-
When NIR radiation is incident on the surface of a fruit or vegetable, a fraction is reflected at the surface (known as specular reflectance) while the remainder penetrates into the fruit. Upon entering the fruit tissue, photons scatter before being absorbed or exiting from the fruit at various distances from the incident point (diffuse reflected light). The scattering of light is dependent on the physical micro structure of the fruit (i.e., density, composition, cell structure, and extra- and intra-cellular matrices of fruit tissue) and the absorption of light refers to the chemical properties[1]. For intact horticultural produce, the spectral signals measured by NIR systems contain information on absorption and scattering of both the skin and internal tissue. The correlation between the quality attributes and the spectral information is generally based on the chemical and physical properties of both the skin and internal tissue, complicating the construction and interpretation of calibration models[2]. Few investigations have been made on the optical properties and the depth of penetration of NIR radiation of intact fruit. The depth of penetration, also known as the information depth, is defined as 'the maximum distance for NIR light traveling inside a sample matrix along the depth direction'[3] and this varies with wavelength. Understanding the depth of penetration in various wavelength regions for transmission and reflectance modes would enhance calibration model development and subsequent model interpretation and inform experimental design for industry implementation.
Hruschka[4] explains that NIR measurement can introduce a sampling error, because the radiation penetrates less than 2 mm into a sample, so only a portion of the sample is actually being measured. Greensill & Walsh[5] report that the intensity of the detected light in a fruit decreases exponentially with the distance from the source, in accordance with the Beer-Lambert law. The rate of exponential decay is related to the scattering and absorption properties of the tissue and are influenced by the skin and other features in the fruit, such as the core and segment boundaries[6]. While there have been some theoretical/simulation studies of the light path within the fruit[1,6−8], very little is known about the actual path that light takes inside an intact fruit, and the attenuation it experiences in different regions of that fruit. Knowing the light distribution in the fruit may enable the selection of the most effective NIR mode of measurement for a given fruit type or shape[6] and hence optimise the non-invasive assessment method.
