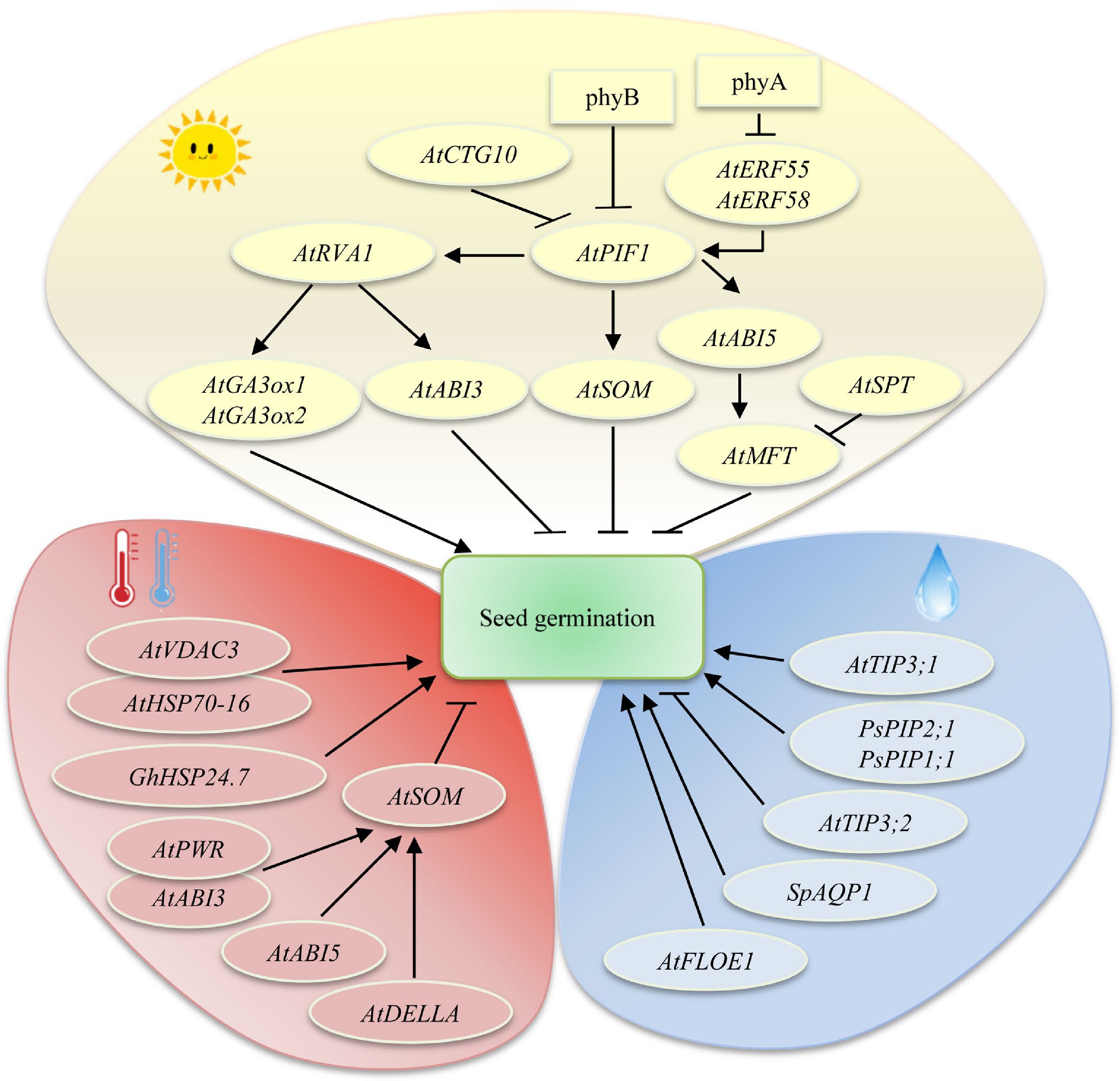
Figure 3.
Environmental factors regulate seed germination. Arrows and lines with slanted dashes indicate positive and negative effects, respectively.
