-
Since the publication of this article, the authors have noted several minor issues requiring corrections:
(1) Error in the Abstract
In the Abstract of the published article, instead of "A. alternate", it should be in italic as "A. alternate".
(2) Error in the section "Determination of antifungal activity of Germacrene D" under Materials and methods
In the published article, "bacterial" should be replaced with "fungus" to align with the original intent.
(3) Error in the section of "Differences in leaf epidermis structure of resistant and susceptible germplasms" under Results
The term "the lower epidermal hairs" was non-standard and has been revised to "the lower epidermal trichome".
(4) Errors in the figures
In Figure 1, C. japonese was mistakenly labeled as C. japones (now corrected); in Figure 2, 'A. parviflora' was erroneously labeled as 'C. parviflora' (now corrected);
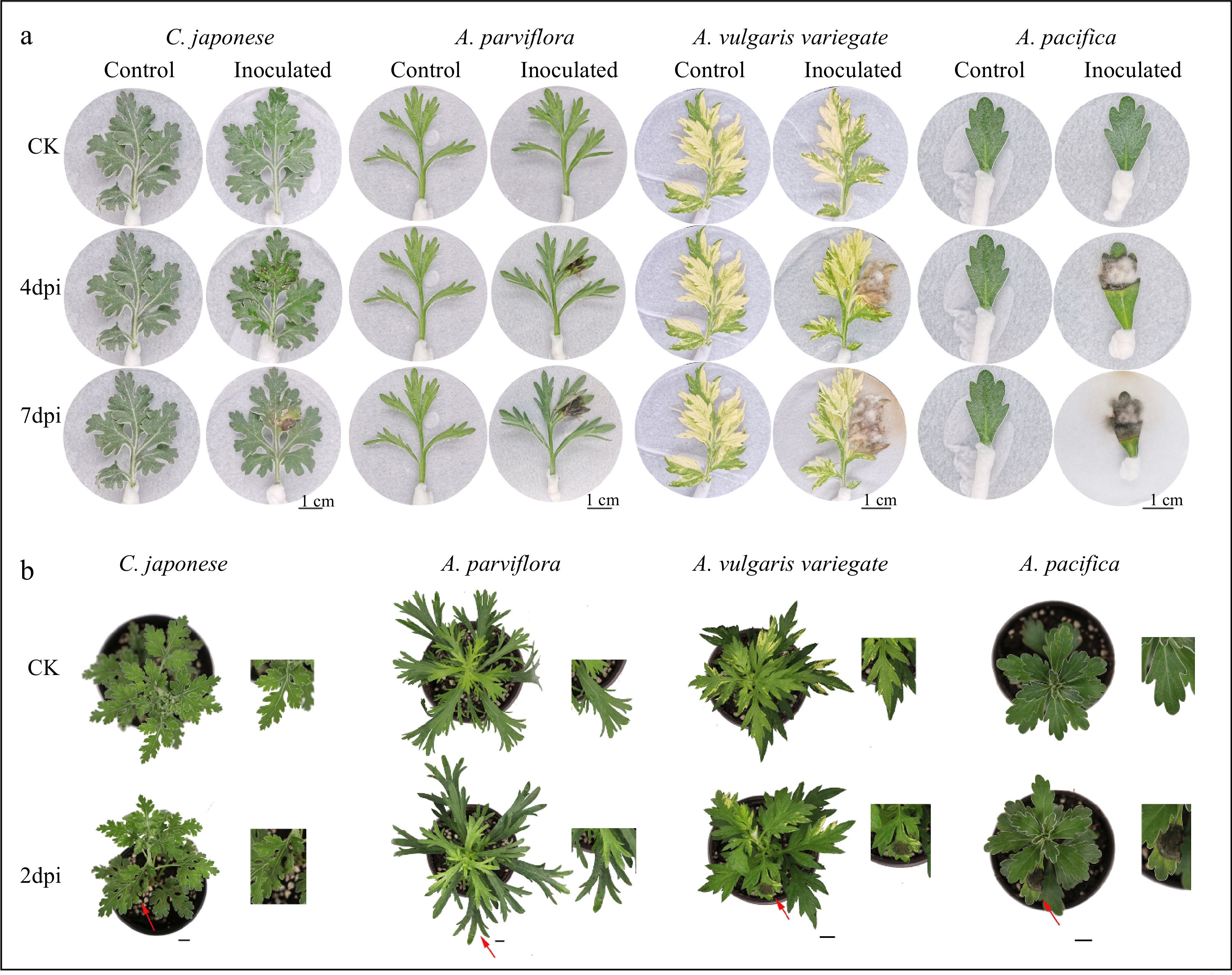
Figure 1.
Differences in disease phenotype of different plants after inoculation. From left to right: the disease degree of leaves deepens. n = 15. (a) Disease symptoms on 4 and 7 d after inoculation of isolated leaves. (b) Disease symptoms of whole plants at post 2 d inoculation. Scale bar = 1 cm.
