-
The development and commercialization of functional food product items has significantly stimulated interest in several sectors over the past ten years, into its business, educational, and health application[1]. When chronic disorders co-exist with other diseases, managing them becomes a burden for both individuals and the healthcare system. This is such that the anticipated therapeutic result is unlikely to occur if one condition is treated without taking the other into account. For instance, diabetes causes other health challenges to develop, which in turn results in at least one type of comorbidity[2] from an assessment involving 1,024 individuals with 98.5% of the participants with at least one comorbid condition. Some of these patients had cases of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obesity, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, coronary heart disease, and stroke and particularly, the cases of co-morbidity diseases in the study were found to be duration-related, with the exception of obesity and hyperlipidemia.
Comorbidity disease research involving patients with type-2 diabetes was conducted by Ekoru et al.[3] with a population of 2784 people. According to this study, 71% of individuals had hypertension, 27% of the individuals had obesity, 11% had hyperglycemia, 35% had erectile dysfunction, 22% had hypercholesterolemia, and 4%, 15%, and 32% of people had cataracts, glaucoma complications and diabetic retinopathy, respectively. This led to the investigators’ conclusion during the study that the long duration of a disease, high body mass index, and old age are risk factors for complications and comorbidities in people with type-2 diabetes. More than half of the older population in developing nations have at least three chronic disorders, and more than a quarter have several comorbid diseases according to Rahmawati & Ahmad[4]. Additionally, in patients with inadequately managed comorbidities, there is an increased likelihood of drug-drug and drug-disease interactions, which can have negative effects[5]. Effective management of the diseases and a decreased risk of mortality will result from the proper treatment of coexisting ailments[6]. Therefore, developing a natural co-treatment therapy for individuals with comorbidities becomes essential. Therefore, this review highlights practical methods for controlling typical co-morbidities utilizing functional food.
-
Due to their distinct medicinal qualities and documented modulatory influence on enzymes which are therapeutic targets for the management of specific diseases, functional food products are in high demand and the market for these substances is expanding[7,8]. Functional meals enhance health status and lower the chance of developing illness repercussions in addition to serving nutritional purposes. They are either a part of diets or the main diet itself. Foods must continue to be consumed as foods and not as pills or capsules in order to qualify as functional foods[9]. Bioactive substances are present in certain fruits, vegetables, cereals, legumes, herbs, spices, oils, dairy products, and other functional food sources. Researchers have discovered that the bioactive substances in coffee, green tea, berries, pomegranates, olive oil, avocado, and ginger can help prevent weight gain. Anthocyanins (C15H11O+), quercetin (C15H10O7), polyphenols, catechins (C15H14O6), caffeine (C8H10N4O2), gallic acid (C7H6O5), capsaicin (C18H27NO3), and oleuropin (C25H32O13) are a few of these substances. Fatty acid oxidation, stimulation of lipid absorption, satiety, etc are some of the mechanisms of action of these phytochemicals[10]. Anthocyanin (C15H11O+), quercetin (C15H10O7), rutin (C27H30O16), green tea (C22H18O11), resveratrol (C14H12O3), pterostilbene (C16H16O3), ellagic acids (C14H6O8), and raspberry ellagitannins (C116H76O) are only a few examples of functional dietary components. For instance, dietary intake of anthocyanin which are the pigments in fruits and various vegetables, such as roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa) leaves, purple onions (Allium cepa), black rice (Oryza sativa), black beans (Phaseolus vulgaris), red sorghum (Sorghum bicolor), purple maize (Zea mays indurate) etc has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and control blood glucose levels[9].
Every food, regardless of whether it be a fruit or a regular meal, is functional if its composition is rich in bioactive chemicals. According to a study by Adebayo et al.[11], the almond fruit and seed is with kaempferol (C15H10O6), quercetin (C15H10O7), catechin (C15H14O6), gallic acid (C7H6O5), isoquercetin (C21H20O12), ellagic acid (C14H6O8), caffeic acid (C9H8O4), rutin (C27H30O16), epicatechin (C15H14O6), and chlorogenic acid (C16H18O9) attested from high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis, which further explains its role in the management of diabetes and erectile dysfunction. Also, garlic, purple onions, and white onions were discovered to block important enzymes linked to diabetes and hypertension[12]. These spices (garlic, white onion, and purple onion) contain apigenin (C15H10O5), caffeic acid (C9H8O4), p-coumaric acid (HOC6H4CH=CHCO2H), shogaol (C17H24O3), vanillic acid (C8H8O4), sinapinic acid (C11H12O5), protocatechuic acid (C7H6O4), myricetin (C15H10O8), and ferrulic acid (C10H10O4) from HPLC analysis. Therefore, it is reasonable to say that a number of additional foods that contain these substances may be helpful in controlling diabetes and hypertension as well as enhancing overall health.
