-
Ascorbic acid (AsA), commonly known as vitamin C, is a vital molecule integral to a wide array of biological processes across various life forms. In plants, AsA assumes multifaceted roles, ranging as a primary antioxidant and serving as a key component in multiple biosynthetic pathways. Its importance is not confined to plant biology alone; in humans, AsA is essential for the prevention of scurvy, the enhancement of immune function, and its potent antioxidant activity. This review seeks to offer an exhaustive examination of the biosynthesis, functions, and regulatory mechanisms of AsA in plants, while also exploring its potential applications in both agriculture and human nutrition.
Importance of AsA in plants
-
AsA is indispensable for plant growth and development, primarily due to its role as a key antioxidant. It protects cellular components from oxidative damage by scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), which are generated as by-products of metabolic activities and environmental stresses[1]. This antioxidant function is particularly crucial under abiotic stress conditions, such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures[2], during which ROS production can exceed the scavenging capacity of the plant, resulting in oxidative stress and subsequent cellular damage[3].
In photosynthesis, AsA plays a crucial role in the xanthophyll cycle, a protective mechanism that prevents the photoinhibition of the photosynthetic apparatus[4]. Additionally, AsA is involved in the biosynthesis of essential molecules such as ethylene, gibberellins, and anthocyanins, which regulate various physiological processes including growth regulation, fruit ripening, and stress responses[5]. Moreover, AsA is indispensable for the proper functioning of enzymes responsible for synthesizing collagen-like proteins in the plant cell wall[6], thereby influencing cell expansion and plant morphogenesis.
AsA in human health
-
The significance of AsA extends beyond its role in plants to its critical importance in human health, where it functions as an essential dietary nutrient. AsA serves as a vital cofactor in enzymatic reactions necessary for collagen synthesis, a process fundamental to maintaining the structural integrity of skin, blood vessels, and connective tissues[7]. Additionally, as an antioxidant, AsA neutralizes free radicals, thereby mitigating oxidative stress and reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. Furthermore, its immune-boosting properties enhance the function of various immune cells, thereby contributing to increased resistance against infections. Given its critical importance, enhancing the AsA content in edible plants through genetic and agronomic interventions presents significant potential for improving public health[8].
Chemical properties and basic biological functions
-
Chemically, AsA is a six-carbon lactone that exists in two interconvertible forms: the reduced form (ascorbate) and the oxidized form (dehydroascorbate)[9]. Ascorbate acts as a donor of electrons in several biochemical reactions, including hydroxylation and amidation processes essential for the synthesis of collagen and neurotransmitters. This electron-donating ability also underlies its potent antioxidant properties, enabling it to regenerate other antioxidants like vitamin E, thereby supporting the overall antioxidant defense system. In plant cells, AsA contributes to the detoxification of ROS by participating in the ascorbate-glutathione cycle[10], a critical pathway for maintaining cellular redox homeostasis. Additionally, AsA enhances the absorption of non-heme iron in humans, enhancing the bioavailability of this essential nutrient and helping to prevent iron deficiency anemia.
Origin and early evolution of plant AsA
-
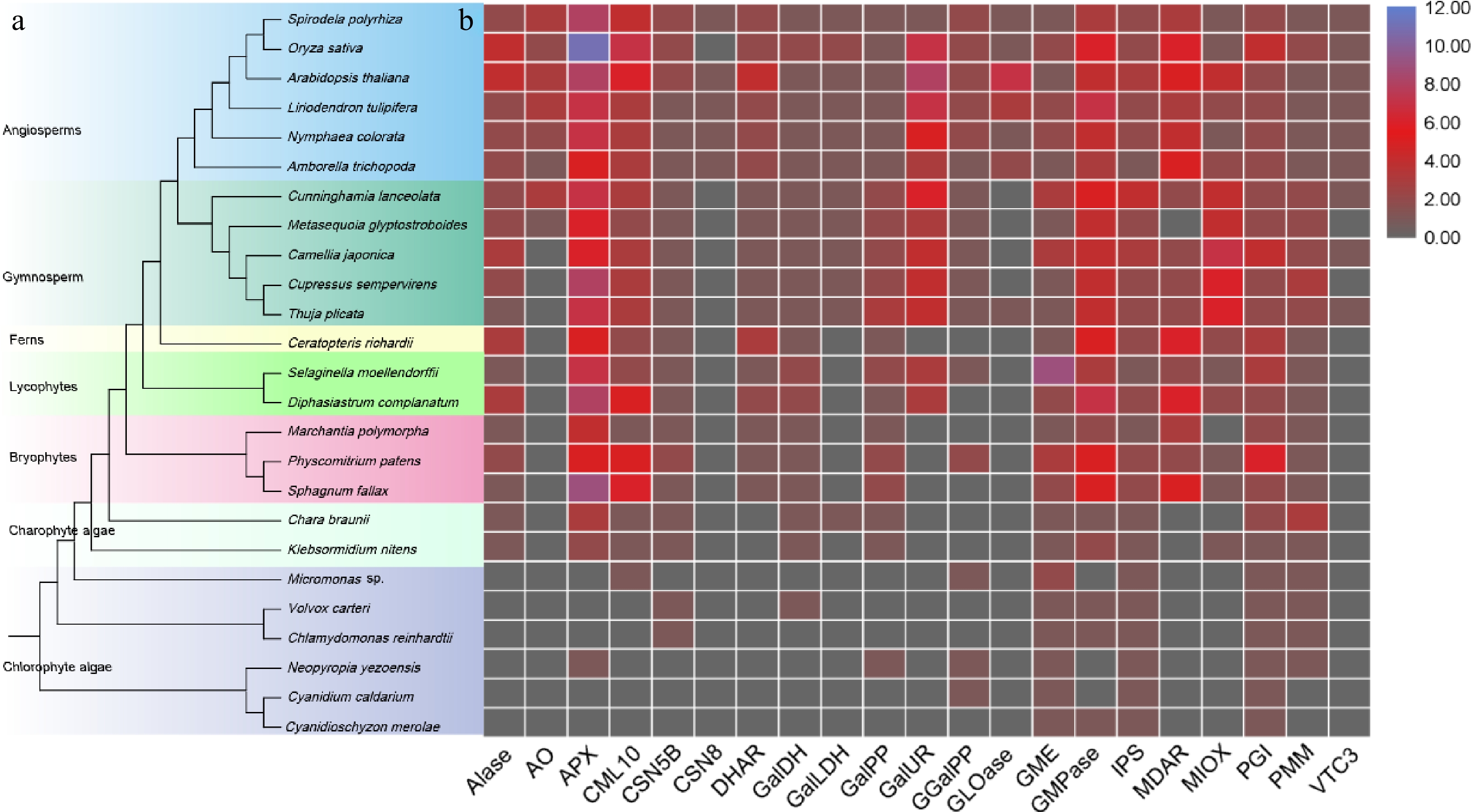
The evolution of AsA in plants is a compelling narrative that underscores the adaptive significance of this essential molecule. The origins of AsA biosynthesis can be traced back to ancient photosynthetic organisms, such as green algae[11], where the biosynthesis pathway of AsA likely emerged as a crucial defense mechanism against reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated during photosynthesis. As plants colonized terrestrial environments, the selective pressures imposed by fluctuating light, temperature, and water availability further refined and diversified the ascorbate biosynthesis pathways[12]. Genetic studies reveal that key enzymes in the ascorbate biosynthesis pathway, including GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase (GMP) and L-galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase (GalLDH), have been highly conserved across plant species, underscoring their fundamental role in plant physiology[13]. The origins of the key enzymes in the biosynthesis of AsA were studied and it was found that these key genes are conserved across land plants (Fig. 1). However, the regulatory mechanisms controlling these pathways exhibit significant evolutionary variation, reflecting adaptations to specific ecological niches. This evolutionary perspective not only highlights the indispensable role of AsA in plant survival and adaptation but also provides valuable insights into the complex interplay between metabolic pathways and environmental challenges throughout the evolutionary history of plants.
-
The detection of AsA in plants commonly employs several advanced analytical techniques. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is highly regarded for its precision and sensitivity, enabling the simultaneous quantification of both total AsA (TAA) and reduced AsA (RA)[14]. This method involves complex sample preparation and the use of specialized equipment, making it particularly suitable for detailed and rigorous analytical studies. Fluorometric assays, which measure fluorescence intensity resulting from reactions with specific dyes, also offer high sensitivity and are well-suited for high-throughput screening, though they require strict control of reaction conditions to ensure accuracy. Electrochemical detection harnesses the inherent electrochemical activity of AsA, providing rapid and highly sensitive quantifications through current signals generated during oxidation-reduction reactions. This method is versatile, being applicable in both laboratory and field applications. In contrast, spectrophotometric assays, which rely on absorbance measurements to quantify AsA offer a more straightforward and cost-effective approach. However, they are comparatively less sensitive and more prone to interference from other components present in the samples[15].