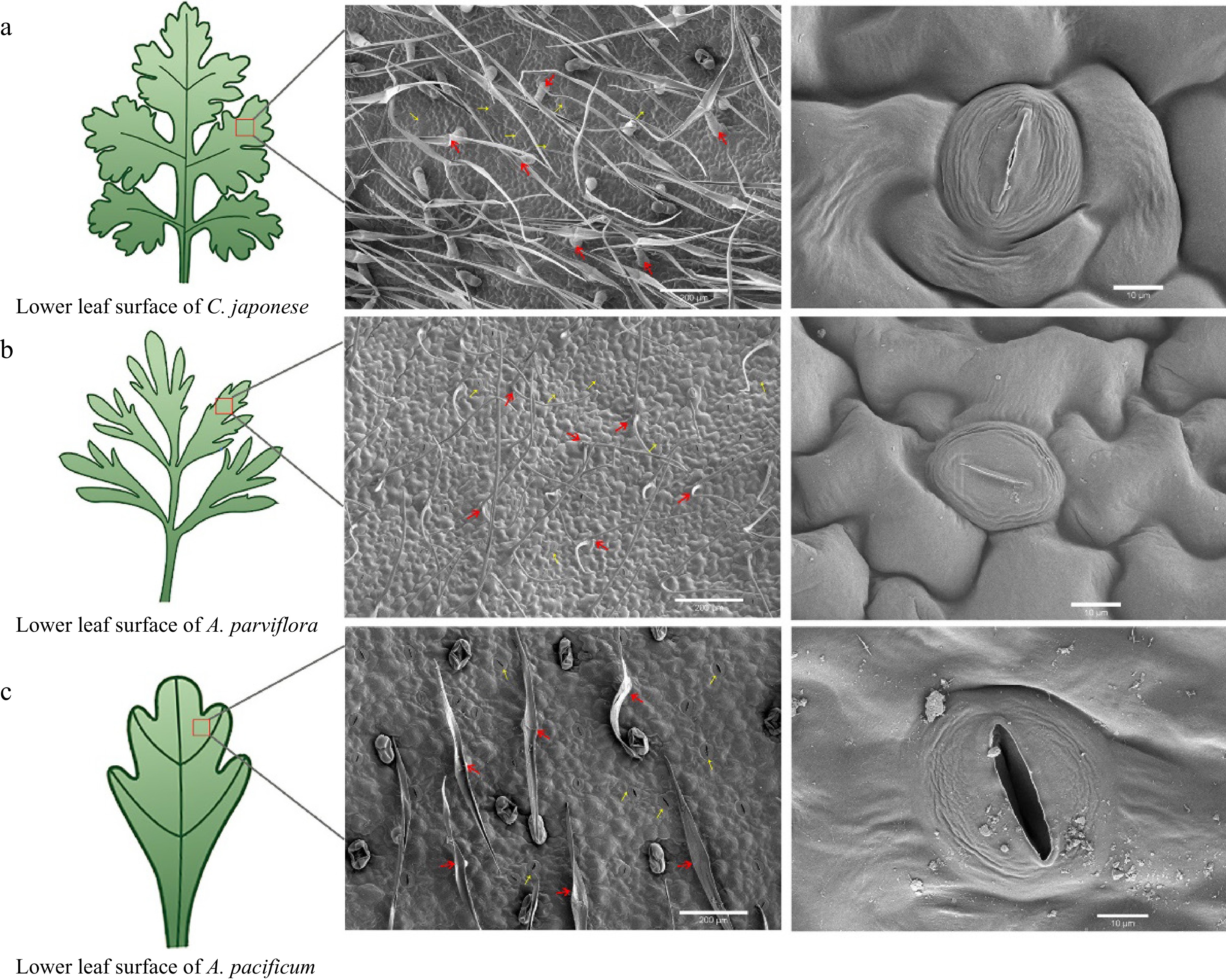
Figure 2.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the lower epidermis of leaves from disease-resistant and susceptible materials. From left to right, the parts that were observed under the scanning electron microscope (red box part) showed the distribution and shape of trichome and stomata respectively. The red arrows indicate epidermal hairs, and the yellow arrows point to the stomata.
The authors would like to apologize for these errors.
The original article has been corrected in the HTML and PDF versions.
HTML
- Copyright: © 2025 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press, Fayetteville, GA. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
| Zhan Q, Li W, Liu Y, Zhao S, Chen S, et al. 2025. Author Correction: Genetic resources resistant to black spot (Alternaria alternate) identified from Chrysanthemum-related genera and potential underlying mechanisms. Ornamental Plant Research 5: e004 doi: 10.48130/opr-0025-0008 |