Exogenous light signals regulate seed germination mainly via the ABA and GA pathways (Fig. 3). For example, PhyA and PhyB mediate ABA and GA synthesis and catabolism by binding to PIF1 and inhibiting SOM activation, thus exerting a regulatory effect on seed germination[168]. In darkness, PIFs directly bind to the promoter of the key transcription factor ABI5 and activate its transcription, thereby positively regulating the ABA signaling pathway[169]. PIF1 can repress the expression of GA biosynthetic genes (GA3ox1 and GA3ox2) and activate that of a GA catabolic gene (GA2ox) in PhyA- and PhyB-dependent seed germination, which blocks GA degradation and increases GA biosynthesis[22,170]. PIF1 interacts with REVILLE1 (RVE1), and, together, they synergistically regulate the expression of multiple genes in the ABA and GA pathways that are involved in PhyB-mediated seed germination[22]. Mutations in the AP2/ERF transcription factors ERF55 and ERF58 result in stronger light dependency during seed germination by influencing ABA and GA levels in Arabidopsis[171]. MFT is a key negative regulatory factor for seed germination; the expression of the MFT gene is promoted by far-red light through the PIF1/SOM/ABI5/DELLA pathway but is inhibited by red light through the transcription factor SPATULA (SPT)[172]. MFT affects the levels of the JA precursor oxylipin cis-12-oxo-phytodienoic acid (OPDA) and ABA under shading conditions, which inhibits seedgermination[173]. Light signals regulate seed germination mainly by influencing ABA and GA signaling pathways; however, whether they also influence seed germination via other signaling pathways is not known.
Temperature
-
Temperature is another important factor affecting seed germination. Both too-high and too-low temperatures inhibit or delay seed germination by disrupting a variety of molecular and physiological processes[174]. Under low-temperature conditions, seeds experience reduced water absorption, protein degradation, carbohydrate metabolism, and energy production but an increase in ABA synthesis, which delays seed germination[175]. When seeds are exposed to heat stress, meanwhile, ROS, malondialdehyde, antioxidant enzyme, and ABA levels are increased, which suppresses seed germination[176]. Molecular analysis indicated that ABI3, ABI5, and DELLA target the promoter of the transcription factor SOM and activate its transcription, which suppresses seed germination under high temperatures (Fig. 3)[177]. Similarly, the epigenetic factor Powerdress (PWR) interacts with ABI3 and activates SOM transcription through epigenetic modifications, leading to the suppression of seed germination under high-temperature conditions[178]. A mitochondrial heat shock protein GhHSP24.7 regulates seed germination in response to temperature in cotton. GhHSP24.7 promotes seed germination under both high and low-temperature conditions by inducing ROS production, thereby accelerating endosperm breakdown[100]. Heat shock protein 70-16 (HSP70-16) and voltage-dependent anion channel 3 (VDAC3) jointly suppress seed germination by promoting ABA flow from the endosperm to the embryo under low-temperature conditions[179].
Water
-
Imbibition is the first step in seed germination, and water movement thus plays a crucial role in the breaking of dormancy[180−182]. Plant aquaporins (AQPs), including plasma membrane intrinsic protein (PIPs), tonoplast intrinsic proteins (TIPs), nodulin 26 like MIPs (NIPs), and small and basic intrinsic proteins (SIPs), are membrane channels that mediate intracellular water movements. Most PIPs and TIPs are water-selective channel proteins[183−186]. In pea, PsPIP1;1, PsPIP2;1, and PsTIP1;1 are expressed in germinating seeds. PsPIP1;1 plays a role in water absorption during seed imbibition, while PsPIP2;1, possibly together with PsPIP1;1, may be involved in the release of phloem water from the seed coat symplast (Fig. 3)[187]. TIP3;1 and TIP3;2 have previously been implicated in water or solute transport during seed germination under water stress conditions in Arabidopsis[185]. Sesuvium portulacastrum SpAQP1 promotes seed germination and root growth in transgenic tobacco and increases salt tolerance by increasing the activities of antioxidative enzymes[188]. Hydration is the key trigger for the initiation of germination. Recent investigations have shown that the Arabidopsis prion-like protein FLOE1 undergoes phase separation upon hydration, which allows the embryo to sense water stress, and hence regulate the best time for seed germination under unfavorable environments[189, 190]. Overall, the mechanisms that determine plant seed germination under drought or submergence conditions remain unclear and require further investigation.