Future methods for AsA detection are anticipated to prioritize advancements in sensitivity, speed, high-throughput capability, and portability[16]. The incorporation of nanosensor technology, utilizing advanced materials such as graphene or gold nanoparticles, is expected to significantly enhance detection sensitivity and speed, yielding faster and more precise results. The development of portable devices, including handheld electrochemical detectors and portable fluorescence analyzers, will enable on-site testing and facilitate large-scale monitoring. Moreover, microfluidic technology, which automates sample processing and detection within compact chip-based systems, is projected to improve efficiency, minimize reagent consumption, and enable rapid analysis[17]. Furthermore, integrated multi-component detection systems are expected to allow simultaneous measurement of various antioxidants, providing a more comprehensive evaluation of a plant's antioxidant capacity and overall health.
In vivo detection
-
Detecting AsA in live plants is technically feasible but presents several significant challenges. Traditional methods have primarily focused on analyzing extracted samples, yet recent technological advancements are paving the way for in vivo detection[18]. The foremost challenges include developing non-invasive measurement techniques to prevent damage to plant tissues, ensuring high sensitivity and selectivity to accurately quantify AsA levels amidst the complex plant tissue matrix, and providing real-time monitoring capabilities to capture dynamic fluctuations in AsA concentrations. Moreover, environmental factors such as light, temperature, and humidity can significantly interfere with AsA measurements, highlighting the need for robust detection systems that perform reliably under varying conditions. Addressing these challenges may involve the utilization of optical methods, such as fluorescence and Raman spectroscopy, which provides non-invasive and highly sensitivity detection[19]. These techniques can incorporate fluorescent dyes that specifically react with AsA, producing measurable signals that can be detected and quantified through optical probes. Nanotechnology offers promising avenues for AsA detection with nanoparticles such as gold or quantum dots being used to construct highly sensitive sensors capable of selectively binding to AsA molecules. Additionally, electrochemical sensors, particularly those in miniaturized versions designed for use in live plants have the potential to provide real-time monitoring by detecting electrochemical signals generated from AsA oxidation-reduction reactions. Furthermore, the integration of microfluidics with portable detection devices, including handheld fluorescence and electrochemical detectors, facilitates rapid, on-site testing and supports large-scale monitoring efforts. Although these approaches require multidisciplinary collaboration and innovation, they offer substantial potential for advancing our understanding of plant physiology and enhancing agricultural practices through real-time, in vivo AsA monitoring[20].
-
In plants, the distribution of AsA is characterized by significant heterogeneity, exhibiting distinct preferences across various tissues and organs. This uneven distribution is closely related to the multifunctionality of AsA, its metabolic pathways, and the specific physiological demands of different plant parts.
Characteristics of AsA distribution in plants
-
AsA is predominantly concentrated in photosynthetic organs, such as leaves, as well as in meristematic tissues, root tips, fruits, and embryos. AsA is involved in root, shoot, leaf, and fruit development in woody plants. In particular, AsA participates in photosystem protection and acts in leaves, enabling the continuation of photosynthesis. Additionally, AsA contributes to seed viability and the reproduction of trees[21]. Generally, higher concentrations are found in photosynthetic and metabolically active tissues, while xylem and mature cells contain relatively lower levels. This preferential distribution reflects the diverse physiological roles that AsA plays in plants[22].
Role of AsA in photosynthesis
-
Leaves, serving as the primary photosynthetic organs of plants, typically have the highest concentrations of AsA. AsA functions as a vital antioxidant in photosynthesis, effectively scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated during this process, thereby protecting chloroplasts and other organelles from oxidative damage[23]. Additionally, AsA is involved in the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) within the photosynthetic electron transport chain, helping to maintain the cellular redox balance[24].
Function of AsA in meristematic tissues and growth points
-
Meristematic tissues and growth points exhibit higher concentrations of AsA due to their rapid cell division, active growth, and high metabolic demand[25]. In these regions, AsA not only serves as an antioxidant but also participates in cell wall synthesis and modification. For instance, it acts as a crucial cofactor in the synthesis and regeneration of peroxisomal enzymes, thereby facilitating several metabolic processes. In addition, AsA plays a key role in the modification of extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen[26]. AsA plays a crucial role in the transition of cells from the S to G1 phase of the cell cycle and in the cross-linking cell wall components, both of which are vital for cell growth[27]. Studies have shown that transgenic rice plants with silenced cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase (Apx) genes exhibited significant developmental changes, resulting in a semi-dwarf phenotype[28]. Similarly, wheat Apx mutants demonstrated reduced photosynthetic activity[29]. Both studies indicated that compensatory antioxidant mechanisms were activated in mutants with ascorbate production deficiencies. However, the deficiency of AsA to DHA exchanges contributed to growth abnormalities.
Accumulation of AsA in fruits and seeds
-
Fruits and seeds often contain high levels of AsA, especially during growth and maturation. Fruits contain significant amounts of AsA, particularly during their expansion and ripening phases. Ascorbate in the apoplasm triggers ROS production, which in turn promotes fruit ripening[30]. Research has shown that large mandarin fruits have high AsA levels indicating the crucial role of this antioxidant in fruit development and quality[31]. One study reported that APX plays a crucial role in the enhanced ROS removal in coffee fruits grown at high altitudes. Additionally, increased ascorbate oxidase (AO) activity during fruit development contributes to fruit expansion[32]. AsA in these organs not only provides antioxidant protection but also plays a vital role in embryo development and seed germination. High concentrations of AsA can protect the embryo from environmental stresses (such as drought and high temperature), thereby promoting normal embryonic development.
Dynamic nature of AsA distribution
-
The distribution of AsA within a plant is not static; it adjusts dynamically with changes in plant growth, environmental conditions, and metabolic demands[33]. For example, under stress conditions such as variations in light intensity, temperature, or pathogen attack, both the distribution and concentration of AsA can change significantly to cope with environmental pressures and meet the plant's metabolic needs. AsA is a non-enzymatic antioxidant compound that reduces oxidative stress in plants by scavenging ROS (reactive oxygen species). Therefore, AsA can serve as a plant growth regulator for wheat in saline environments, enhancing the capacity of plants to cope under stressful conditions[34].
Regulatory mechanisms of AsA distribution
-
The distribution and concentration of AsA in plants are regulated by multiple factors, including gene expression, enzyme activity in metabolic pathways, transport mechanisms, and environmental stimuli[35]. Plants use a series of precise mechanisms to control the synthesis, degradation, and regeneration of AsA, thereby maintaining appropriate levels in different tissues and organs. For instance, the L-galactono-1,4-lactone pathway, which is responsible for AsA biosynthesis, exhibits uneven activity across tissues, with higher activity in certain organs such as leaves and fruits, leading to the accumulation of AsA in these regions[36].
AsA distribution in plants is uneven, showing clear tissue and organ specificity. This distribution pattern is intricately linked to the diverse physiological roles of AsA, ranging from antioxidant defense to cell division and growth regulation. Through precise metabolic regulation and transport mechanisms, plants ensure the accumulation of AsA in critical regions to meet the specific demands of different tissues and organs. This selective distribution not only reflects the plant's adaptability to its environment but also represents a vital component of the complex metabolic network within plants.