-
In connection with functional foods’ importance in promoting health and wellness, they are renowned for their special therapeutic characteristics finding importance in alternative medicine for the treatment of chronic disorders[16] and the onset of comorbidity diseases. Individuals with comorbidities have a limited food selection based on their health conditions and as this can exacerbate their condition[17]. Hence, the need for vast, tasty, inexpensive, healthy, and therapeutic food options. Before a product can be referred to as a 'functional food', its health benefits must be supported by evidence from science[18]. They include, among other things, foods that are low in fat and sugar. For instance, low-fat diets lower the risk of obesity, hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and other associated chronic disorders, while low-sugar foods are known to lower the risk of diabetes and its complications. Metabolic syndrome may be reversed with increased dietary fiber consumption, fruits, and vegetables[19]. Wheat noodles have been supplemented with citrus peels and unripe plantain flour by Ademosun et al.[17] in diabetic rats. According to Oboh et al.[20], bioactive substances in plant-based sources enable the blocking of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-1 (ACE-1), a common enzyme linked to the onset of hypertension which pharmacologically these active substances are frequently chemically manufactured into medicines. Therefore, the potential of functional food products aids in the control of the comorbidities of diabetes and hypertension amongst other comorbidity diseases.
-
Oftentimes comorbidity may not even show any overt symptoms or telltale signs. The prevalence of comorbidity may occasionally be brought on by a chronic ailment that has been poorly controlled or by a disease that has been present for a long time. Therefore, it is crucial to address chronic illnesses as soon as possible in order to prevent complications and dependency diseases. Diabetes is one of the common diseases that is known to be associated with other disease risk factors. It is a metabolic condition that develops and worsens as a result of either low insulin secretion or insulin resistance/insensitivity. In the end, this causes a high blood glucose level[6, 13]. According to literary works, this condition typically co-occurs with other diseases, causing comorbidities, rather than occurring on its own. In the words of Iglay et al.[6], comorbidities with diabetes can include hypertension, cancer, kidney disease, dyslipidemia, cardiovascular disease, and dyslipidemia.
To illustrate, insulin resistance and diabetes stimulate the sympathetic nervous system and the renin-angiotensin system, which causes salt retention and ultimately results in hypertension. The causes of diabetes and hypertension share an adequate amount of similarity. Between the development of diabetes and hypertension, insulin is a mediating cause. By raising the amount of salt that is re-absorbable by the kidney and stimulating the sympathetic nervous system and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, insulin insensitivity can cause hypertension. The transport of glucose and insulin to skeletal muscle cells can also be altered by hypertension. Insulin resistance eventually results in diabetes mellitus which can impede glucose absorption, and untreated insulin resistance can lead to problems such as diabetes retinopathy, nephropathy, and diabetic neuropathy. In addition to this, numerous neurological disorders and other comorbidities can develop as type-2 diabetes progresses[14].
Another typical example of a comorbid disease is the improper functioning of the penile arteries that defines erectile dysfunction, which is typically brought on by vascular dysfunction and cardiovascular illnesses. Vasoconstriction and high artery blood pressure are frequently connected with erectile dysfunction. This is as a result of the link between both pathologies wherein, occurrence of elevated blood pressure subsequently leads to endothelial dysfunction and damaged penile arteries. With this damage, there is the flaccidity of the penis due to decreased penile blood flow termed as erectile dysfunction seen to occur more in hypertensive men[15]. Also, as a significant risk factor for developing cardiovascular illnesses and type-2 diabetes mellitus, obesity continues to be a global health concern. Due to its function in raising low density lipoprotein, which causes atherosclerosis (blockage of the heart arteries), hypertension, and myocardial attacks, it is also a risk factor for hypertension. Obesity and type-2 diabetes have been linked by insulin resistance, according to the findings of Kashif et al.[14].