In this study the wavelength dependence of the depth of penetration into 'Hass' avocado fruit of NIR radiation in both transmission and reflectance modes were investigated.
-
Whole mature hard green 'Hass' avocado (Persea Americana Mill) fruit were cut in half (longitudinally), the seed removed, and the cut surface trimmed to remove the seed cavity providing a flat surface. Spectral measurements of five fruit cut in half, providing 10 samples, were collected in both transmission and reflectance modes as detailed below. For both modes, the sample depth at the spectral collection point was recorded. Once the spectrum had been collected for the known thickness, a thin longitudinal slice (1−2 mm) of the avocado fruit from the cut flat side was removed using a V-slicer. The thickness of the now trimmed sample was recorded using Vernier calipers before subsequent spectral collection. This process was repeated until the sample was reduced to approximately 1−2 mm in thickness. One spectrum was captured for the sample at each trimmed thickness.
Spectral acquisition
-
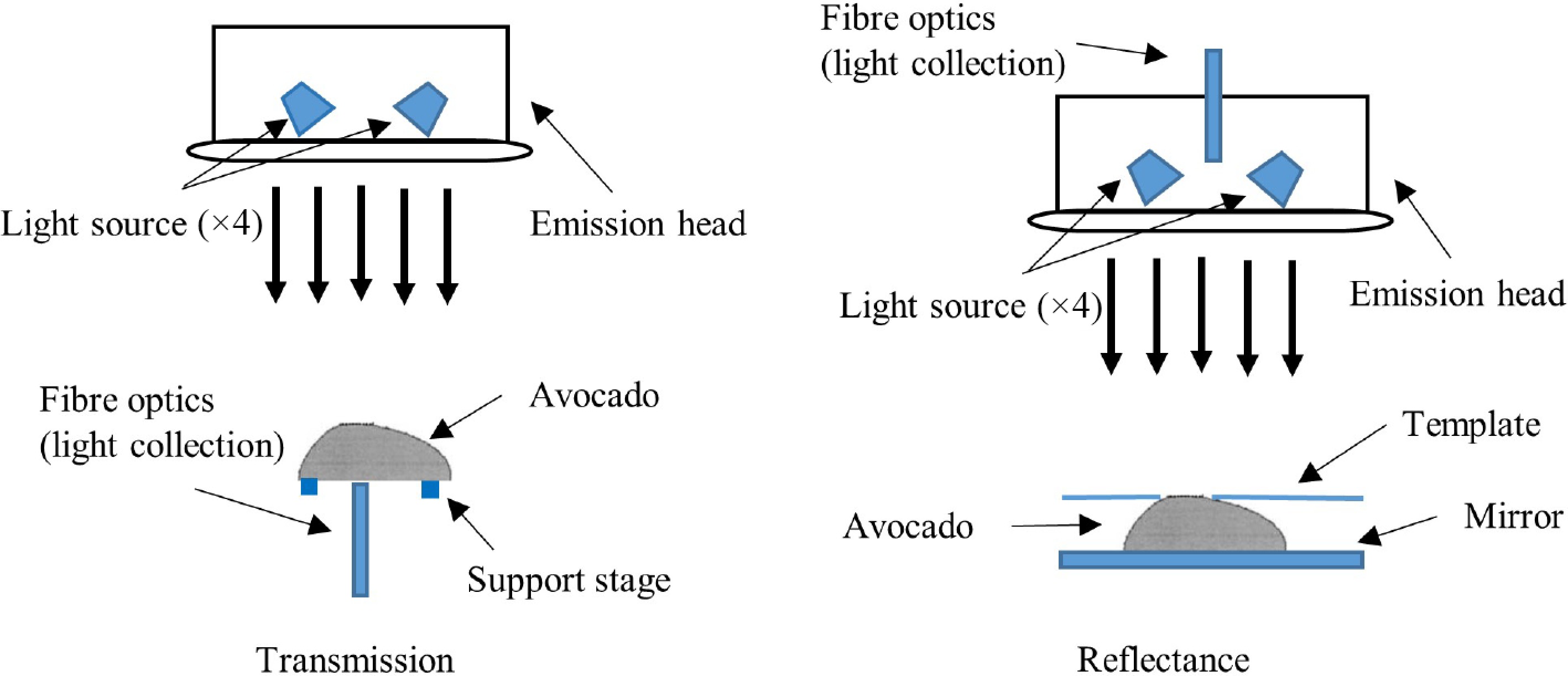
For transmission mode, a Bruker Matrix-F Fourier Transform (FT)-NIR spectrophotometer which measured in the 12,820–4,000 cm−1 (780–2,500 nm) range, linked with an external fibre-coupled emission head utilising a 4 × 20 W tungsten halogen light source was employed. The fibre optic probe in the emission head used to relay the spectral signal to the Matrix-F spectrophotometer was removed from the emission head and placed directly under the emission head light source at a distance of 170 mm to provide a transmission configuration (Fig. 1). For spectral collection, the avocado half with a known thickness was placed onto the fibre optic head with the cut side to the fibre optic head and the skin side to the light source.
For reflectance mode, the Bruker Matrix-F FT-NIR spectrometer and emission head was again employed (Fig. 1). The cut flat surface of the avocado half was placed onto a mirror to provide a reflective surface and the skin side of the avocado was presented to the light source. A template was placed at a path-length of 170 mm from the light source to the skin surface of the thickest section of the fruit to provide a spectral scan area on the avocado sample of 30 mm in diameter. In obtaining each sample spectrum, 8 scans at a resolution of 16 cm−1 were collected and averaged.
Typical transmission and reflectance (absorbance) mode spectra for an avocado fruit at varying thicknesses (values of which were determined after cutting) are shown in Fig. 2. The error associated with the thickness measurements was estimated to be less than 1 mm, which accounts for nodule sizes and curvature of the fruit.