-
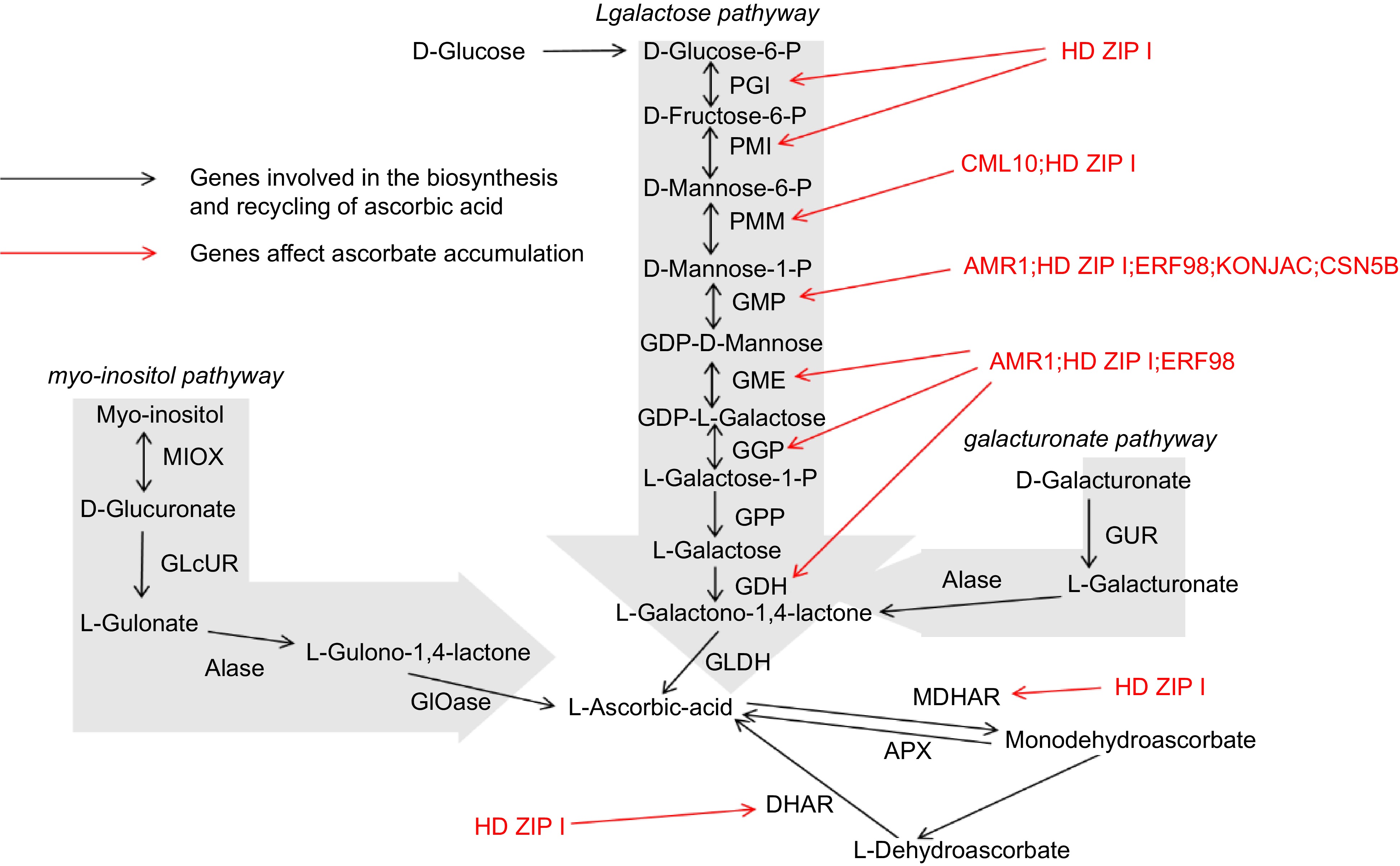
The biosynthesis of AsA in plants is a complex process involving multiple enzymatic steps (Fig. 2). Among the various biosynthetic routes, the L-galactose pathway, commonly referred to as the Smirnoff-Wheeler pathway, is the most thoroughly characterized route for ascorbate synthesis in higher plants. This pathway illustrates the intricate biochemical transformations required to convert glucose into AsA, highlighting the central role of carbohydrate metabolism in AsA production[37].
The L-galactose pathway (Smirnoff-Wheeler pathway)
-
The L-galactose pathway initiates with the phosphorylation of glucose-6-phosphate, a key metabolite involved in both glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway[38]. Glucose-6-phosphate undergoes a series of enzymatic reactions, being first converted to L-galactose-1-phosphate via the intermediate L-galactose-6-phosphate through a series of reactions catalyzed by enzymes such as phosphoglucomutase and phosphomannose isomerase. Subsequently, L-galactose-1-phosphate is reduced to L-galactose, a reaction mediated by the enzyme L-galactose dehydrogenase (L-GalDH)[39]. This reduction step is crucial, as it channels metabolites toward ascorbate synthesis rather than diverting to competing pathways.
The subsequent conversion of L-galactose to L-galactono-1,4-lactone is catalyzed by L-galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase (GLDH), an enzyme localized in the mitochondria[40]. GLDH catalyzes the oxidation of L-galactono-1,4-lactone to ascorbate, with cytochrome c serving as an electron acceptor. This reaction represents the final and rate-limiting stage in the ascorbate biosynthetic pathway, making its regulation critical for controlling the overall production of AsA within the plant[41].
Alternative pathways
-
While the L-galactose pathway is predominant in most plants, alternative biosynthetic routes have been identified, particularly in lower plants and certain algae. One alternative pathway is the L-mannose pathway, which involves the conversion of GDP-mannose into L-galactono-1,4-lactone through intermediate compounds such as GDP-L-galactose and L-gulose[42]. This pathway underscores the evolutionary diversity in ascorbate biosynthesis, illustrating how different plant species have adapted their metabolic processes to reflect adaptations to different ecological niches and physiological demands.
The myo-inositol pathway, identified in certain plants, converts myo-inositol to ascorbate through a series of oxidative reactions[43]. This pathway illustrates the metabolic flexibility of plants, enabling them to adjust AsA biosynthesis in response to environmental and developmental signals. Such diversity in biosynthetic routes not only highlights the adaptability of plant metabolism but also provides multiple targets for genetic manipulation aimed at increasing AsA content in crops[44].
Evolutionary perspectives
-
The evolution of diverse biosynthetic pathways for AsA in plants reflects the adaptive strategies developed to address varying environmental pressures. Comparative genomic and phylogenetic studies reveal that the L-galactose pathway is highly conserved among higher plants, whereas alternative pathways exhibit greater variability across different plant lineages[45]. This evolutionary perspective offers valuable insights into the functional significance of ascorbate in plant physiology and its critical role in adapting to terrestrial environments[46].
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the complex biosynthetic pathways and regulatory mechanisms of AsA in plants offer valuable opportunities for improving crop nutritional quality and stress tolerance through targeted genetic and metabolic engineering approaches[47]. By deepening our comprehension of these processes, we can more effectively leverage the potential of AsA to tackle global challenges in agriculture and human health.
-
AsA is a multifaceted molecule that plays a pivotal role in plant physiology, influencing a myriad of biochemical and cellular processes. Beyond its well-established antioxidant properties, AsA is crucial in photosynthesis, growth regulation, and stress response mechanisms[48]. The diverse functionalities of AsA underscore its importance in maintaining plant health and enhancing productivity[46].
Antioxidant defense mechanism
-
One of the primary roles of AsA in plants is its function as a potent antioxidant. Plants face continuous exposure to a wide range of environmental stressors, including ultraviolet (UV) radiation, extreme temperatures, drought, and pathogen attacks, all of which can result in the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS)[49]. ROS, including superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals, can inflict substantial damage to cellular components such as lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, leading to oxidative stress. AsA alleviates oxidative stress by directly scavenging these ROS[50]. AsA donates electrons to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby converting these harmful molecules into less detrimental substances. The oxidized form of AsA, known dehydroascorbate, can be recycled back to its reduced form via the ascorbate-glutathione cycle, thereby sustaining antioxidant defense mechanisms[51]. This recycling process is mediated by the enzyme dehydroascorbate reductase[52], which uses glutathione as a substrate to regenerate ascorbate, thereby maintaining cellular redox homeostasis.
In addition to its direct ROS-scavenging activity, AsA also functions synergistically with other antioxidants. It plays a pivotal role in regenerating the oxidized forms of antioxidants, such as tocopherol (vitamin E), thereby extending their protective effects[53]. This collaborative action among antioxidants is essential for preserving the integrity and functionality of cellular membranes and organelles under stress conditions.
Role in photosynthesis
-
AsA is integral to the process of photosynthesis, the primary mechanism by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. Within chloroplasts, where photosynthesis occurs, the generation of ROS is an unavoidable consequence of the high-energy electron transfers involved in the light reactions[54]. In this context, AsA serves a protective role by scavenging ROS, thereby mitigating photoinhibition and preventing photodamage to the photosynthetic apparatus.
Moreover, AsA is involved in the regulation of the xanthophyll cycle, a mechanism that dissipates excess light energy as heat to protect the photosynthetic machinery. Under high light intensity, AsA facilitates the conversion of violaxanthin to zeaxanthin, a process that helps dissipate the excess energy and mitigating the formation of ROS[55]. This photoprotective mechanism is essential for maintaining the efficiency of photosynthesis, particularly under fluctuating light conditions.