Pathogenesis of common comorbidity diseases
Diabetes and hypertension
-
Diabetes is becoming a more significant health issue worldwide[13]. According to numerous research, diabetes is the most prevalent metabolic condition and it causes comorbidities by affecting a number of internal organs[3]. The hormonal imbalance that results in an unregulated blood glucose level damages the blood vessels in many organs, such as the kidneys, eyes, and so on, and is the likely cause of the comorbidities and other effects. Seventy one percent of the 2,784 people with type-2 diabetes who were diagnosed in the study of Ekoru et al.[3] also had hypertension. In contrast to other co-occurring diseases discovered, Akin & Bölük[2] reported that 84.9 % of a total diabetes population had a high prevalence of hypertension. Several studies have shown that there is typically a high prevalence of hypertension among diabetic patients with comorbidities[2,5,13,21] similarly, there is typically a high prevalence of diabetes among hypertensive patients with comorbidities[4]. If hypertension is present together with other comorbidities, treatment might be challenging. This is because comorbidities affect how hypertensive patients are treated and how well they respond to therapy, necessitating more intensive and sophisticated therapeutic management strategies for these patients than for those without comorbidities[4].
Obesity and diabetes
-
According to Küster-Boluda & Vidal-Capilla[18], obesity is considered a disease epidemic of the 21st century and has increased the burden of chronic diseases worldwide[22]. A total of 27% of the 2,784 type-2 diabetes cases in a study by Ekoru et al.[3] were also diagnosed with obesity. Akin & Bölük's study from 2020 revealed that obesity was prevalent in 54.4% of the overall population of diabetics[2]. Obesity is a risk factor for diabetes because it lowers glucose tolerance. and according to another study by Jha & Kusum[23], 68 % of all diabetics had obesity-related diagnoses. Obesity and diabetes are closely related and it's believed that excess weight contributes to 90% of occurrences of type 2 diabetes mellitus. These investigations showed that people with type-2 diabetes frequently have obesity as an associated illness. Thus, the consumption of fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products is recommended for obese people[24]. Due to the serious threat of obesity, experts have gone further than ever in finding a cure for this distressing chronic disease by looking at natural sources that contain anti-obesity compounds. With full knowledge that they include large amounts of unsaturated fatty acids, fibers, and bioactive chemicals capable of regulating metabolic illnesses, these ingredients, which are primarily derived from plants, have been proven to be suitable for generating functional food items[22].
Hypertension and erectile dysfunction
-
The global health issue of hypertension affects people from all social classes, especially those in high- and middle-income countries[25]. By 2025, there are estimated to be 1.56 billion hypertension patients worldwide, as referenced by Ajeigbe et al.[25]. The mortality rate will unquestionably rise as a result of this, particularly in circumstances where the patients have concomitant conditions. In the opinion of Rahmawati & Ahmad[4], common hypertensive patients have cases of comorbidity. Therefore, it is inevitable that people with hypertension would require methods for controlling it. Both people with and without complications from hypertension are at risk of developing comorbidity with other diseases, as well as death in the case of comorbidity with hypertension. As a result, treating hypertension early on as a sickness or comorbidity will significantly lower the likelihood of problems[25] as it helps in improving the outcome of high blood pressure. Erectile dysfunction is one of the often-occurring morbidities that co-occur with hypertension. Erectile dysfunction has significantly worsened the health of hypertension patients and has also led to a decline in health of men who are suffering from the condition.
Despite patients' reluctance to discuss their sexual issue, studies have indicated that more than 150 million men worldwide suffer from erectile dysfunction to a certain extent. This suggests that there are more patients whose information has been overlooked because they were reluctant to share it. In individuals with hypertension, the prevalence of hypertension is often twice as high as in people with normotension state. When erectile dysfunction coexists with hypertension, it can be challenging to successfully control it, especially when utilizing a pharmacological intervention to prevent future consequences since when a patient has arterial hypertension, the anti-hypertensive pharmaceutical therapy method is likely to contribute to the development of erectile dysfunction[15]. Given that atherosclerosis is one of the anomalies that define erectile dysfunction, it is obvious that hypertension or cardiovascular disease is one of the risk factors for erectile dysfunction. Since the penis is a vascular system extension, problems with it also affect the cardiovascular system and vice versa. When blood flow through the arteries is low, the penis becomes flaccid; conversely, a high blood flow through the arteries results in an erect penis[26]. As a result, problems with the cardiovascular system always leads to problems with the penile, and high blood pressure prevents penile erection (Fig. 1).