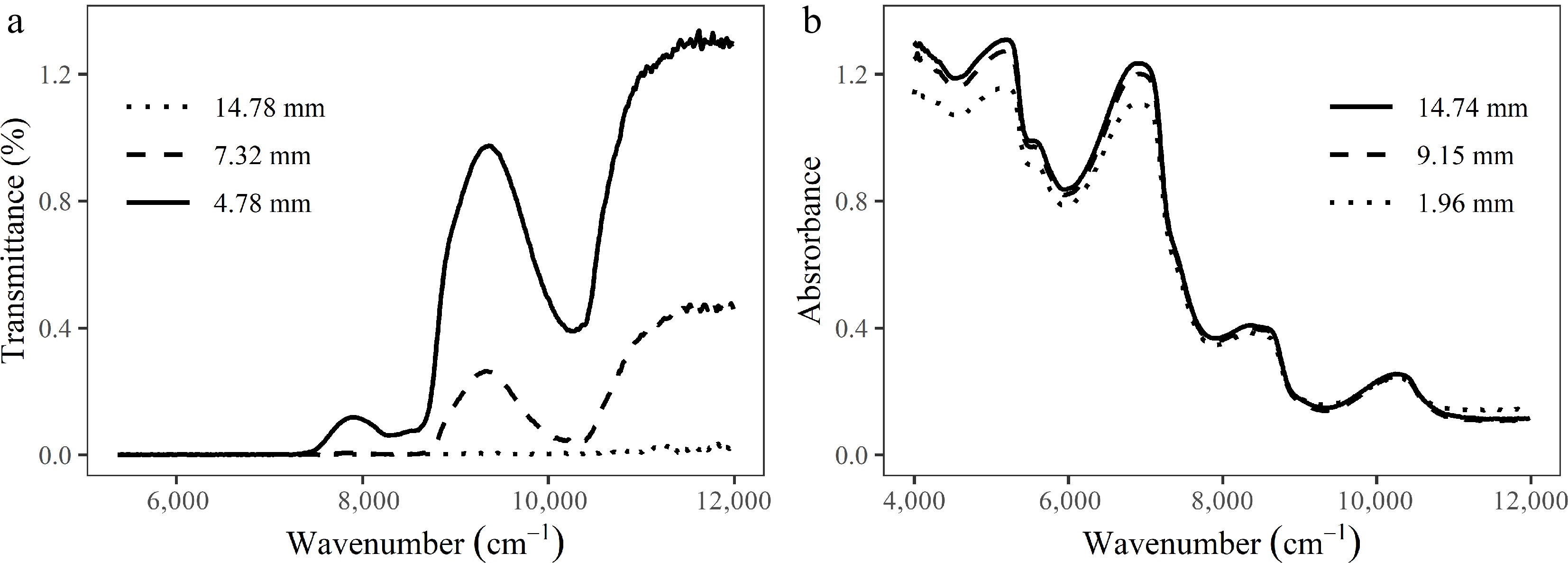
Figure 2.
(a) Typical transmission and (b) reflectance spectra for an avocado at varying thicknesses.
Data analysis
-
In transmission mode, the transmitted spectrum,
$ T({ \lambda ,\theta})$ $ \theta $ $ T({ \lambda }) $ $ T\left(\lambda ,\theta \right)=T\left(\lambda \right)\mathrm{exp}\left(-{\beta }_{1}\left(\lambda \right)\theta \right), $ $ {\beta }_{1}\left(\lambda \right) $ In reflectance mode, a similar procedure to that adopted by Lammertyn et al.[9] was followed. The measured spectrum obtained from the thickest part of the whole avocado half was utilised as the reference spectrum,
$ {R}_{ref}({ \lambda }) $ $ \theta $ $ R({ \lambda ,\theta}{)} $ $ g({ \lambda ,\theta}{)}={log}_{10}({R}_{ref}\left({ \lambda }\right))/{log}_{10}(R({ \lambda },\theta )) $ $ g({ \lambda ,\theta}{)} $ $ g\left({ \lambda, \theta}\right)=\delta \left(\lambda \right)+\alpha \left(\lambda \right)\mathrm{e}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{p}(-{\beta }_{2}\left(\lambda \right)\theta ) $ $ g\left(\lambda ,\theta \right)=\frac{{log}_{10}\left[se\left(\hat{\delta }\right)\;\times\; 2.576/\hat{\alpha }\left(\lambda \right)\right]}{-\hat{{\beta }_{2}}\left(\lambda \right)} $ $ se\left(\hat{\delta }\right) $ The software package 'R' was utilised for the analysis of the depth of penetration data for both transmission and reflectance modes.