AsA also influences the function of several key enzymes involved in the Calvin cycle, the series of biochemical reactions that fix carbon dioxide into organic compounds[56]. For instance, AsA stabilizes ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO), the principal enzyme responsible for carbon fixation[57]. By enhancing the activity and stability of such enzymes, AsA contributes to the overall efficiency of photosynthetic carbon assimilation.
Growth regulation and development
-
AsA serves as a crucial regulator of plant growth and development, significantly influencing cell division, expansion, and differentiation, processes that are fundamental to plant morphogenesis[58]. One of the primary mechanisms by which AsA affects growth is through its involvement in the biosynthesis of plant hormones, such as ethylene and gibberellins, which are essential regulators of different developmental processes[59].
In cell division, AsA is essential for the synthesis of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins, which are crucial components of the plant cell wall necessary for its extensibility and stability[60]. As cells divide and expand, the structural integrity and flexibility of the cell wall must be maintained, and AsA contributes to this process by modulating the activity of prolyl hydroxylase. This enzyme is responsible for the hydroxylation of proline residues in cell wall proteins, thereby ensuring proper cell wall function and stability[61].
Furthermore, AsA acts as a cofactor for enzymes involved in the synthesis of collagen-like proteins within the cell wall matrix, which are essential for maintaining cell wall structure during periods of rapid cell expansion[62]. This function is particularly critical in the developing tissues, such as young leaves, root tips, and meristems, where rapid cell division and growth are occurring.
Besides its structural roles, AsA is implicated in the regulation of gene expression related to growth and development. It influences the transcription of genes encoding various growth regulators and enzymes, thereby influencing developmental pathways[63]. For instance, AsA modulates the expression of genes involved in the synthesis of abscisic acid (ABA), a hormone crucial for regulating seed dormancy, germination, and stress responses.
Stress responses and signal transduction
-
AsA is central to a plant's ability to respond to and tolerate a range of different biotic and abiotic stresses. Its role encompasses more than just antioxidant defense, extending to the modulation of stress signal transduction pathways[64]. Under stress conditions, such as pathogen attacks or environmental challenges, plants activate complex signaling networks that coordinate and regulate defensive responses[65].
In addition, AsA plays a crucial role as a cofactor in the oxidation of tyrosine, an essential amino acid involved in protein synthesis and the production of various biomolecules[66]. The oxidation of tyrosine is a critical step in the biosynthesis of several important compounds, including neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, as well as pigments like melanin. The enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase catalyzes the initial step in this pathway, converting tyrosine to L-DOPA (L-dihydroxyphenylalanine), a precursor to dopamine. AsA acts as a reducing agent in this process, maintaining the enzyme's active site in a reduced state, which is essential for the catalytic activity of tyrosine hydroxylase[67].
In plants, AsA acts as a cofactor in the oxidation of tyrosine and extends its role to other enzymes involved in the hydroxylation of various substrates, thereby contributing to the synthesis of plant hormones, defense compounds, and structural components[68]. By facilitating these enzymatic reactions, AsA is involved in regulating growth, development, and stress responses. Additionally, its antioxidant properties protect plant cells from oxidative damage that can occur during these metabolic processes[69]. Overall, the function of AsA as a cofactor in tyrosine oxidation and other biochemical pathways underscores its indispensable role in both plant and animal physiology, highlighting its evolutionary conservation and significance across diverse biological kingdoms. Furthermore, AsA plays a critical role in the synthesis and signaling of several phytohormones, including salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA), which are essential for plant defense mechanisms[70]. For example, during pathogen attacks, AsA modulates the accumulation of salicylic acid (SA), a hormone that triggers systemic acquired resistance (SAR), thereby starting a comprehensive immune response. Additionally, AsA influences the jasmonic acid (JA) signaling pathway, which is essential for defense against herbivorous insects and necrotrophic pathogens[71].
Moreover, AsA plays a significant role in the regulation of redox-sensitive signaling pathways. It modulates the redox state of cellular components, thereby influencing the activity of redox-sensitive transcription factors and signaling molecules[72]. This redox regulation is critical for the activation of defense genes and for coordinating the metabolic adjustments required for stress tolerance[73].
AsA also contributes to the detoxification of harmful compounds generated during stress responses. It is involved in the synthesis of secondary metabolites such as flavonoids and anthocyanins, which possess antioxidant properties and bolster the plant’s defense mechanisms[74]. These metabolites can scavenge ROS, chelate metal ions, and inhibit the growth of pathogens, thereby enhancing the plant’s capacity to withstand stress[75].
Reproductive development
-
Reproductive development in plants, encompassing flowering, fruit set, and seed development, represents a critical phase in which AsA plays a pivotal role[76]. These stages involve complex metabolic and physiological processes that demand tight regulatory mechanisms to ensure proper coordination and successful reproduction.
AsA contributes to the synthesis of pollen and ovules, thereby ensuring successful fertilization and subsequent seed formation. It is also integral to the development of floral organs and the maintenance of pollen viability[26]. During fruit development, AsA accumulates in high concentrations, where it serves to protect developing tissues from oxidative damage and supports the synthesis of essential metabolic compounds.
Additionally, AsA is implicated in the regulation of seed dormancy and germination, with its levels fluctuating during seed maturation and germination, indicating its active involvement in these processes. By modulating the activity of key enzymes and influencing the synthesis of hormones such as gibberellins and ABA, AsA plays a critical role in the transition from dormancy to active growth. This regulatory function of AsA is essential for ensuring successful seedling establishment and subsequent plant development[77].
-
The regulatory mechanisms of AsA in plants is a tightly regulated process, designed to maintain optimal levels of ascorbate to meet the physiological and metabolic demands of the plant[78]. This regulation occurs at multiple levels, including gene expression, enzyme activity, and feedback inhibition, ensuring precise control over AsA production. A thorough understanding of these regulatory mechanisms is crucial for the manipulation of ascorbate levels in plants, with potential applications in enhancing stress tolerance and improving nutritional quality[79].
Genetic regulation
-
Over 90 years ago, researchers first discovered that polyploidization, such as tetraploidy, can lead to increased accumulation of metabolic products in plants, including vitamin C[80]. Polyploid plants have been observed to exhibit higher antioxidant capacity and elevated vitamin C content, a phenomenon that may be attributed to increased gene dosage and enhanced metabolic enzyme activity resulting from polyploidization. Although the specific molecular mechanisms underlying this phenomenon have not been extensively documented, this finding provides a valuable foundation for exploiting polyploidization in crop improvement strategies.
Transcriptional regulation
-
The regulation of AsA biosynthesis at the transcriptional level involves the coordinated expression of genes encoding enzymes within the biosynthetic pathway[81]. Several transcription factors have been identified that modulate the expression of these genes in response to developmental cues and environmental stresses, thereby ensuring that AsA levels are appropriately adjusted to meet the physiological needs of the plant.
One key regulator of AsA is the transcription factor SOG1 (SUPPRESSOR OF GAMMA RESPONSE 1), which plays a crucial role in the plant´s response to DNA damage and oxidative stress. SOG1 has been shown to influence the expression of genes involved in the ascorbate biosynthesis pathway, thereby linking the oxidative stress response to increased ascorbate production[82]. In addition, the transcription factor ANAC078 (NAC DOMAIN CONTAINING PROTEIN 78) has been involved in the regulation of ascorbate biosynthesis during abiotic stress, such as salt and drought stress. ANAC078 directly binds to the promoters of ascorbate biosynthesis genes, enhancing their expression under these stress conditions[83].
Moreover, the circadian clock, which orchestrates numerous physiological processes in plants, plays a pivotal role in the regulation of AsA biosynthesis. The circadian rhythms modulate the expression of key genes involved in this pathway, including those genes encoding enzymes like GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase and L-galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase. This modulation ensures that ascorbate levels align with the plant’s metabolic demands throughout the day[84].
Post-transcriptional regulation
-
In addition to transcriptional regulation, post-transcriptional mechanisms are crucial in regulating AsA biosynthesis[85]. These mechanisms encompass mRNA stability, translation efficiency, and protein modification.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), which are small non-coding RNAs, regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally by binding to target miRNAs, thereby inhibiting their translation or promoting their degradation[86]. Notably, several miRNAs have been identified that target mRNAs encoding enzymes involved in ascorbate biosynthesis, modulating their levels in response to developmental signals and stress conditions. For instance, miR398 targets the mRNA of copper/zinc superoxide dismutase (SOD), an enzyme that plays an indirect role in maintaining redox balance and AsA homeostasis[87,88].