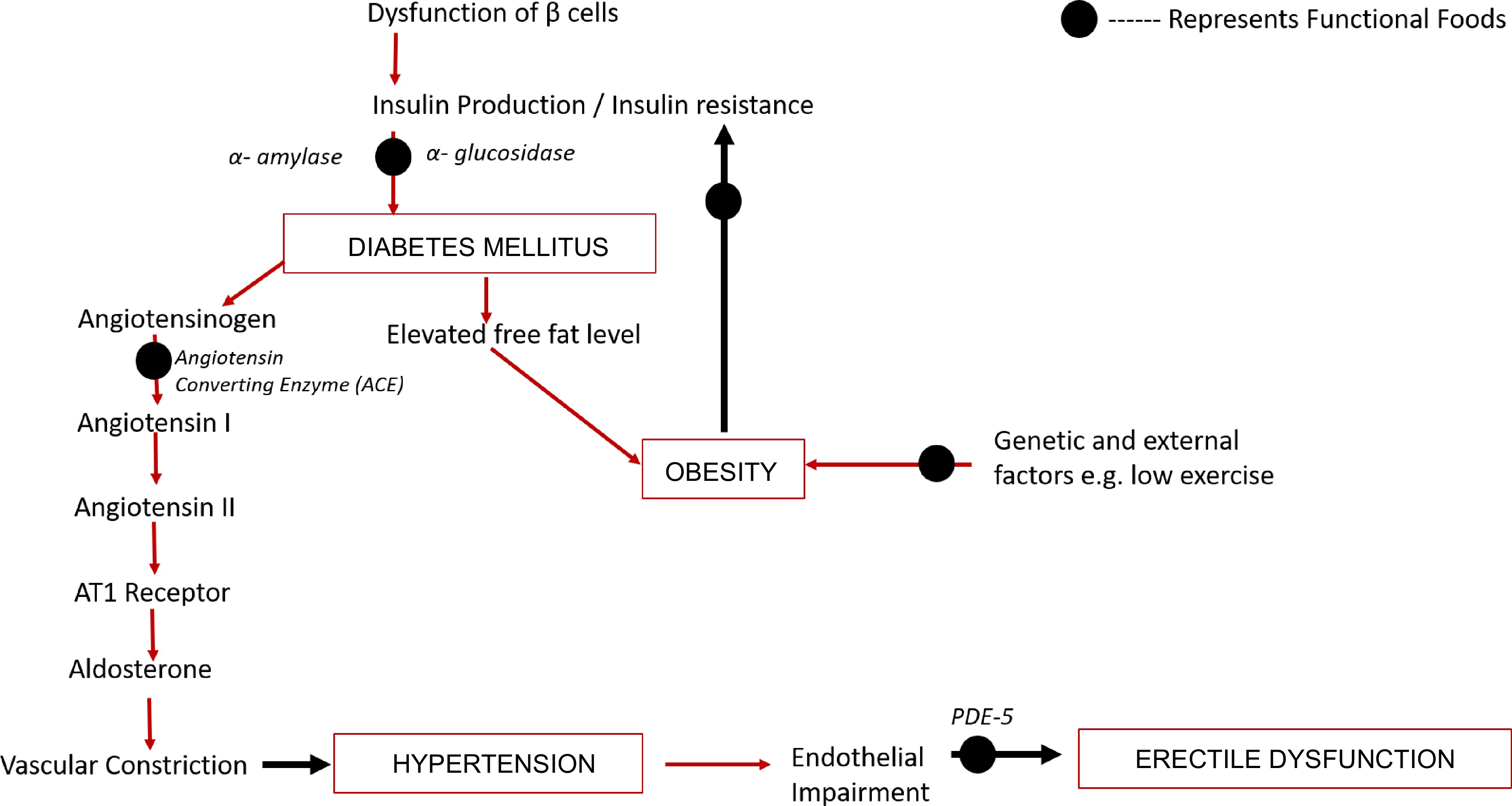
Figure 1.
Flowchart shows the notable target points where functional foods can modulate the mechanism behind the onset of comorbidities.
Table 1. Relevance of functional food sources in the management of comorbidity diseases.