-
Seed germination is a key determinant of crop production and final yield. An in-depth understanding of the internal and external regulatory factors that determine seed germination is crucial for achieving high crop yields. In this review, we summarized the findings relating to molecular mechanisms involved in seed germination in plants. Studies on seed germination to date have mainly focused on Arabidopsis and rice, and relatively little is known about this process in crops such as maize, wheat, and barely. This situation needs to be addressed in the future. Seed germination is a complex trait that is determined by both genetic and environmental factors. Abiotic stresses, such as drought, flooding, salt, heat, and cold, are the most common adverse environmental conditions affecting seed germination in plants. Further unraveling the molecular mechanisms of seed germination under stress conditions is needed in the future.
The hormones ABA and GA are the key regulators of seed germination. Other hormones involved in this process, such as AUX, CTK, JA, and BR, in addition to ROS, function mainly through the ABA and GA signaling pathways. However, how to precisely control the levels and distribution of hormones and ROS in germinating seeds remains unclear. It is well known that there is crosstalk among hormones and ROS involved in seed germination; nevertheless, the detailed molecular mechanisms underlying their synergistic and antagonistic relationships remain to be resolved. Additionally, it would be interesting to reveal whether other as yet unidentified molecules, besides hormones and ROS, are involved in seed germination in plants. The recent rapid development of omics technologies provides important tools for the identification of factors involved in seed germination at the transcript, protein, and metabolite levels[191]. To date, the functional validation of newly identified regulators of seed germination is lacking.
Seed germination is regulated by extremely complex signaling networks. The endosperm not only constitutes a source of nutrients but also controls seed germination by actively secreting signals. The molecular mechanisms underlying how cell-to-cell communication coordinates seed germination and the role of the endosperm in seed germination also require further investigation[174]. Environmental factors such as light, temperature, and humidity play crucial roles in the regulation of seed germination in plants, but how seeds sense these environmental factors remains incompletely understood. Recent studies have indicated that environmental factors regulate seed germination mainly via the ABA pathway, and whether other hormones (AUX, CTK, JA, BR) and/or ROS-related pathways are also involved needs to be further analyzed. Abiotic stresses are the predominant environmental determinants of crop productivity worldwide. Despite this, the mechanisms that regulate crop seed germination under stress conditions such as drought, flooding, salt, heat, and cold have not been studied in depth. A combination of molecular, organismal, and ecological studies will reveal the mechanisms of seed germination with direct implications for the design of elite crops in the face of climate change.
-
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: study conception and design: Wang Z, Zhang H; data collection: Zhao J, He Y; draft manuscript preparation: Wang Z, Zhao J. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
This work was supported by grants from the Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou (2023A04J0749, 2023A04J1452) and the project of Hainan Yazhou Bay Seed Laboratory (B21HJ1002).
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
- Copyright: © 2024 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press on behalf of Hainan Yazhou Bay Seed Laboratory. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao J, He Y, Zhang H, Wang Z. 2024. Advances in the molecular regulation of seed germination in plants. Seed Biology 3: e006 doi: 10.48130/seedbio-0024-0005
Advances in the molecular regulation of seed germination in plants
- Received: 11 December 2023
- Revised: 11 February 2024
- Accepted: 11 March 2024
- Published online: 15 April 2024
Abstract: Seed germination is a key process in the life cycle of seed plants. The initiation of seed germination requires the activity of specific internal signaling molecules, such as hormones and reactive oxygen species (ROS), and is dependent on external environmental factors, such as water, temperature, and light. Seed germination is a complex trait that is regulated by multiple factors, including transcript, protein, and metabolite levels. This review highlights current knowledge relating to the regulatory roles of hormones, ROS, small RNAs, epigenetic modifications, post-translational modifications, and environmental cues on seed germination, mainly focusing on Arabidopsis and rice. The review on the molecular regulation of seed germination contributes to the improvement of crop seed quality using bio-breeding approaches.