Protein modifications such as phosphorylation and ubiquitination, play a significant role in regulating the activity and stability of enzymes involved in the ascorbate biosynthesis[89]. For example, the phosphorylation of L-galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase has been shown to enhance its enzymatic activity, thereby promoting increased ascorbate production. On the contrary, ubiquitination followed by the degradation of key biosynthetic enzymes acts as a regulatory mechanism to downregulate ascorbate synthesis when cellular levels are sufficient[90].
Feedback regulation
-
Ascorbate levels are tightly regulated by feedback mechanisms to prevent overproduction and maintain homeostasis at the cellular level. Elevated ascorbate concentrations can inhibit the activity of enzymes involved in its biosynthetic pathway through feedback inhibition[91]. For example, L-galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase, the terminal enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway, is subjected to feedback inhibition by ascorbate. This regulatory mechanism ensures that ascorbate synthesis is attenuated when its levels are sufficient, thereby preventing unnecessary energy expenditure and metabolic imbalance[92].
Additionally, ascorbate can modulate the expression of its biosynthetic genes through feedback regulation. Elevated ascorbate levels have been shown to downregulate the transcription of genes encoding key biosynthetic enzymes, consequently reducing their synthesis and activity[93]. This style of feedback regulation is essential for maintaining optimal ascorbate concentrations, and adapting to varying cellular and environmental conditions.
Environmental and developmental regulation
-
Environmental factors such as light, temperature, and nutrient availability play a significant role in regulating the biosynthesis of AsA in plants. Light is a particularly critical factor, as it directly influences the photosynthetic process and the production of ROS[94]. High light intensity increases the demand for ascorbate, which is essential for scavenging excess ROS generated during photosynthesis. Consequently, the expression of ascorbate biosynthesis genes is upregulated under high light conditions, leading to elevated ascorbate levels.
Temperature also impacts ascorbate biosynthesis, with both low and high temperatures inducing oxidative stress and consequently increasing the demand for ascorbate. For instance, cold stress induces the upregulation of ascorbate biosynthesis genes to bolster the plant’s antioxidant defenses and mitigate cold-induced oxidative damage[95].
Nutrient availability also significantly influences ascorbate levels. Specifically, deficiencies in elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and iron can modulate ascorbate levels. Nitrogen deficiency has been observed to increase ascorbate levels in leaves, potentially serving as a protective mechanism against nutrient stress[96]. In addition, iron, a crucial cofactor for several enzymes in the ascorbate biosynthesis pathway, is essential for maintaining optimal ascorbate levels. Iron deficiency can disrupt ascorbate synthesis, highlighting the necessity of sufficient nutrient supply for effective ascorbate homeostasis.
Developmental stages significantly impact ascorbate biosynthesis, with different tissues displaying variable ascorbate concentrations throughout plant growth. Young, actively growing tissues, such as leaves, shoot tips, and developing fruits, typically have higher ascorbate concentrations compared to mature tissues[97]. This variation is indicative of the higher metabolic activity and heightened need for antioxidant protection in developing tissues.
Hormonal regulation
-
Plant hormones, or phytohormones, are integral in modulating ascorbate biosynthesis in response to both developmental cues and environmental stimuli. Notably, ABA, SA, and JA are central to these regulatory mechanisms[98].
ABA, a key regulator of stress responses, has been shown to upregulate the expression of ascorbate biosynthesis genes under abiotic stress conditions such as drought and salinity. By enhancing ABA signaling, plants can bolster their antioxidant capacity, thereby better managing increased oxidative stress linked to these challenging conditions[99].
SA plays a crucial role in regulating defense responses against pathogens and also modulates ascorbate biosynthesis. During a pathogen attack, SA signaling can upregulate the expression of ascorbate biosynthesis genes, leading to increased ascorbate levels. This elevation in ascorbate concentration helps to mitigate oxidative damage and supports the plant´s defense mechanisms[100].
Jasmonic acid (JA) is a hormone critical for stress responses such as those produced by herbivory and wounding and also regulates ascorbate biosynthesis. JA signaling can upregulate the expression of ascorbate biosynthesis genes, thereby increasing ascorbate levels. This modulation enhances the plant's capacity to counteract oxidative stress induced by wounding and herbivore damage[101].
-
Genetic engineering and breeding strategies aimed at enhancing AsA content in plants have been driven by the dual objectives of improving plant stress tolerance and increasing the nutritional value of crops[102]. These approaches have capitalized on our understanding of ascorbate biosynthesis pathways, regulatory mechanisms, and natural genetic variation, leading to significant advancements in crop improvement[103]. Genetic engineering has been employed to increase AsA accumulation in potatoes by introducing genes associated with the L-galactose pathway, the initial pathway for ASA biosynthesis in plants[104]. For instance, the overexpression of the GLOase gene, which encodes an enzyme responsible for converting L-gulono-1,4-lactone to L-ascorbic acid, has been demonstrated in transgenic potato plants. This overexpression leads to increased levels of AsA in the tubers, thereby enhancing the plants tolerance to various abiotic stresses.
Genetic engineering approaches
-
Genetic engineering has emerged as a potent tool for manipulating ascorbate biosynthesis in plants. Several strategies have been employed, including the overexpression of rate-limiting enzymes, the manipulation of multiple genes involved in the biosynthetic pathway, the enhancement of ascorbate recycling processes, RNA interference (RNAi) to suppress negative regulators, and the application of CRISPR/Cas9 technology for precise genome editing[105]. For instance, the introduction of exogenous novel genes has been used to engineer alternative biosynthetic pathways, as demonstrated in transgenic tobacco and lettuce plants expressing a rat cDNA encoding L-gulono-γ -lactone oxidase[106].
Overexpression of biosynthetic genes
-
One of the main strategies in genetic engineering for enhancing ascorbate biosynthesis involves the overexpression of genes encoding key enzymes within the biosynthetic pathway[107]. For example, overexpressing the gene encoding L-galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase (GLDH), the terminal enzyme in the ascorbate biosynthesis pathway has been shown to significantly increase ascorbate levels in various plant species, including Arabidopsis (Table 1), tomato, and potato. This enzyme catalyzes the final step in ascorbate biosynthesis, converting L-galactono-1,4-lactone to ascorbate, and its overexpression promotes a greater flux through the pathway[108]. With the rapid development in plant genomics[109], the identification of the biosynthetic genes relying on homology deep learning is of special interest to researchers.
Table 1. AsA-related genes in model plant Arabidopsis.
Enzyme / protein name Abbreviation Arabidopsis
genesAldonolactonase Alase AT3G03060 AT5G169300 AT2G18330 AT4G36580 l-Ascorbate oxidase AO AT5G21100 AT5G21105 AT4G39830 Ascorbate peroxidase APX AT1G07890 AT3G09640 AT4G35000 AT4G35970 AT4G32320 AT4G09010 AT4G08390 AT1G77490 Calmodulin-like protein CML10 AT2G41090 Cop9-signalosome 5b CSN5B At1g71230 Dehydroascorbate reductase DHAR AT1G19570 AT1G19550 AT1G75270 AT5G16710 l-Galactose-1-phosphate phosphatase GalPP AT3G02870 Galactose dehydrogenase GalDH AT4G33670 Galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase GalLDH AT3G47930 Galacturonosyltransferase GalUR AT1G59950 AT1G59960 AT2G37760 AT2G37770 AT2G37790 AT5G62420 AT5G01670 AT3G53880 GDP-l-galactose phosphorylase GGalPP AT4G26850 AT5G55120 GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase GMPase AT1G74910 AT2G39770 AT3G55590 AT4G30570 l-Gulono-γ-lactone oxidase GLOase AT2G46740 AT2G46750 AT2G46760 AT5G11540 AT1G32300 AT5G56490 AT5G56470 GDP-mannose-3′,5′-epimerase GME AT5G28840 Monodehydroascorbate reductase MDAR AT5G03630 AT3G09940 AT3G52880 AT3G27820 AT1G63940 Myo-inositol oxygenase MIOX AT1G14520 AT2G19800 AT4G26260 AT5G56640 Phosphoglucose isomerase PGI AT4G24620 AT5G42740 Phosphomannose isomerase PMI AT1G67070 AT3G02570 Phosphomannomutase PMM AT2G45790 Protein kinase/protein phosphatase VTC3 AT2G40860 Similarly, the overexpression of GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase (GMP), which is involved in the early stages of the ascorbate biosynthesis pathway, has proven to be effective. Transgenic plants overexpressing GMP exhibit higher ascorbate levels and enhanced tolerance to oxidative stress[110]. These studies highlight the effectiveness of targeting key enzymes within the biosynthetic pathway to boost ascorbate production.