S/N Functional food sources Bioactive compounds Modulatory enzymes/signaling molecules Comorbidity managed Examples of functional food products References 1. Citrus paradisi (Grapefruit) peel Naringin, Rutin, Caffeic Acid, Quercitrin, Quercetin, Kaempferol Glycoside Nitric oxide (NO) Adenosine deaminase (ADA) PDE-5 antioxidant enzymes activities Erectile dysfunction Yoghurt Ademosun et al.[41]; Oboh & Ademosun[42] α-Amylase α-Glucosidase ACE-1 Diabetes, Hypertension 2. Citrus sinensis (Orange) & Citrus limon (Lemon)
Peel-Essential oilLimonene, β-Myrcene, α-Pinene, β-Pinene, Linalool β-Caryophyllene, Linalyl acetate, 1,8-Cineole α-Amylase α-Glucosidase Diabetes Syrup Oboh et al.[43]; Oboh & Ademosun[51] ACE-1 Hypertension Parfait 3. Pepper Mint Powder Eriocitrin α-Glucosidase Hypertension Beverage Cam et al.[44] ACE-1 Diabetes 4. Terminalia catappa (Almond) leaf & stem bark Galic Acid, Catechin, Caffeic Acid, Ellagic Acid, Chlorogenic Acid, Rutin, Quercetin, Resveratrol. ACE-1 Hypertension Pasta Oyeleye et al.[45] PDE-5 Arginase Erectile dysfunction AChE 5. Psidium guajava (Guava) Catechin, Protocatechuic Acid, Carvacrol, P-Coumaric Acid, Eugenol, Caffeic Acid, Rosmarinic Acid, Vanillic Acid, Ferulic Acid, Shogaol, Glycitein, Isoeugenol Apigenin, Diadzein ACE-1 Hypertension Jelly Oboh et al.[46] Milk shake 6. Citrus sinensis (Orange) peel Epicatechin, Kaempferol, Isoquercitrin, Rutin, Quercetin Naringin, Kaemferol Glycoside, Caffeic Acid Increased NO Erectile dysfunction Noodles Ademosun et al.[47]; Oboh & Ademosun[51] PDE-5 AChE Adenosine deaminase (ADA) 7. Ficus asperifolia (Fig) leaves Salicylic Acid, Vanillic, Syringic, Naringenin, Kaemferol, Luteolin, Quercetin, Ellagic Acid, Myricetin, Chlorogenic Acid, Salicylic Acid, Vanillic, Syringic, Naringenin, Kaemferol, Luteolin, Quercetin, Ellagic Acid, Myricetin, Chlorogenic Acid Lipase Enzyme Hyperlipidemia cookies Ajeigbe et al.[38] Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), Glutathione-s-transferase (GST), Catalase (CAT) Hypertension 8. Ripe and unripe Plantago major (plantain) peel Gallic Acid, Chlorogenic Acid, Ellagic Acid, Epicatechin, Quercitrin, Kaempferol Catechin, Caffeic Acid, Quercetin, Rutin Arginase ACE-1 PDE-5 AChE Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Erectile dysfunction Bread Oboh et al.[48]; Oyeleye et al.[49] 9. Terminalia catappa (Almond) fruit Apigenin, Coumaric Acid, Shogaol, Protocatechuic Acid, Ferrulic Acid, Myricetin, Vanillic Aid, Caffeic Acid Blood glucose level Diabetes Jam Adebayo et al.[11] PDE-5 Erectile dysfunction 10. Physalis angulate (cherry) leaves Caffeic acid, rutin, chlorogenic acid, gallic acid, quercetin, quercitrin, kaempferol. Arginase ACE-1 PDE-5 AChE Erectile dysfunction Drink Akomolafe et al.[50] 11. Ficus exasperata (Fig) leaves Quercitrin, Chlorogenic, Caffeic, Rutin, Isoquercitrin ACE-1 Hyper- cholesterolemia hyperlipidemia Cookies Oboh et al.[20] 12. Newbouldia laevis leaves Ellagic Acid, Gallic Acid, Rutin, Chlorogenic Acid Arginase ACE-1 PDE-5 AChE Erectile dysfunction Crackers Akomolafe et al.[50] 13. Hunteria umbeluta seeds & Cylicodiscus gabunensis bark Caffeic Acid, Apigenin,Ellagic Acid, Gallic Acid, Luteolin, Quercetin, Rutin, Chlorogenic Acid α-Amylase α-Glucosidase Diabetes Non-alcoholic beer Akerele et al.[56], Oboh et al.[43] Arginase PDE-5 Erectile dysfunction 14. Viscum album (Mistle toes) Resorcinol, Salicylic Acid, Coumarin, Cinnamic Acid,
O-Coumarin, Vanillic Acid, Protocatachuic Acid, Phenol,
P-Coumarinα-Amylase α-Glucosidase Diabetes Smoothie Oboh et al.[12] ACE-1 Hypertension 15. Moringa oleifera (Moringa) Gallic Acid, Catechin, Chlorogenic Acid, Ellagic Acid, Epicatechin, Rutin, Quercitrin, Isoquercitrin, Quercetin, Kaempferol ACE Hypertension Ice cream Oboh et al.[46] Arginase erectile dysfunction 16. Mentha spicata (Spearmint) powder Rosmarinic acid α-glucosidase Hypertension Beverage Cam et al.[44] ACE-1 Diabetes 17. Citrus maxima (Shaddock) peel Rutin, Narirutin, Tangeretin, Sinensetin, Nobiletin, Naringin, Aringenin,Isosinensetin, Auraptene, Neoponcirin LDL-Cholestrol ROS Antioxidant Enzymes Activities Obesity, Hyperlipidemia, Ice cream Ademosun et al.[31], Oboh & Ademosun[42]. α-Amylase α-Glucosidase ACE-1 Diabetes, Hypertension 18. Piper nigrum (Black pepper) essential oil α-pinene, β-pinene, cis-Ocimene, Myrcene allo-Ocimene, α-Thujene, gamma-Terpene, 1,8-Cineole. α-Amylase, α-Glucosidase Diabetes Cake Oboh et al.[20] ACE-1 Hypertension The role of functional foods in common comorbidity diseases