-
Figure 3 is a plot of the representative depth of penetration for each wavelength for both transmission and reflectance modes. Representative depths of penetration are only reported where the estimates were conclusive and deemed reliable. Calculated depths of penetration for the reflectance mode that were based on estimates of
$ \hat{\delta } $ 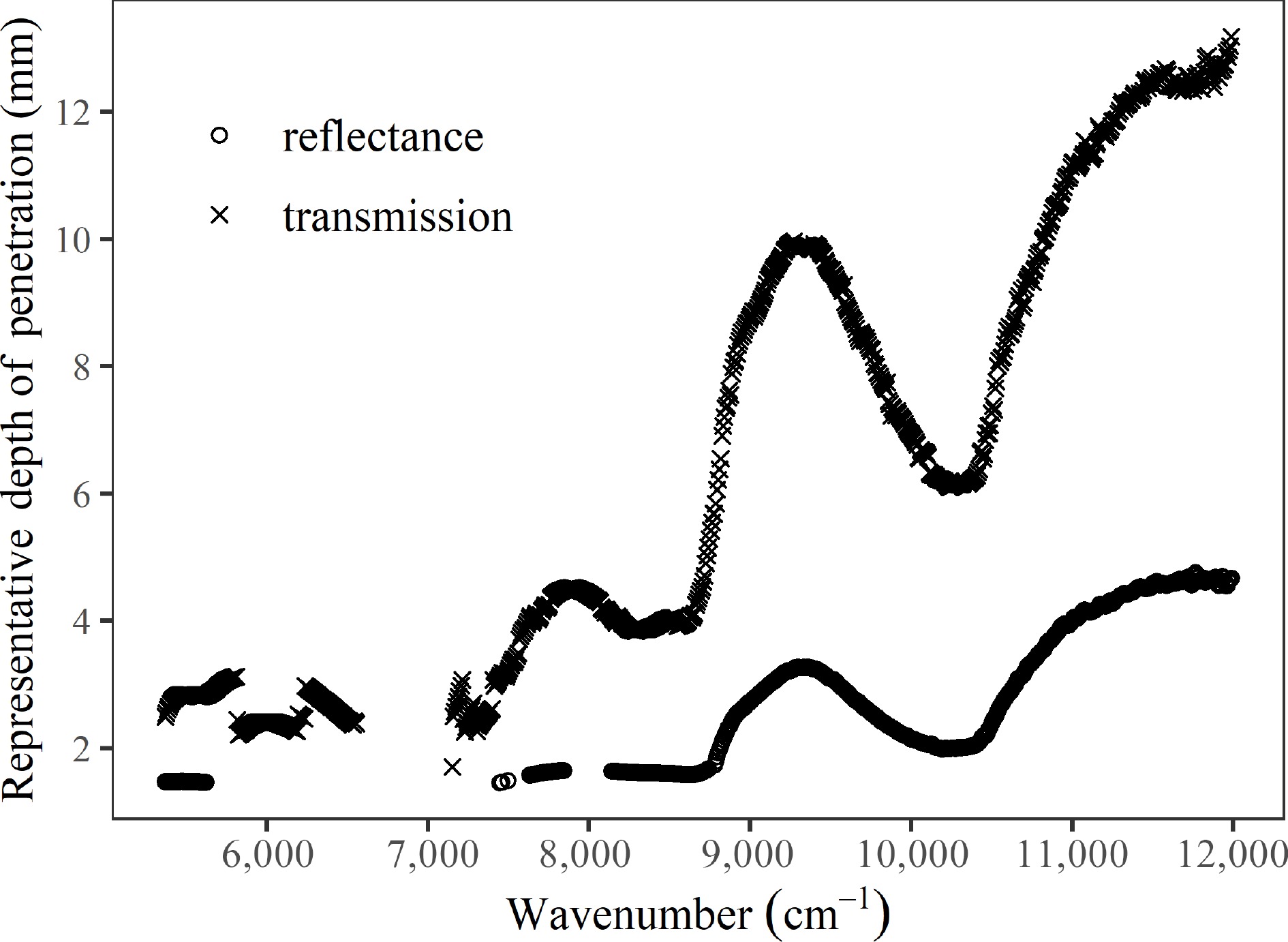
Figure 3.
The representative depth of penetration for each wavelength for both transmission and reflectance modes in avocado fruit.
An example of the fitted model
$ g({ \lambda,\theta}{)} $ -
In this study both transmission and reflectance modes have different penetration depth classifications. In transmission mode, as detailed above, the penetration depth is defined as the depth at which the light intensity drops to 1/e of the initial intensity. In reflectance mode, the depth of penetration is based on the classification developed by Lammertyn et al.[9]. It should be highlighted that the differences in definitions of penetration distance between transmittance and reflectance will result in differences in the absolute measures. Aside from these differences, physically the two processes also differ. In transmission mode, the radiation passes through skin and flesh, and each will have different absorption and scattering characteristics. In reflectance mode, the measurable radiation (excluding specular reflection) must pass through the skin twice. Furthermore, the wavelength variation of penetration depth between the two techniques may be quite different if the scattering of light within the fruit is highly anisotropic in nature.