RNA interference (RNAi) and gene silencing
-
RNA interference (RNAi) technology has been effectively employed to downregulate or silence genes that negatively affect ascorbate biosynthesis[111]. For instance, the silencing of the gene encoding ascorbate oxidase- an enzyme responsible for the degradation of ascorbate- can result in elevated ascorbate levels. The reduction in ascorbate oxidase activity allows plants to maintain higher ascorbate concentrations, thereby enhancing their antioxidant capacity and improving stress tolerance.
Furthermore, RNAi has been employed to suppress the expression of VTC2, which encodes GDP-L-galactose phosphorylase, a key regulatory enzyme in the ascorbate biosynthesis pathway. Silencing VTC2 leads to the accumulation of its substrate, GDP-L-galactose, which can subsequently be redirected towards enhanced ascorbate synthesis via alternative pathways[112].
CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing
-
The advent of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing has revolutionized genetic engineering by enabling precise modifications to target genes. This technology has been applied to edit genes linked to ascorbate biosynthesis and regulation[113]. For example, CRISPR/Cas9 has been used to knock out genes encoding ascorbate oxidase or other negative regulators, leading to increased ascorbate accumulation.
CRISPR/Cas9 technology can also be employed to insert beneficial alleles of ascorbate biosynthesis genes from other species or natural variants into crop plants[114]. This approach enables the incorporation of traits that enhance ascorbate production without generating transgenic plants, which is particularly advantageous in regions with stringent regulations on genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
Breeding strategies
-
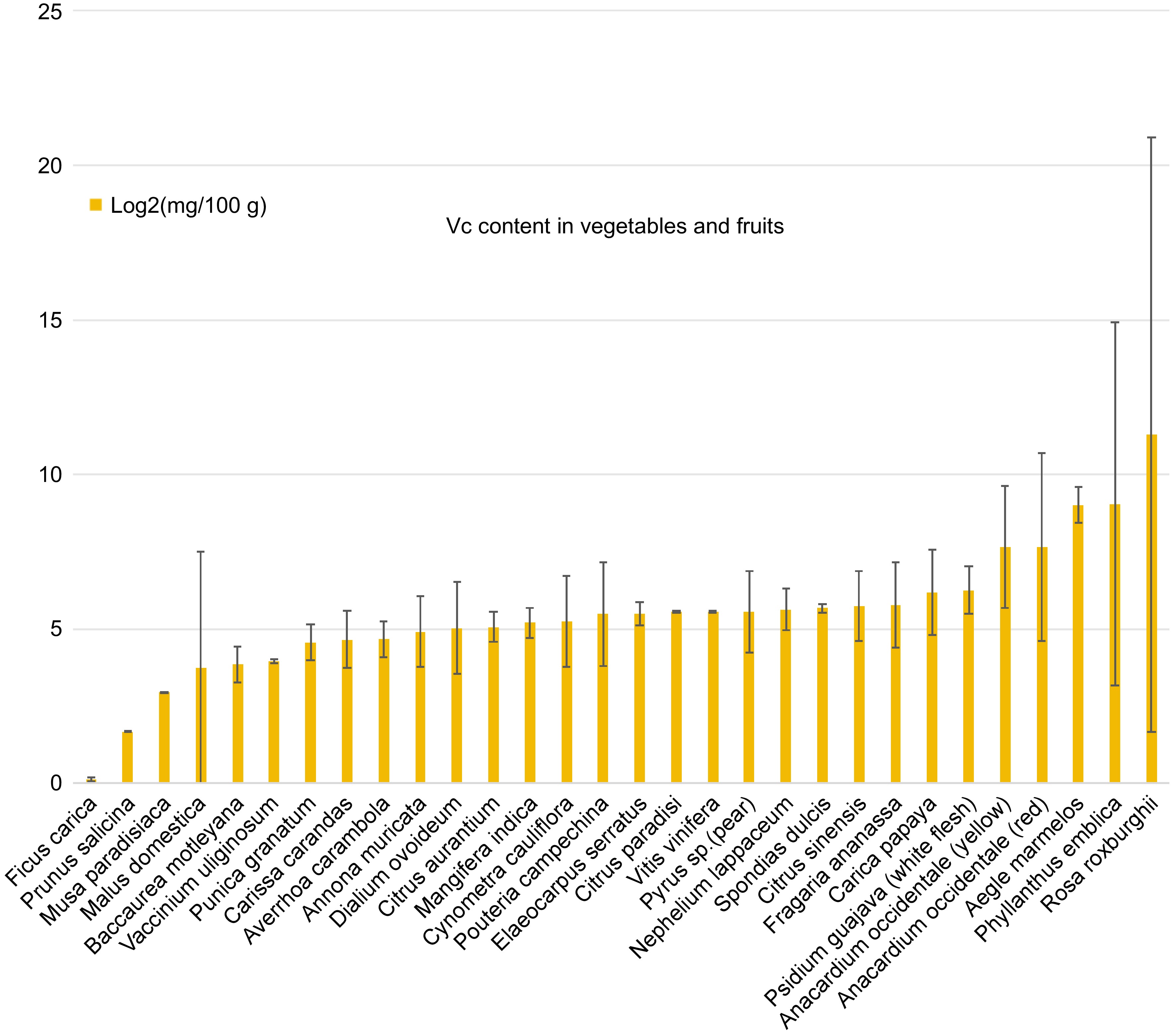
In addition to genetic engineering, both traditional and modern breeding techniques have been employed to enhance ascorbate content in crops[115]. These techniques encompass Conventional Breeding, Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS), Genomic Selection, and Induced Mutagenesis. These methods can select and cross-breeding plants with naturally high ascorbate levels (Fig. 3), as well as introducing new genetic variation through mutagenesis, genomic selection, and big data analyses using artificial intelligence[116,117]. These approaches collectively contribute to the development of genetically improved varieties of fruits and vegetables enriched with AsA content[118].
Conventional breeding
-
Conventional plant breeding leverages the inherent genetic diversity within plant populations. Through the systematic screening of germplasm collections, breeders can identify varieties exhibiting naturally elevated ascorbate levels[122]. These high-ascorbate genotypes can subsequently be crossed with commercial cultivars, facilitating the integration of desirable traits such as increased yield and enhanced disease resistance, alongside augmented ascorbate content.
For example, in tomato breeding programs, wild relatives characterized by high ascorbate levels have been crossed with cultivated varieties to generate hybrids with enhanced ascorbate content. By employing successive generations of selection and backcrossing, breeders can stabilize these traits and ultimately develop new cultivars with improved nutritional quality[123].
Marker-assisted selection (MAS)
-
Marker-assisted selection (MAS) is an advanced breeding technique that utilizes molecular markers linked to desirable traits, such as elevated ascorbate content, to accelerate the breeding process. By identifying and selecting plants carrying specific genetic markers linked to increased ascorbate levels, breeders can more efficiently develop high-ascorbate cultivars[124].
MAS has been successfully applied in crops such as maize, where quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with ascorbate content have been reported. By using these markers, breeders can select plants possessing favorable QTLs and combine them through cross-breeding, thereby enhancing ascorbate levels in the resulting progeny[125].
Genomic selection
-
Genomic selection is a cutting-edge breeding technique that uses genome-wide markers to predict the genetic value of individual plants for complex traits, such as ascorbate content[126]. By developing prediction models that integrate genomic data with phenotypic information, breeders can identify the most promising candidates for breeding, thereby reducing the reliance on extensive field trials.
In crops such as rice and wheat, genomic selection has demonstrated to be effective in enhancing ascorbate content[127]. By integrating genomic selection with conventional breeding programs, breeders can accelerate the development of high-ascorbate varieties, thereby reducing the time and resources necessary for cultivar development.
Induced mutagenesis
-
Induced mutagenesis entails exposing plants to physical or chemical mutagens to induce genetic diversity. This technique can produce novel alleles of ascorbate biosynthesis genes, potentially leading to increased ascorbate synthesis. Such mutagenesis has been employed to develop high-ascorbate mutants in crops like barley and soybean[128].
By screening mutagenized populations for plants with elevated ascorbate levels, breeders can identify and select appropriate mutations. These mutants can subsequently be incorporated into breeding programs to introduce high-ascorbate traits into commercial cultivars.