Functional foods in the management of diabetes and hypertension
-
According to research conducted by Brown et al.[9] quercetin-containing diets were found to improve insulin sensitivity whereas rutin-containing diets reduced hypertension and obesity in rats. Since it is widely acknowledged that angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are the first line of treatment for hypertension patients, foods with these characteristics must be welcomed in the treatment of comorbidities[19]. It has been looked at if specific plants and herbs have anti-diabetic characteristics. Among the plants in this group are cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum), ginger (Zingiber officinale), aloe vera, cocoa (Theobroma cacao), garlic (Allium sativum), coffee (Coffea arabica), soybean (Glycine max), and walnut (Juglans regia)[27,28]. Peptide-rich diets have helped people with diabetes and hypertension live healthier lives for decades. There are ACE-1 inhibitory peptides, especially in cow milk. Based on in-vitro analyses, milk from other animals, such as yak and goat, also includes inhibitory peptides, despite the fact that clinical trials have not been conducted on these other milk sources. ACE-1 inhibitors can also be found in meat and fish peptides. Plant sources also contain peptides with soybean as an illustration[29] as represented in Table 1. A helpful supplement for managing diabetes and hypertension through food is soybean, which has an inhibitory effect on amylase and ACE-1[30] and there are reports that systolic and diastolic blood pressure have decreased as a result of its inclusion[29]. Another supplement family that has been shown to enhance the therapeutic qualities of food is the citrus family. These plants are effective inhibitors of the enzymes-amylase and -glucosidase, which are connected to the development of type-2 diabetes: sinensis, maxima, reticulata, limetta, macrocarpa, aurantofolia, and hystrix. Because the inhibition of these enzymes is essential for regulating glucose metabolism, it is advantageous as a preventative and management medication for type-2 diabetes[8]. Citrus peel had an anti-diabetic impact by lowering blood glucose levels in rats fed unripe plantain noodles flavored with citrus peel as compared to the control groups[31].
Functional foods for obesity and diabetes comorbidity
-
Functional foods have been shown to be more successful than conventional drugs at treating obesity while posing a lower risk of side effects[9]. Functional foods frequently derived from plants including fruits, grains, and vegetables have been shown to reduce body weight increase and the weight of white adipose tissue[22] as illustrated in Fig. 1. Patients who are overweight or obese must follow low-calorie diets. Foods with a high glycemic index encourage insulin resistance. Therefore, diabetic patients should include foods with low glycemic index in their diets as this would successfully manage the comorbidity of obesity and diabetes[32]. Green tea contains significant levels of polyphenols (catechins, C15H14O6), which improve insulin sensitivity and metabolic control by enhancing fat oxidation. This results in an increased metabolic rate and better weight management[52]. With the help of cinnamaldehyde (C9H8O), cinnamon has the power to affect metabolic functions and enhance insulin sensitivity in diabetics for improved metabolic control[53]. Cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum) increases insulin sensitivity and improves insulin signaling. Due to the abundance of anthocyanins (C15H11O+). Berries play a role in metabolic system regulation and in ensuring insulin sensitivity by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and improving lipid metabolism[54]. In contrast, turmeric (Curcuma longa) modulates lipid metabolism, reduces inflammation, and improves mitochondrial function to induce insulin sensitivity, as seen in increased glucose uptake and improved insulin signaling in diabetic mice[55].