It is noted that, for both transmission and reflectance modes, signal variability was introduced by repositioning the sample for subsequent spectra collection following removal and slicing of the sample. The sample could not be placed in the exact same position each time which resulted in a slight change in the optical properties for each spectra. The 10 avocado halves ranged in initial thickness from 16.53 to 22 mm with final depth thickness ranging from 0.97 to 1.88 mm at the spectral collection point. Each avocado half had a minimum of 10 thicknesses assessed and the skin thickness at each assessment decreased by approximately 1−2 mm.
The depth of penetration for transmission and reflectance modes in this study compare favourably with other studies found in literature. The depth of penetration is strongly dependent on tissue matrix and composition, and on wavelength[11]. Peirs et al.[12] report penetration depths for 'Jonagold' apple vary between 1 and 5 mm, depending on the wavelength, the instrument and ripeness stage of the fruit. Similarly, Lammertyn et al.[9] report that penetration depth of NIR into apples was wavelength dependent, where the authors obtained up to 4 mm penetration in the 700−900 nm range and between 2 and 3 mm in the 900−1900 nm range. Lammertyn et al.[9] suggest a penetration depth of 1−5 mm for a typical reflectance setup.
Fraser et al.[6] assessed light distribution through mandarin fruit using a laser light at a wavelength of 808 nm. Results showed that there was a rapid reduction in light level across the thick skin (3−5 mm), a less rapid but still high reduction in light in the flesh due to light scattering, with some perturbation through the central pith and air gap, and a rapid drop in light across the distal skin[6]. Investigations by Scotter[13] with fruit, fish and meat products indicate that good reflectance data can be achieved with a sample thickness of between 0.5 and 2 cm, depending upon the absorbance of the sample material.
-
This study measured the wavelength dependence of the depth of penetration of NIR radiation in avocado in both transmittance and reflectance modes, thus sampling different optical paths within the fruit. The results obtained in this study show that NIR radiation in both transmittance and reflectance modes have qualitatively similar wavelength dependencies in penetration. However, it is noted that the transmittance and reflectance methods have different threshold classification of penetration depth. The study highlighted some spectral windows where the depth of penetration in transmission mode was as high as 12.5 mm in the region around 11,500 cm−1 (869 nm) and 10 mm in the region around 9,400 cm−1 (1,063 nm). At certain wavelengths a very low signal to noise ratio caused much uncertainty on the calculated depths, and further study is required to enable an estimate of the penetration distance in these regions.
-
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: study planning and experimental design: Wedding BB, Wright C, White RD; experimental work and data collection: Wedding BB, Grauf S; data analysis and interpretation: Wedding BB, Wright C, White RD; All authors participated in draft manuscript preparation. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Australian Research Council and the provision of equipment and facilities by the Department of Agriculture and Fisheries (DAF) and James Cook University (JCU).
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
- Copyright: © 2024 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press, Fayetteville, GA. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Wedding BB, Wright C, Grauf S, White RD. 2024. Wavelength variation of the depth of penetration of near infrared radiation in 'Hass' avocado fruit. Technology in Horticulture 4: e008 doi: 10.48130/tihort-0024-0005
Wavelength variation of the depth of penetration of near infrared radiation in 'Hass' avocado fruit
- Received: 13 October 2023
- Revised: 25 January 2024
- Accepted: 22 February 2024
- Published online: 02 April 2024
Abstract: This study reports on the wavelength dependence of near infrared (NIR) radiation penetration depth into 'Hass' avocado fruit for both transmission and reflectance modes in the wavelength range from 12,820−4,000 cm−1 (780−2,500 nm). For transmission mode, depths of penetration less than 3 mm occurred in the 5,369 to 7,413 cm−1 (1,862−1,348 nm) range, while the maximum depth of penetration of approximately 12 mm occurred in the region 11,293 to 11,987 cm−1 (885−834 nm). Two other wavelength regions were identified with significant depth of penetration in transmission mode, one around 9,272 cm−1 (1,078 nm) and the second at approximately 7,899 cm−1 (1,265 nm) with approximately 10 and 4.5 mm penetration respectively. In reflectance mode, despite the difference in the optical paths sampled, qualitatively similar trends in wavelength dependence of the depth of penetration were observed, with a lower penetration depth of 3.3 mm occurring around 9,311 cm−1 (1,074 nm) and maximum depth of penetration of approximately 4.8 mm occurring in the 11,625 to 11,987 cm−1 (860−834 nm) region.