Case studies and applications
-
The application of genetic engineering and traditional breeding techniques has yielded remarkable success in enhancing the ascorbate content in several crops[129]. These advancements are crucial not only for enhancing the nutritional quality of food but also for increasing crop resilience to environmental stresses. The following case studies provide detailed examples that demonstrate the potential of these strategies in practical agricultural contexts[130].
Transgenic tomatoes
-
Transgenic tomatoes overexpressing the gene encoding GLDH have demonstrated a significant increase in ascorbate content. These transgenic lines exhibit enhanced tolerance to oxidative stress, improved fruit quality, and extended shelf life[131]. The elevated ascorbate levels also enhance the nutritional value of these tomatoes, rendering them a significant addition to the human diet[132].
Previous studies have demonstrated that the suppression of the ascorbate oxidase (AO) gene in tomato plants by RNA interference results in a significant decrease in AO enzyme activity, which in turn leads to enhanced AsA accumulation in the fruit. This alteration in AsA metabolism suggests that the targeting of the AO gene could be a viable strategy for improving the antioxidant content and stress tolerance in tomato plants[133].
High-ascorbate maize
-
Marker-assisted selection (MAS) has been utilized in maize breeding to develop varieties with elevated ascorbate levels. Through the identification of QTLs associated with ascorbate content, breeders have been able to select and propagate plants that carry favorable genetic markers. As a result, maize lines with significantly enhanced ascorbate levels have been produced[134]. These high-ascorbate maize varieties not only offer superior nutritional benefits but also exhibit enhanced stress tolerance, making them particularly well-suited for cultivation in regions prone to environmental stresses.
CRISPR/Cas9-edited rice
-
Recent advancements in genome editing have enabled significant progress in enhancing the resilience and nutritional quality of crops. Using CRISPR/Cas9 technology, researchers successfully edited the gene encoding ascorbate oxidase in rice, resulting in increased ascorbate accumulation. The genetically modified rice plants show enhanced growth and improved stress tolerance, particularly under water scarcity[135]. This study demonstrates the potential of CRISPR/Cas 9 mediated gene editing to create rice varieties with improved resilience and nutritional profiles, thereby offering promising solutions for agricultural sustainability and food security.
In conclusion, genetic engineering and breeding strategies represent potent approaches for enhancing ascorbate content in plants. By harnessing insights into biosynthesis pathways, regulatory mechanisms, and natural genetic variation, substantial progress has been achieved in the development of high-ascorbate crops[136]. These advancements not only elevate the nutritional value of crops but also bolster their resilience to environmental stresses, thereby supporting sustainable agriculture and contributing to global food security.
-
The integration of multi-omics approaches and systems biology has significantly advanced the study of AsA in plants, offering comprehensive insights into its biosynthesis, regulation, and functional roles[137]. These cutting-edge methodologies enable researchers to discern complex biological networks and interactions across multiple levels, encompassing genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and beyond[138,139]. This section delves into the applications of multi-omics and systems biology in AsA research, highlighting key findings and discussing prospects for this evolving field.
Genomics and transcriptomics
-
Genomic and transcriptomic analyses have been fundamental in identifying genes and regulatory elements involved in AsA biosynthesis and metabolism[140]. Genomics and transcriptomics related to ascorbate involve the investigation of the genetic basis and gene expression patterns associated with ascorbate metabolism in plants. This field explores how the manipulation of genes can lead to increased AsA content, thereby enhancing both human nutrition and plant tolerance to abiotic stresses[141]. The advent of high-throughput sequencing technologies, particularly RNA-Seq, has greatly enhanced the discovery of novel genes and provided detailed insights into their expression patterns across various conditions. These advancements have deepened our understanding of the genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying AsA biosynthesis, paving the way for targeted genetic interventions.
Gene identification and functional annotation
-
Genomic studies have been instrumental in identifying key genes involved in the Smirnoff-Wheeler pathway as well as alternative biosynthetic routes for AsA. Notably, researchers have identified and characterized genes encoding crucial enzymes such as GDP-mannose 3',5'-epimerase (GME), L-galactose dehydrogenase (GalDH), and L-galactono-1,4-lactone dehydrogenase (GLDH) through genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and functional genomics approaches[142].
Transcriptomic profiling and expression analysis
-
Transcriptomic profiling using RNA-Seq has provided detailed insights into the gene expression dynamics associated with ascorbate biosynthesis and regulation. For instance, research has demonstrated that the expression of GLDH and GME genes are upregulated in response to light and stress conditions, highlighting their role in plant adaptive responses[143]. Moreover, differential expression analysis has identified candidate regulatory genes, including transcription factors and microRNAs, which modulate ascorbate biosynthesis pathways.
Proteomics
-
Proteomic approaches have been instrumental in the identification and quantification of proteins involved in ascorbate metabolism, offering valuable insights into the post-translational regulation of key enzymes[144]. This field enhances our understanding of the complex molecular mechanisms underlying ascorbate synthesis, distribution, and function across various organisms, as well as the role of proteins in mediating these biological functions. Proteomics offers a valuable approach for further investigation into ascorbate-related processes, providing insights into how specific proteins contribute to ascorbate metabolism and its associated physiological effects. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics, in particular, has proven to be highly effective in characterizing protein-protein interactions and uncovering potential regulatory networks in the ascorbate metabolism.
Protein identification and quantification
-
Proteomic analyses have elucidated a wide array of enzymes and transporters integral to ascorbate biosynthesis, recycling, and transport, thereby advancing the understanding of ascorbate metabolism. Among the enzymes identified, ascorbate peroxidase (APX) and monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDHAR) are particularly noteworthy due to their pivotal roles in the ascorbate-glutathione cycle, a critical pathway for maintaining cellular redox balance and protecting against oxidative stress. Furthermore, the application of quantitative proteomics revealed significant variability in the abundance of these proteins under varying environmental conditions, such as drought and high light intensity. These findings offer valuable insights into the regulatory mechanisms modulating ascorbate metabolism in plants, highlighting how these organisms are able to adapt to these external stresses, thereby enhancing their survival and resilience in fluctuating environments[145].
Post-translational modifications
-
Post-translational modifications of proteins involved in ascorbate metabolism can modify the accumulation and stability of AsA in plants. Post-translational modifications (PTMs) including phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and acetylation, are critical in regulating the activity and stability of enzymes. For instance, phosphorylation and ubiquitination are recognized as regulatory mechanisms that modulate the activity and degradation of enzymes such as ascorbate oxidase, which plays a key role in the catabolism of ascorbate. Proteomic analyses have identified PTMs on key ascorbate-related enzymes, thereby uncovering regulatory mechanisms that operate under stress conditions[146]. For example, phosphorylation of APX has been shown to enhance its activity, thereby contributing to increased ROS detoxification during stress conditions.
Metabolomics
-
Metabolomic approaches provide detailed profiles of metabolites involved in ascorbate biosynthesis and degradation. Techniques such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) have been employed to quantify ascorbate and its related metabolites, offering valuable insights into metabolic fluxes and the regulation of these pathways[147,148]. This approach allows researchers to delve deeper into the complex biochemical networks that sustain plant life. By integrating metabolomic data with other omics approaches, such as genomics and proteomics, a holistic view of how metabolic pathways are interconnected and regulated can be obtained. This systems-level understanding is crucial for identifying key metabolic nodes and regulatory mechanisms that control the synthesis and degradation of vital compounds like ascorbate.
Metabolite profiling
-
Metabolomic studies have quantified ascorbate levels and intermediates of the Smirnoff-Wheeler pathway across various plant tissues and environmental conditions. These investigations have demonstrated significant variability in ascorbate content, which fluctuates with tissue type, developmental stage, and stress conditions, thereby emphasizing the dynamic nature of its metabolism[149]. Additionally, metabolite profiling has identified potential biomarkers associated with elevated ascorbate content, which can be used in breeding programs to develop crops with enhanced ascorbate levels.
Flux analysis
-
Metabolic flux analysis (MFA) has provided quantitative insights into the flow of carbon through ascorbate biosynthetic pathways[150]. By integrating isotope labeling with mass spectrometry, researchers have discerned the contributions of different pathways to the ascorbate pool and revealed how metabolic fluxes are regulated under different conditions. Additionally, MFA has been employed to investigate the effects of genetic modifications on AsA biosynthesis, thereby informing strategies for the development of high-ascorbate crops[151].