Functional foods in the management of hypertension and erectile dysfunction
-
Given that there is a connection between the food we eat and our general health status, nutrition can both improve one's health status as well as cause issues. High-fat diets with a low proportion of meals rich in vegetables can cause consequences from a blood pressure imbalance. Studies have also shown that some food elements can provide anti-hypertensive treatment, thus it is advisable to prompt the development of functional food products to manage the comorbidity of hypertension and erectile dysfunction[25] (Table 1). Omega-3 fatty acids are one of these active substances. Due to their antihypertensive properties[33], omega-3 fatty acids additionally regulate the inflammatory signaling that controls cytokine expression and prostaglandin synthesis, both of which are important in controlling arterial pressure. Because plant oils are often unsaturated, foods containing them are healthy for the body. Unsaturated fats can assist one's health and lower the risk and difficulties of hypertension because they are present in foods like soybean oil, flaxseed oil, avocado oil, and peanut oil[25].
Notable functional foods with promising roles in comorbidity diseases
-
Citrus peels are said to contain bioactive chemicals for the control of elevated blood pressure according to the research of Ademosun et al.[7]. Citrus peels exert a hypertensive effect by blocking ACE-1 and lowering the production of Angiotensin II, a significant vasoconstrictor that plays a role in the development and progression of hypertension[8]. By decreasing angiotensin II and enhancing dilatation, root vegetables like garlic (Allium sativum), beetroot (Beta vulgaris), ginger (Zingiber officinale), and grape (Vitis vinifera) reveals their anti-hypertensive properties[33]. Medical professionals advise against consuming salt if you have hypertension or erectile dysfunction[34, 35]. This is due to the fact that excessive salt consumption causes the kidney to retain more fluid and also raises blood volume. As a result, blood passes through the body at a higher pressure, which requires the heart to work harder to pump blood into the arteries[36] (Fig. 1). Dietary potassium has been reported to significantly lower blood pressure and be helpful in the treatment of cardiovascular illnesses and hypertension[37] through membrane channel to generate an influx of potassium and an efflux of sodium simultaneously, lowering blood vessel pressure.
Other fruits that lower blood pressure include Chinese celery, bananas, mango peel, which inhibits adipogenesis, and concord grape (Vitis vinifera) juice’s polyphenols. Additionally, potato and its metabolites contribute to ACE inhibition[30]. A typical example is the Hibiscus sabdarifa, whose leaves are also known as zobo leaves[25]. For rats with hypertension induced by L-NAME, Ficus asperifolia caused a reduction in blood pressure. When compared to the control group, the rats with high blood pressure showed a drop in blood pressure. The herb's anti-hyperlipidemia and weight gain management abilities are further apparent[38]. Additionally, the polyphenols in green tea and cocoa lower diastolic blood pressure[30]. In the human diet, replacing carbs with proteins (such as soybeans) has also been proven to have antihypertensive effects[33] and Mohammed[30], identified seaweed peptides which promote vasodilation, lower blood pressure, and inhibit angiotensin-converting enzymes.
Dietary fiber
-
Dietary fibers have become popular for their ability to prevent diabetes and obesity. They have been discovered to play a significant role in limiting gastrointestinal food absorption, which slows both the pace of gastric emptying and the rate of nutritional absorption. Studies have shown that consuming foods high in fiber over an extended length of time, such as pectins, gum, cellulose, and -glucans, can reverse body weight increase[22]. Juice from plantain stems is used to treat diabetes and obesity. Seaweeds have a high fiber content, which helps lower blood sugar, triglycerides, and obesity. Fiber-rich diets increase lipolysis while decreasing lipogenesis[30]. Citrus peels from orange (Citrus sinensis) and shaddock (Citrus maxima) trees are high in fiber and helpful for controlling weight. They have been integrated into several functional food products as a diet supplement and play a part in the development of those foods' therapeutic capabilities and other desirable traits. Among other foods, some of these include drinks, yoghurt, jam, ice cream, cakes, biscuits, and noodles[8]. Additionally, citrus peels' phenol and antioxidant characteristics have been linked to weight management and anti-obesity effects in rats fed citrus peel-enriched ice cream as opposed to the control group, according to Ademosun et al.[31].