Integrative omics and systems biology approaches
-
Integrative omics approaches combine data from genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics to construct comprehensive models of ascorbate metabolism and its regulation. This has contributed to a more integrated understanding of plant metabolism, enabling researchers to examine the intricate layers of biological information, from gene expression to protein function and metabolite dynamics, in a more integrated and systematic manner. This integrated perspective is crucial for unraveling the multifaceted regulation of vital processes such as ascorbate metabolism. In addition, systems biology approaches further enhance this understanding by employing computational models to predict the behavior of metabolic networks and identify key regulatory nodes[152]. Insights gained from integrative omics and systems biology approaches can guide efforts to genetically manipulate organisms, to enhance the production of bioactive phytochemicals like AsA.
Network construction and analysis
-
Integrative omics studies have developed detailed metabolic and regulatory networks of ascorbate biosynthesis and recycling. By incorporating data on gene expression, protein-protein interactions, and metabolite levels, these networks provide a comprehensive overview of ascorbate metabolism[153]. Network analysis has identified key regulatory nodes and hub genes that are central to the regulation of ascorbate levels, thereby identifying potential targets for genetic manipulation.
Computational modeling
-
Computational models have been created to simulate ascorbate biosynthesis and predict the effects of genetic and environmental perturbations. These models integrate multi-omics data to offer insights into the dynamic regulation of ascorbate metabolism. For example, constraint-based modeling and kinetic modeling have been used to examine the effect of gene overexpression and knockout on ascorbate production, thereby informing metabolic engineering strategies[154].
Case studies and practical applications
-
The convergence of multi-omics technologies has significantly advanced the field of plant science, enabling more comprehensive and nuanced insights into complex biological processes. For instance, the application of transcriptome sequencing has shed light on the genetic underpinnings of AsA biosynthesis and recycling pathways. The identification of key enzymes and their corresponding genes has been crucial in elucidating the metabolic pathways underlying AsA production. Furthermore, investigations into metabolite dynamics have revealed the complex relationships between gene expression, protein functionality, and metabolite concentrations within plant systems. This comprehensive approach is crucial for enhancing crop resilience and nutritional quality by identifying potential targets for genetic manipulation and breeding strategies[155]. The integration of multi-omics and systems biology in AsA research has yielded numerous successful case studies, illustrating the practical benefits of these advanced approaches in enhancing plant traits and optimizing metabolic pathways.
Enhancing AsA content in crops
-
Multi-omics approaches have been employed to enhance ascorbate content in crops such as tomatoes, rice, and maize. By integrating genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data, researchers have identified key genes and regulatory mechanisms that can be targeted to increase ascorbate levels[156]. For example, the overexpression of GLDH and the application of marker-assisted selection have facilitated the development of high-ascorbate varieties of tomato and rice.
Improving stress tolerance
-
Systems biology approaches have been used to discern the role of ascorbate in stress tolerance and to develop crops with enhanced resilience to environmental stresses. Integrative omics studies have elucidated key regulatory networks that control ascorbate-mediated stress responses, thereby informing the development of stress-tolerant crop varieties[157]. For example, the manipulation of transcription factors and signaling pathways involved in ascorbate biosynthesis has led to improved drought and salt tolerance in various crops.
-
The integration of multi-omics and systems biology approaches is indeed driving significant breakthroughs in plant science. For example, the study of AsA biosynthesis and its regulatory mechanisms can be greatly enhanced by combining transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome data. This holistic approach enables researchers to identify and understand the complex interactions among genes, proteins, and metabolites involved in the production and function of AsA. The discovery of the translational feedback mechanism that regulates AsA levels in plants is a prime example of how such integrative research can yield novel insights into plant biology[158]. Furthermore, this knowledge can be leveraged to develop crops with improved nutritional profiles and enhanced stress tolerance, which is crucial for addressing challenges in agriculture and food security. The ongoing advancement of multi-omics technologies and systems biology approaches offers substantial promise for AsA research.
Elucidating complex regulatory networks
-
Multi-omics approaches will be crucial in understanding how environmental factors influence ascorbate metabolism and for developing crops capable of thriving under variable climatic conditions. Enhanced integration of multi-omics data will facilitate a more profound understanding of the intricate regulatory networks that govern ascorbate metabolism[159].
A promising area of research is the investigation of induced resistance (IR) and its potential relationship to AsA metabolism. IR is a plant defense mechanism triggered by various stimuli, including pathogen infection, insect herbivory, wounding, beneficial microbes, or exogenous application of natural or synthetic compounds. This defense response can either directly activate plant defenses or prime them for more rapid and robust responses to subsequent pathogen challenges. While IR has been shown to enhance disease resistance and stress tolerance, it may also affect plant growth and development, highlighting the importance of monitoring potential fitness costs associated with this defense strategy.
Developing precision breeding strategies
-
Future research directions should be focused on refining biotechnological methodologies to enhance AsA content while minimizing any negative impacts on plant performance. This effort requires a more profound understanding of the key regulatory factors and pathways involved in AsA synthesis, as well as the feedback mechanisms that maintain homeostasis within the plant[160]. Furthermore, research is needed to identify the potential advantages of synthetic nutrients, which can offer high bioavailability and be produced through controlled chemical reactions or bacterial fermentation[161]. These studies will be critical for developing effective strategies to bolster AsA levels while ensuring human nutrition and overall plant health and productivity. The application of CRISPR/Cas9 and other gene-editing technologies, using the information provided by multi-omics data, will enable the precise manipulation of ascorbate biosynthesis pathways. For example, the QTLs vitc10.1 and vitc8.1 have been proposed for tomato nutrient improvement[162] CRISPR-Cas9 editing in tomato has been already implemented[163] as well as in various plants[164].
In conclusion, the application of multi-omics and systems biology approaches has significantly advanced our understanding of AsA metabolism and regulation. These approaches have enabled the identification of key genes, pathways, and regulatory mechanisms, leading to practical applications in crop improvement and stress tolerance[165]. The ongoing integration of multi-omics data, coupled with the development of sophisticated computational models, is expected to further enhance our capability to manipulate ascorbate levels in plants. This will contribute to improved crop resilience and nutritional quality, fostering advancements in agricultural sustainability and food security.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32172614), the Hainan Province Science and Technology Special Fund (ZDYF2023XDNY050), Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (324RC452), and supported by the Project of National Key Laboratory for Tropical Crop Breeding (NO. NKLTCB202337). We thank the editor and reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
-
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: study conception and design, supervision: Chen F; data collection: Wang C, Li Z; draft manuscript preparation, review: Chen F, Wang C, García-Caparros P. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Fei Chen is the Editorial Board member of Tropical Plants who was blinded from reviewing or making decisions on the manuscript. The article was subject to the journal's standard procedures, with peer-review handled independently of this Editorial Board member and the research groups.
-
Received 25 August 2024; Accepted 17 October 2024; Published online 18 December 2024
-
# Authors contributed equally: Chong Wang, Pedro García-Caparros, Zhidong Li
- Copyright: © 2024 by the author(s). Published by Maximum Academic Press on behalf of Hainan University. This article is an open access article distributed under Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
-
About this article
Cite this article
Wang C, García-Caparros P, Li Z, Chen F. 2024. A comprehensive review on plant ascorbic acid. Tropical Plants 3: e042 doi: 10.48130/tp-0024-0042
A comprehensive review on plant ascorbic acid
- Received: 25 August 2024
- Revised: 16 October 2024
- Accepted: 17 October 2024
- Published online: 18 December 2024
Abstract: This review delves into the multifaceted roles of ascorbic acid (AsA) in plants and the underlying regulatory mechanisms. The critical roles of AsA in plant physiology are discussed, including its involvement in plant hormone synthesis, the regulation of plant growth and development, and its pivotal role in the response to environmental stress. The review also evaluates various methods for detecting ascorbic acid (AsA), providing an analysis of their respective advantages and disadvantages. The uneven distribution of AsA across various tissues and organs is summarized. This uneven distribution is closely related to the multifunctionality of AsA, its diverse metabolic pathways, and the specific physiological demands of different plant parts. Additionally, this review explores the evolutionary origins of AsA in plants and the development of its complex biosynthetic pathways. It offers a comprehensive description of the Smirnoff-Wheeler pathway, as well as other alternative biosynthetic pathways, demonstrating the metabolic flexibility of plants. This review concludes by examining strategies for enhancing AsA content and improving stress resistance in crops through genetic engineering and multi-omics approaches, underscoring their potential for agricultural applications.
-
Key words:
- Ascorbic acid /
- Plant physiology /
- Biosynthetic pathways /
- Genetic engineering /
- Multi-omics