Probiotics and prebiotics
-
Prebiotics and probiotics are crucial for maintaining the balance of the immune system. Prebiotics are the dietary sources that help probiotics grow in order to maintain a balanced gut microbiome, whereas probiotics are bacteria that dwell in the host[33]. Studies have demonstrated that type-2 diabetes and obesity can be influenced by gut microorganisms, and some clinical studies have proven that some probiotics can reduce weight growth and body fat. These probiotics include Lactobacillus gaserri, as a good example. Probiotics begin with a method that controls hunger, the host's metabolic process, inhibits the absorption of lipids, and maintains liver homeostasis[22]. Prebiotic-enriched foods are helpful for managing obesity and improving insulin sensitivity. Particularly, Naringin (C15H12O5) and Hisperidin (C28H34O15) are bioactive substances that are vital in promoting the development of advantageous bacteria and restraining harmful microbes in the gut. Citrus peels contain large amounts of these substances, which have prebiotic effects[8].
Phytochemicals in fruits, vegetables, and herbs
-
Marrelli et al.[39] identified the advantages of Allium cepa for health. The common onion, Allium cepa, has shown anti-obesity qualities by having the ability to inhibit lipase and adipogenesis. Both in-vitro and in-vivo investigations, discussed by Marrelli et al.[39], demonstrated that onion extract dramatically reduced the amount of cholesterol in the liver when rats were fed a high-fat diet. One group had a high-fat diet supplemented with onion powder, whereas the other received a high-fat diet alone. Another class of compounds found in fruits is the compound called anthocyanins which lowers blood sugar and improves insulin sensitivity. Pomegranate (Punica granatum), watermelon (Citrullus lanatus), strawberry's anthocyanin (C15H11O+) and resveratrol (C14H12O3) also contribute in the prevention of diabetes by enhancing insulin sensitivity, exerting hypoglycemic effects, and lowering low density cholesterol. Citrus polyphenols' act as a lipolytic mediator and prevent weight gain. Insulin resistance and body weight growth are decreased by cocoa powder. Blueberry both improves and raises insulin sensitivity. According to Venkatakrishnan et al.[33] and Mohamed[30] cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum), clove (Syzygium aromaticum), ginger (Zingiber officinale), turmeric (Curcuma longa), and curcumin significantly suppress adipogenesis and enhance insulin sensitivity. Similarly, Shi et al.[40] identified that blueberries contain tannins that are known to prevent the onset of diabetes and have anti-obesity characteristics. According to Ajeigbe et al.[38], weight gain was regulated in L-NAME-induced hypertension rats fed Ficus asperifolia leaves which can serve as an herb in fortified biscuits
-
As more functional foods become apparent with their obvious overwhelming benefits in health maintenance. They can thus serve as a dependable medicine for illness prevention and management. Particularly, with the rise in comorbidity disease conditions, the development of functional food products would become more crucial in the management of comorbidities. Nevertheless, more investigation into additional functional foods which may be able to control the enzymes that attach, react or inhibit comorbidity.
-
The data that support the findings of this study are made available by contacting the author (olufunke2017@gmail.com).
-
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
- Copyright: © 2023 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press on behalf of Nanjing Agricultural University. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Awodire EF, Ademosun AO, Ajeigbe OF, Oboh G. 2023. Functional foods and their applications in managing globally common disease-linked comorbidities. Food Materials Research 3:34 doi: 10.48130/fmr-0023-0034
Functional foods and their applications in managing globally common disease-linked comorbidities
- Received: 24 May 2023
- Accepted: 28 August 2023
- Published online: 04 December 2023
Abstract: A disturbing amount of people are being diagnosed with several chronic ailments, which raises the prevalence of comorbidity diseases. Comorbidity frequently emerges from a disease state's first complications. The conventional medications used to treat these comorbidities frequently have negative side effects and may be hazardous to organs that were not the medications' intended targets. As a result, the necessity to create more efficient strategies to manage these chronic illnesses emerged. Bioactive substances and functional food have been utilized for therapeutic purposes over time without experiencing any discomfort, and several studies have demonstrated the health benefits of these substances and foods. In order for a food product to serve not only as a nutritional source but also for medical and therapeutic purposes, functional food products are created by integrating bioactive substances that have been shown to be helpful in the management of specific chronic conditions. In this review, the management of common non-communicable diseases namely diabetes, hypertension, obesity and erectile dysfunction and the possible functional foods that can be used to manage them singularly and as comorbidity conditions is taken into account.
-
Key words:
- Comorbidity /
- Functional food /
- Diabetes /
- Hypertension /
- Erectile dysfunction












